RARE 1945 KYUSHU JAPAN Operation Olympic WAR ROOM Operation Downfall Invasion Planning Map


















RARE 1945 KYUSHU JAPAN Operation Olympic WAR ROOM Operation Downfall Invasion Planning Map
Comes with hand-signed C.O.A.
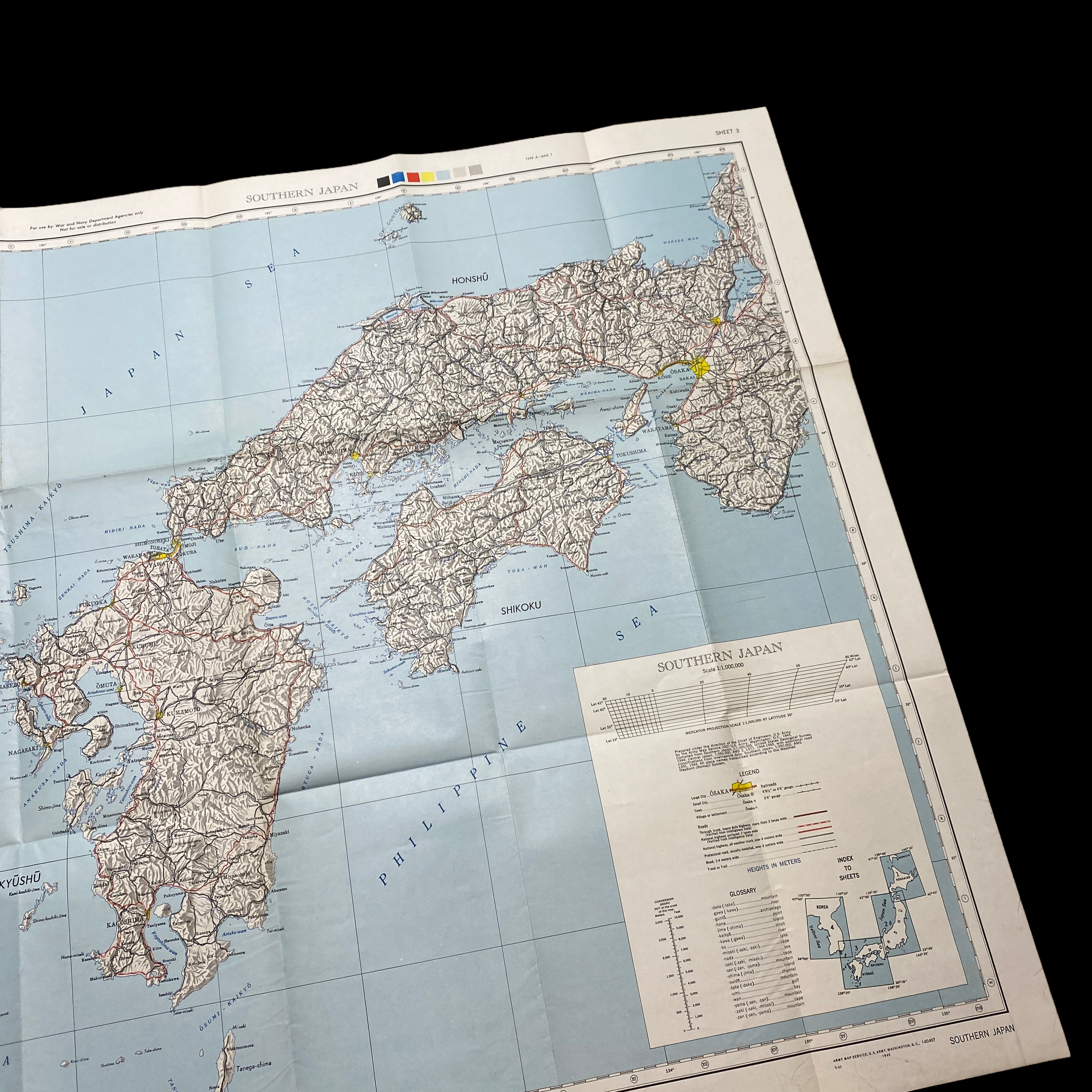
That's incredibly rare and museum-grade 1945 WWII high command war room map was used for the strategic military planning of Operation Downfall. Operation Downfall was the the proposed D-Day Allied plan for the invasion of the Japanese home islands near the end of World War II. The planned operation was canceled when Japan surrendered following the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
The operation had two parts: Operation Olympic and Operation Coronet. Set to begin in November 1945, Operation Olympic was intended to capture the southern third of the southernmost main Japanese island, Kyūshū, with the recently captured island of Okinawa to be used as a staging area. In early 1946 would come Operation Coronet, the planned invasion of the Kantō Plain, near Tokyo, on the main Japanese island of Honshu. Airbases on Kyūshū captured in Operation Olympic would allow land-based air support for Operation Coronet. If Downfall had taken place, it would have been the largest amphibious operation in history.
