RARE! WWII U.S. Navy SECRET SAILING DIRECTIONS CENTRAL PACIFIC AREA (Saipan, Tinian, Guam, Iwo Jima, Okinawa)
























RARE! WWII U.S. Navy SECRET SAILING DIRECTIONS CENTRAL PACIFIC AREA (Saipan, Tinian, Guam, Iwo Jima, Okinawa)
Comes with a hand-signed C.O.A.
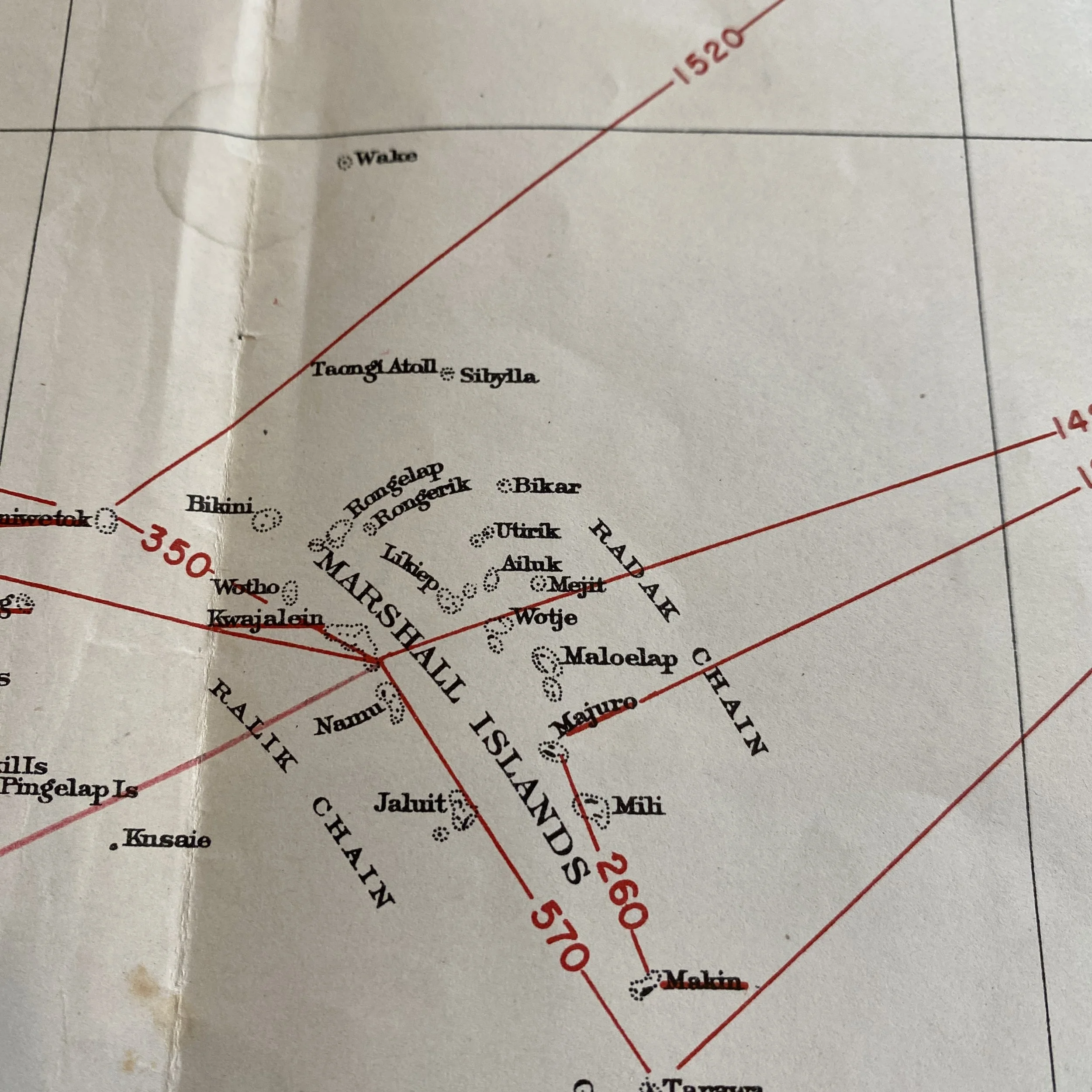
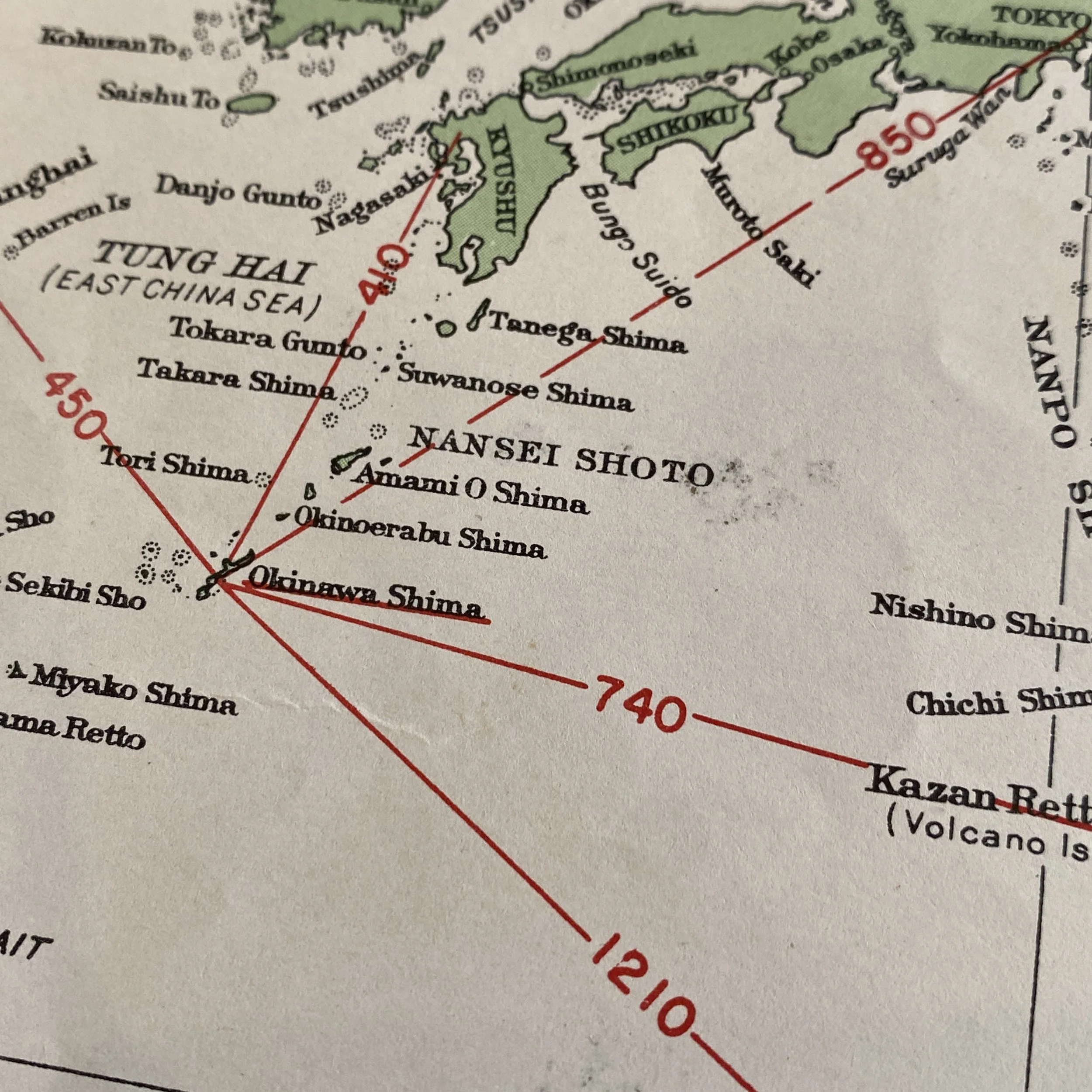
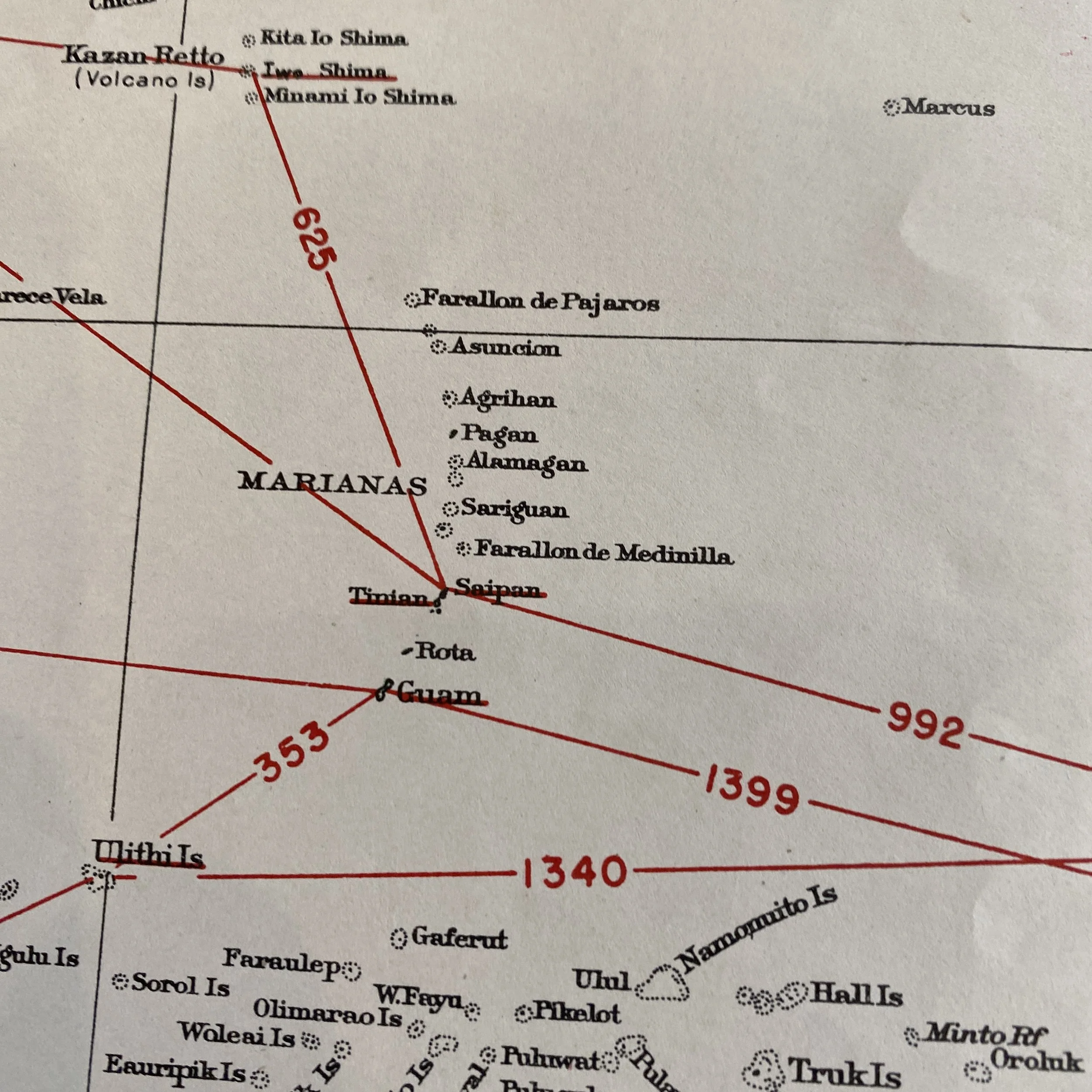
This very rare and museum-grade World War II artifact titled SECRET SAILING DIRECTIONS - CENTRAL PACIFIC AREA is marked CONFIDENTIAL and was used to navigate U.S. Navy ships in the Pacific Theater. This navigational sailing map was used by aircraft carriers, destroyers, landing ship tanks, escorts, etc.
This map is used extensively in the Pacific Theater as it shows some of the most famous battlegrounds including directional navigation lines to Saipan, Tinian, Guam, Iwo Jima, Okinawa, Marshall, islands, Phoenix Islands, and Pearl Harbor/Hawaiian Islands.
This map would have been used by commanding officers and high-ranking officials aboard U.S. Navy vessels while operating in the Pacific Theater during some of the most intense combat operations.
On December 7, 1941, Japan staged a surprise attack on Pearl Harbor, severely damaging the US Pacific Fleet. When Germany and Italy declared war on the United States days later, America found itself in a global war. Japan launched a relentless assault that swept through the US territories of Guam, Wake Island, and the Philippines, as well as British-controlled Hong Kong, Malaya, and Burma. Yet, with much of the US fleet destroyed and a nation unprepared for war, America and its allies decided they needed to save Great Britain and defeat Germany first.