Japan's geography made this invasion plan quite obvious to the Japanese as well; they were able to accurately predict the Allied invasion plans and thus adjust their defensive plan, Operation Ketsugō, accordingly. The Japanese planned an all-out defense of Kyūshū, with little left in reserve for any subsequent defense operations. Casualty predictions varied widely, but were extremely high. Depending on the degree to which Japanese civilians would have resisted the invasion, estimates ran up into the millions for Allied casualties.
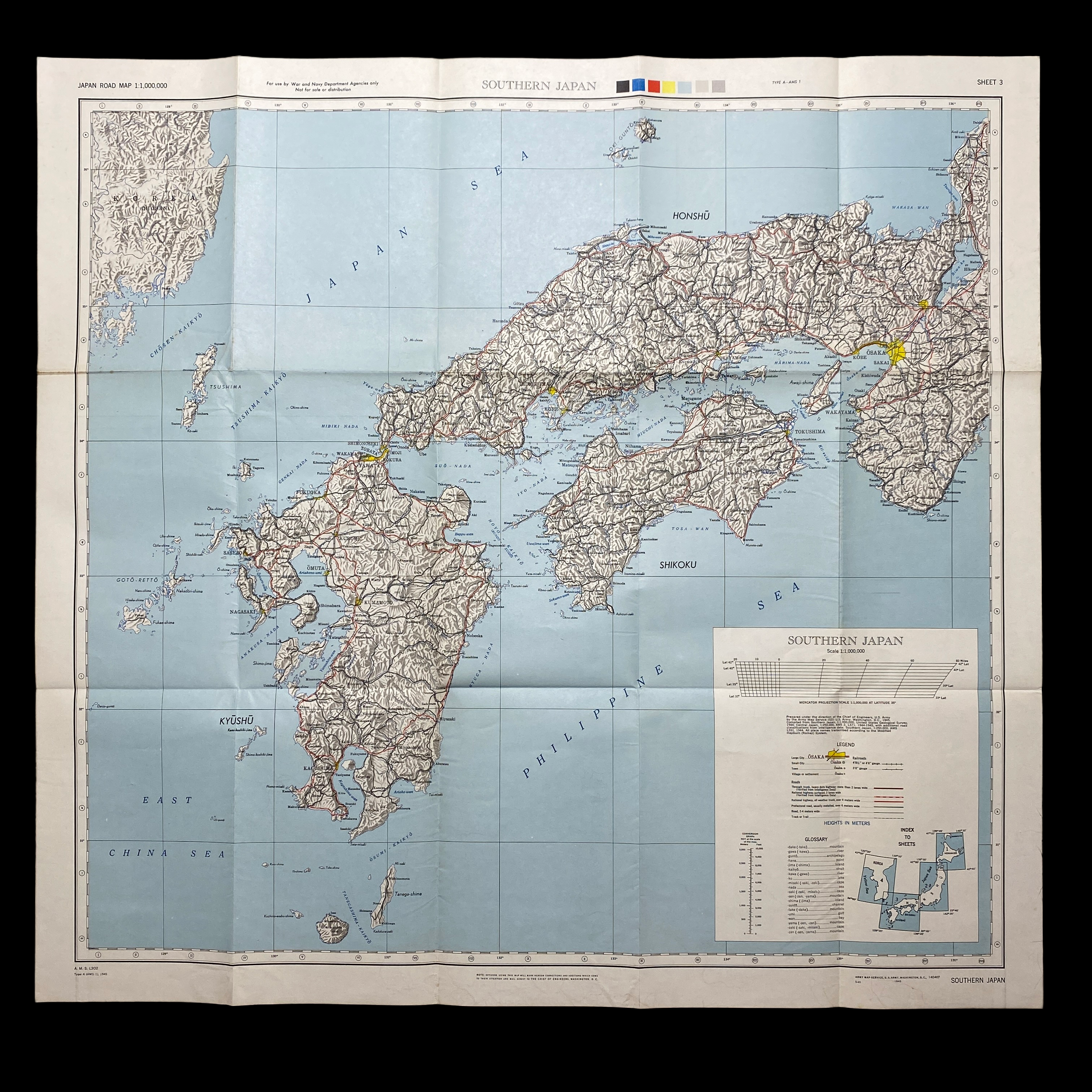
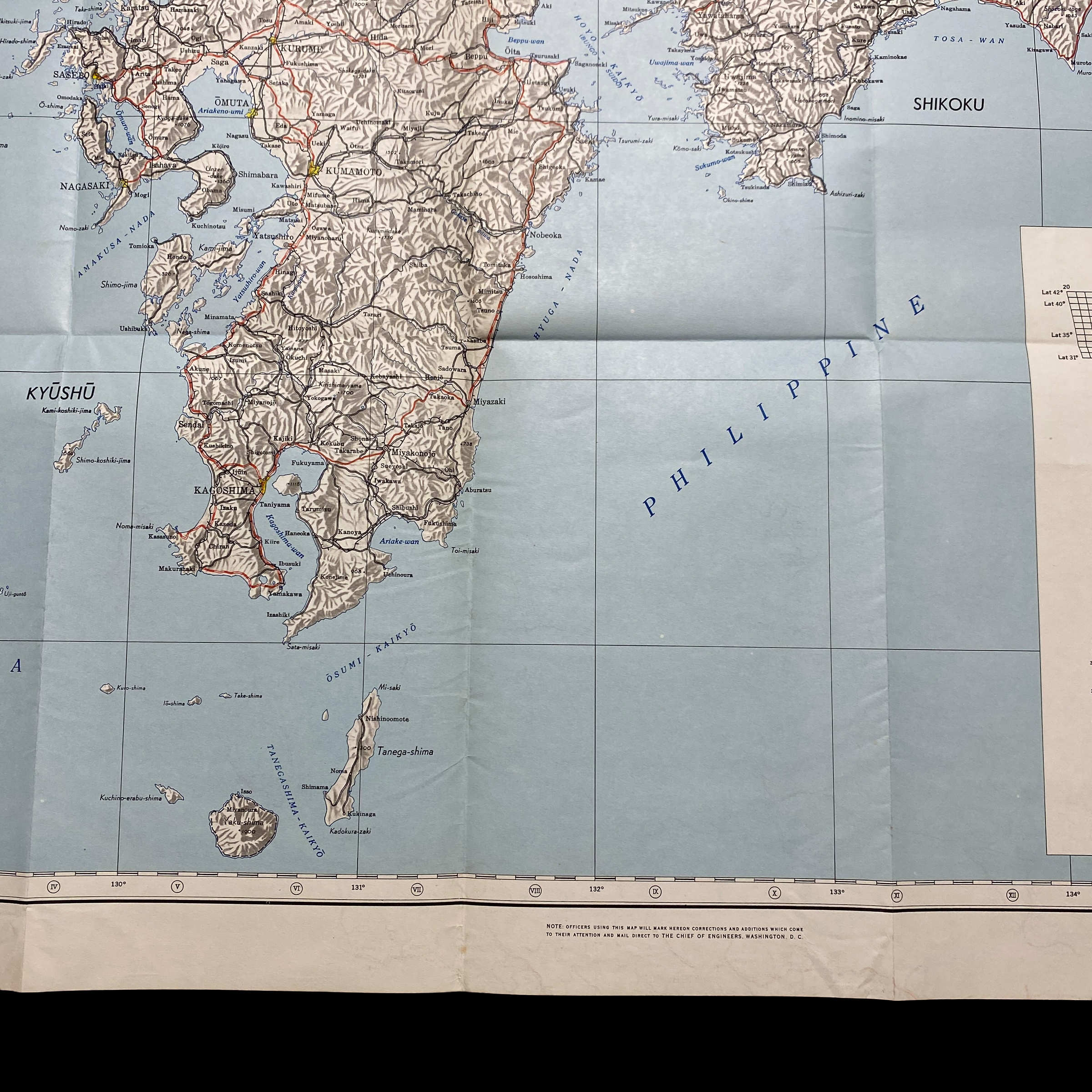
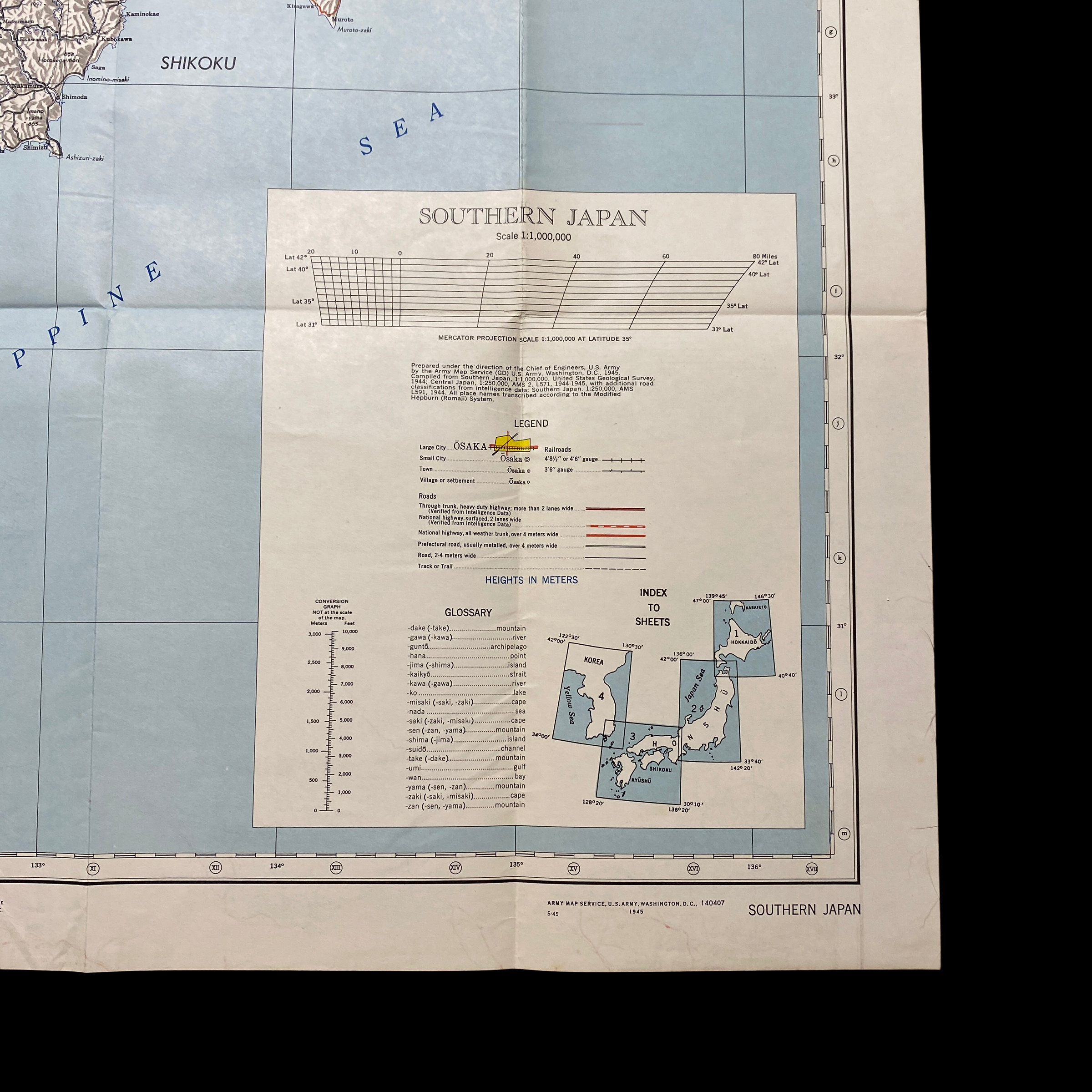
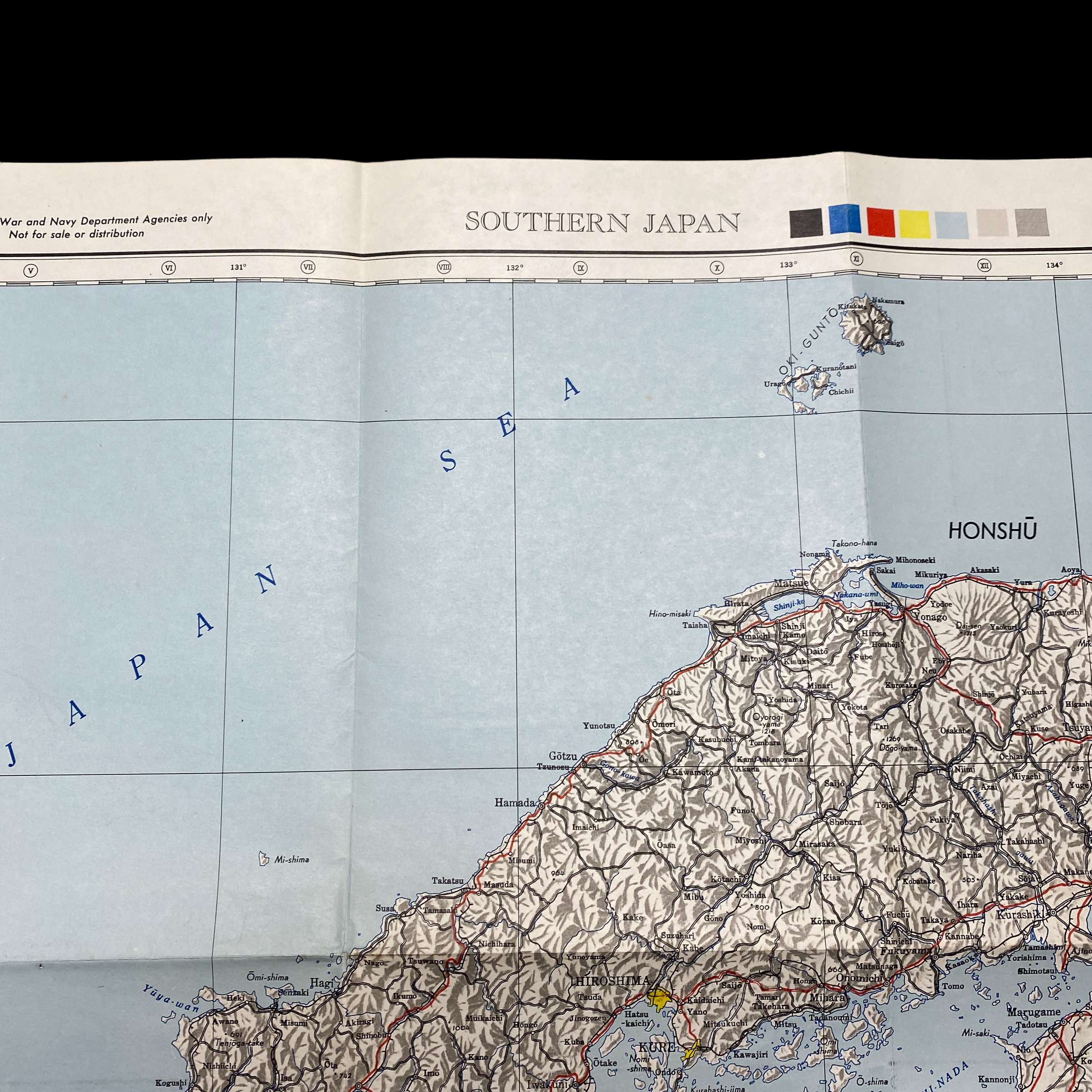
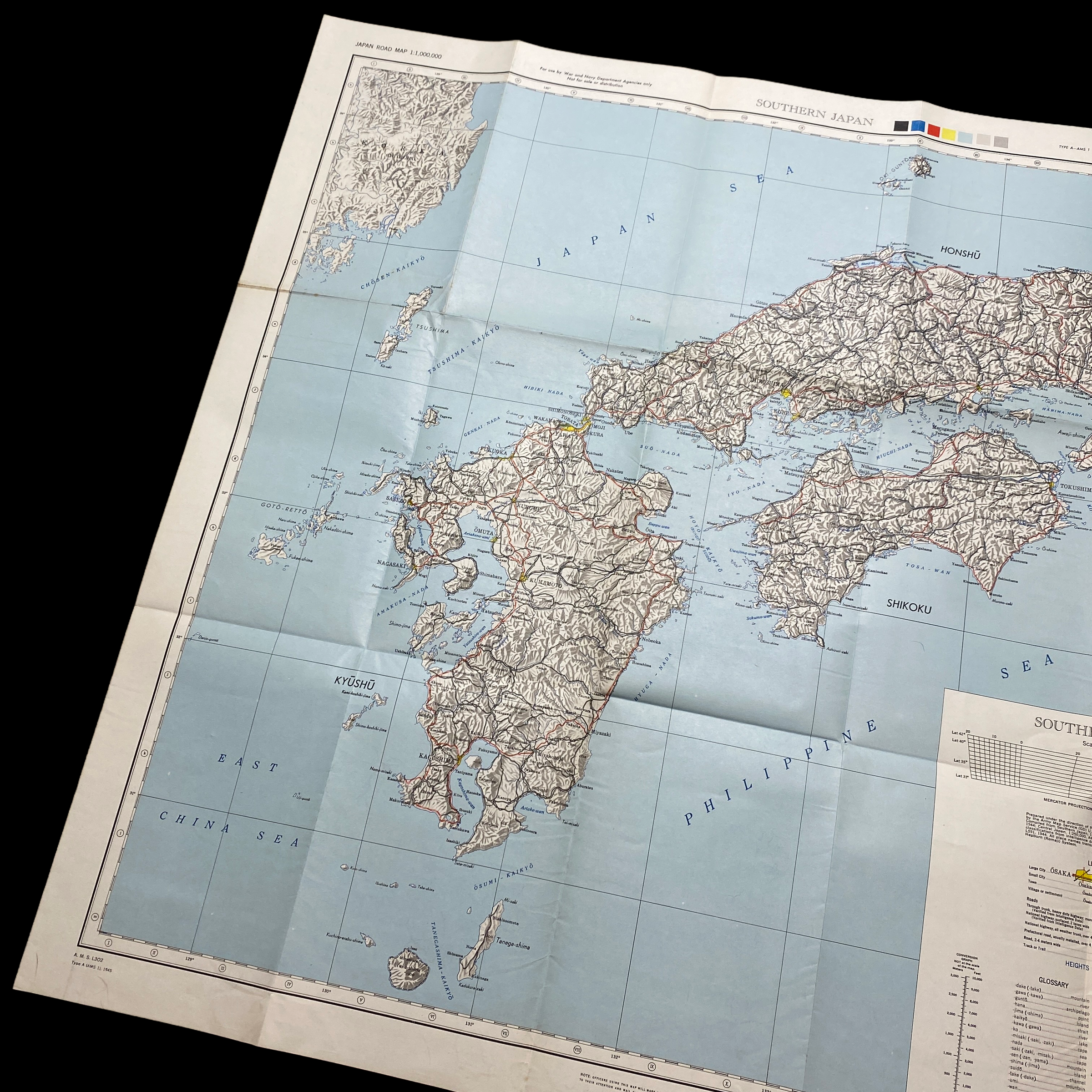
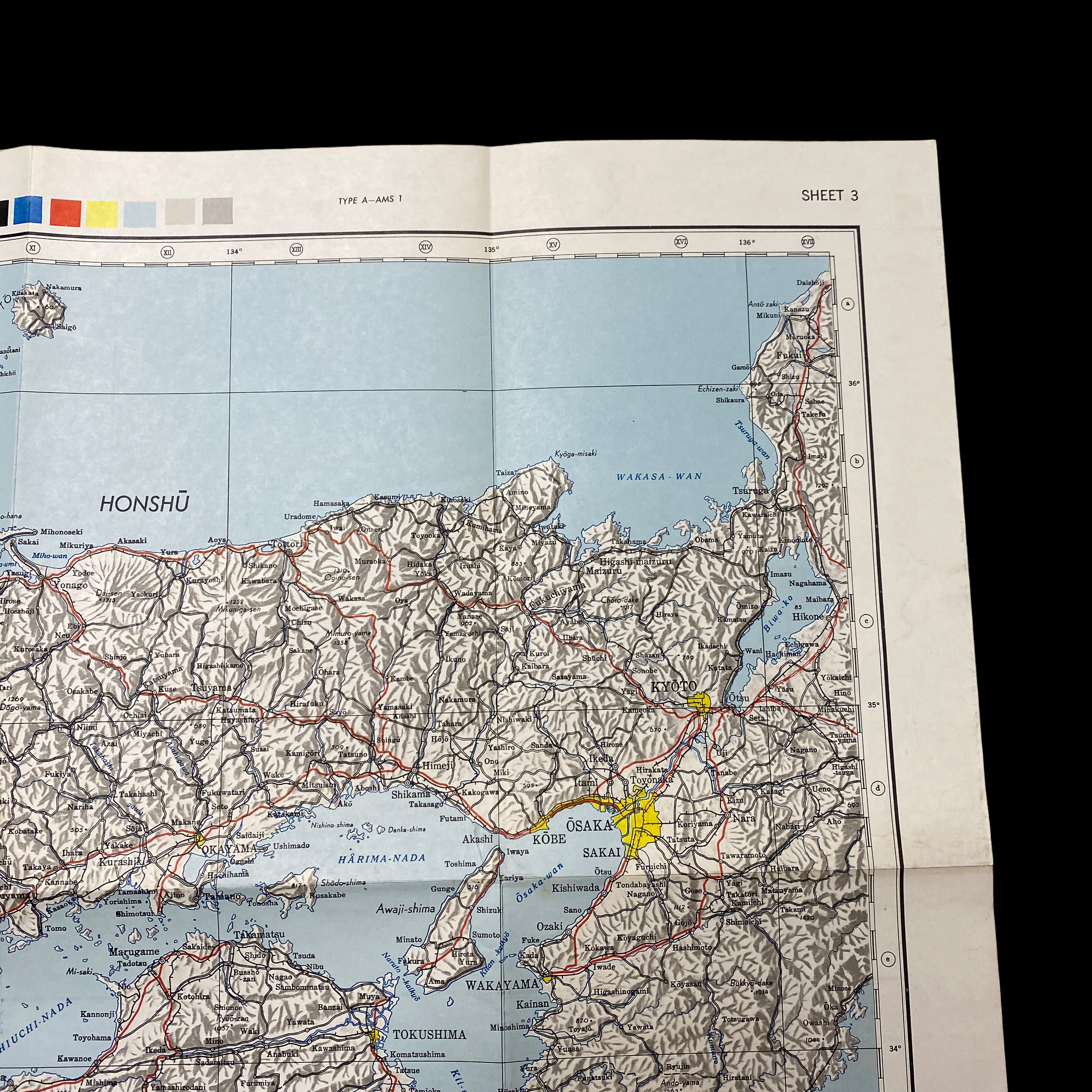
This war room map is extremely large in size and was printed in May 1945 (3 month prior to the detonated two atomic bombs over the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki on 6 and 9 August 1945). This specific war room map was to be used in the first initial phase of Operation Downfall, known as Operation Olympic. This map shows an extremely detailed view of southern Japan and labels its strategically important large cities, roads, and trails. Understanding the terrain and meticulously planning the invasion of the southern Japanese island was crucial in the Allied amphibious assault that was expected to occur.