The Japanese, meanwhile, sought to complete what they began at Pearl Harbor. They aimed to destroy the US carrier fleet in a victory so decisive that the United States would negotiate for peace. With its battleship fleet crippled in Hawaii, the US Navy turned to two surviving assets. Aircraft carriers and submarines mounted a serious challenge to Japan’s triumphant fleet and were critical to protecting mainland America. But as US attacks on Japanese naval forces and merchant ships escalated from isolated raids to full-scale battles, the learning curve proved costly and deadly.
Blunting the Japanese Onslaught
Throughout the winter and spring of 1942 the war news reaching the United States from the Pacific was grim. The Japanese amassed a vast new empire with a defensive perimeter that ranged from western Alaska to the Solomon Islands. In the southwest Pacific, Japan threatened American supply lines to Australia, complicating US plans to use Australia as a staging ground for offensive action.
But within months, the tide of battle started to turn as the United States and its allies in Australia and New Zealand first blunted Japan’s advance and then began a long counterattack across the Pacific. The amphibious invasion soon became the hallmark of the Allied counterattack. As they advanced westward toward Japan, Allied forces repeatedly bombed and stormed Japanese-held territory, targeting tiny islands as well as the jungles of New Guinea and the Philippines. The goal was to dislodge the enemy and to secure airfields and supply bases that could serve as the launching points for future attacks.
Turning Points
In early May 1942, US and Japanese carrier forces clashed in the Battle of the Coral Sea. While both sides suffered major losses, the US Navy checked a major Japanese offensive for the first time. Then, in the Battle of Midway the following month, US carrier aircraft dealt a devastating blow to the Japanese navy, destroying four aircraft carriers. The battle marked the first major US victory against Japan and was a turning point in the war.
By shifting the balance of naval power in the Pacific, Midway allowed US forces to take the offensive for the first time. The Allies soon set their sights on Guadalcanal in the Solomon Islands and on New Guinea.
Amphibious Invasions and Island Hopping
In August 1942, the United States mounted its first major amphibious landing in World War II at Guadalcanal, using innovative landing craft built by Higgins Industries in New Orleans. By seizing a strategic airfield site on the island, the United States halted Japanese efforts to disrupt supply routes to Australia and New Zealand. The invasion ignited a ferocious struggle marked by seven major naval battles, three major land battles, and almost continuous air combat as both sides sought to control Henderson Field, named after Loy Henderson, an aviator killed at the Battle of Midway. For six long months US forces fought to hold the island. In the end they prevailed, and the Allies took the first vital step in driving the Japanese back in the Pacific theater.
With Guadalcanal in American hands, Allied forces continued to close in on Rabaul in New Britain. As forces under the command of Admiral William F. “Bull” Halsey moved north through the Solomons, General Douglas MacArthur’s troops pushed west along the northern coast of Papua New Guinea, grinding out a hard-fought victory by March 1943. But rather than follow this success with a risky invasion of the heavily defended Rabaul, American military planners hatched an ingenious plan: Allied planes and ships would isolate and neutralize Rabaul from the air and sea while the bulk of MacArthur’s forces pushed westward to invade less-well-defended islands. This practice—skipping over heavily fortified islands in order to seize lightly defended locations that could support the next advance—became known as island hopping. As Japanese strongholds were isolated, defenders were left to weaken from starvation and disease. This new strategy turned the vast Pacific distances into an American ally, and the United States used it to leapfrog across the Pacific.
Advancing on Two Fronts
In addition to hopping from one less-defended island to another, the Allies’ Pacific strategy developed another key feature: soldiers, sailors, and US Marines pressed forward on two fronts. As MacArthur’s troops leapt from island to island in the southwest Pacific, a central Pacific campaign began with the invasion of Tarawa in the Gilbert Islands in November 1943. By the end of the year, a two-pronged assault on Japan was well underway.
As 1944 began, the southwest Pacific was largely under Allied control. By February, the Allies were also making progress in the central Pacific. Naval and air strikes reduced most of the Japanese bases throughout the area, and after several intense, bloody campaigns, most of the central Pacific was secure. As the islands in the Marshall and Mariana chains fell to US Army and Marines forces by that summer, troops constructed airfields in preparation for air strikes on Japan itself. The Marianas were a particularly valuable asset since they were close enough to Japan for the United States’ new, technologically advanced B-29 bombers to reach the mainland.
As the United States geared up for this aerial bombardment of Japan, military leaders lobbied to continue their campaigns in the southwest and central Pacific. In the southwest, General Douglas MacArthur and Admiral Chester W. Nimitz pushed for an assault on the Philippines, while in the central Pacific, Admiral Ernest J. King pressed for an attack on Formosa (now Taiwan).