Operation Olympic:
Operation Olympic, the invasion of Kyūshū, was to begin on "X-Day", which was scheduled for 1 November 1945. The combined Allied naval armada would have been the largest ever assembled, including 42 aircraft carriers, 24 battleships, and 400 destroyers and destroyer escorts. Fourteen U.S. divisions and a "division-equivalent" (two regimental combat teams) were scheduled to take part in the initial landings. Using Okinawa as a staging base, the objective would have been to seize the southern portion of Kyūshū. This area would then be used as a further staging point to attack Honshu in Operation Coronet.
Olympic was also to include a deception plan, known as Operation Pastel. Pastel was designed to convince the Japanese that the Joint Chiefs had rejected the notion of a direct invasion and instead were going to attempt to encircle and bombard Japan. This would require capturing bases in Formosa, along the Chinese coast, and in the Yellow Sea area.
Tactical air support was to be the responsibility of the Fifth, Seventh, and Thirteenth Air Forces. These were responsible for attacking Japanese airfields and transportation arteries on Kyushu and Southern Honshu (e.g. the Kanmon Tunnel) and for gaining and maintaining air superiority over the beaches. The task of strategic bombing fell on the United States Strategic Air Forces in the Pacific (USASTAF)—a formation which comprised the Eighth and Twentieth air forces, as well as the British Tiger Force. USASTAF and Tiger Force were to remain active through Operation Coronet. The Twentieth Air Force was to have continued its role as the main Allied strategic bomber force used against the Japanese home islands, operating from airfields in the Mariana Islands. Following the end of the war in Europe in May 1945, plans were also made to transfer some of the heavy bomber groups of the veteran Eighth Air Force to airbases on Okinawa to conduct strategic bombing raids in coordination with the Twentieth. The Eighth was to upgrade their B-17 Flying Fortresses and B-24 Liberators to B-29 Superfortresses (the group received its first B-29 on 8 August 1945).
Before the main invasion, the offshore islands of Tanegashima, Yakushima, and the Koshikijima Islands were to be taken, starting on X-5. The invasion of Okinawa had demonstrated the value of establishing secure anchorages close at hand, for ships not needed off the landing beaches and for ships damaged by air attack.
Kyūshū was to be invaded by the Sixth United States Army at three points: Miyazaki, Ariake, and Kushikino. If a clock were drawn on a map of Kyūshū, these points would roughly correspond to 4, 5, and 7 o'clock, respectively. The 35 landing beaches were all named for automobiles: Austin, Buick, Cadillac, and so on through to Stutz, Winton, and Zephyr. With one corps assigned to each landing, the invasion planners assumed that the Americans would outnumber the Japanese by roughly three to one. In early 1945, Miyazaki was virtually undefended, while Ariake, with its good nearby harbor, was heavily defended.
The invasion was not intended to conquer the entire island, just the southernmost third of it, as indicated by the dashed line on the map labeled "general limit of northern advance". Southern Kyūshū would offer a staging ground and a valuable airbase for Operation Coronet.
After the name Operation Olympic was compromised by being sent out in unsecured code, the name Operation Majestic was adopted.