VERY RARE! Original 1st Edition Apollo 16 CSM "Casper" Lunar Module Descartes Orbit Monitor Chart


































VERY RARE! Original 1st Edition Apollo 16 CSM "Casper" Lunar Module Descartes Orbit Monitor Chart
Comes with C.O.A.
Second Apollo mission with lunar rover. CSM main engine failure detected in lunar orbit. Landing almost aborted.AKA: Caspar. Launched: 1972-04-16. Returned: 1972-04-27. Number crew: 3 . Duration: 11.08 days.
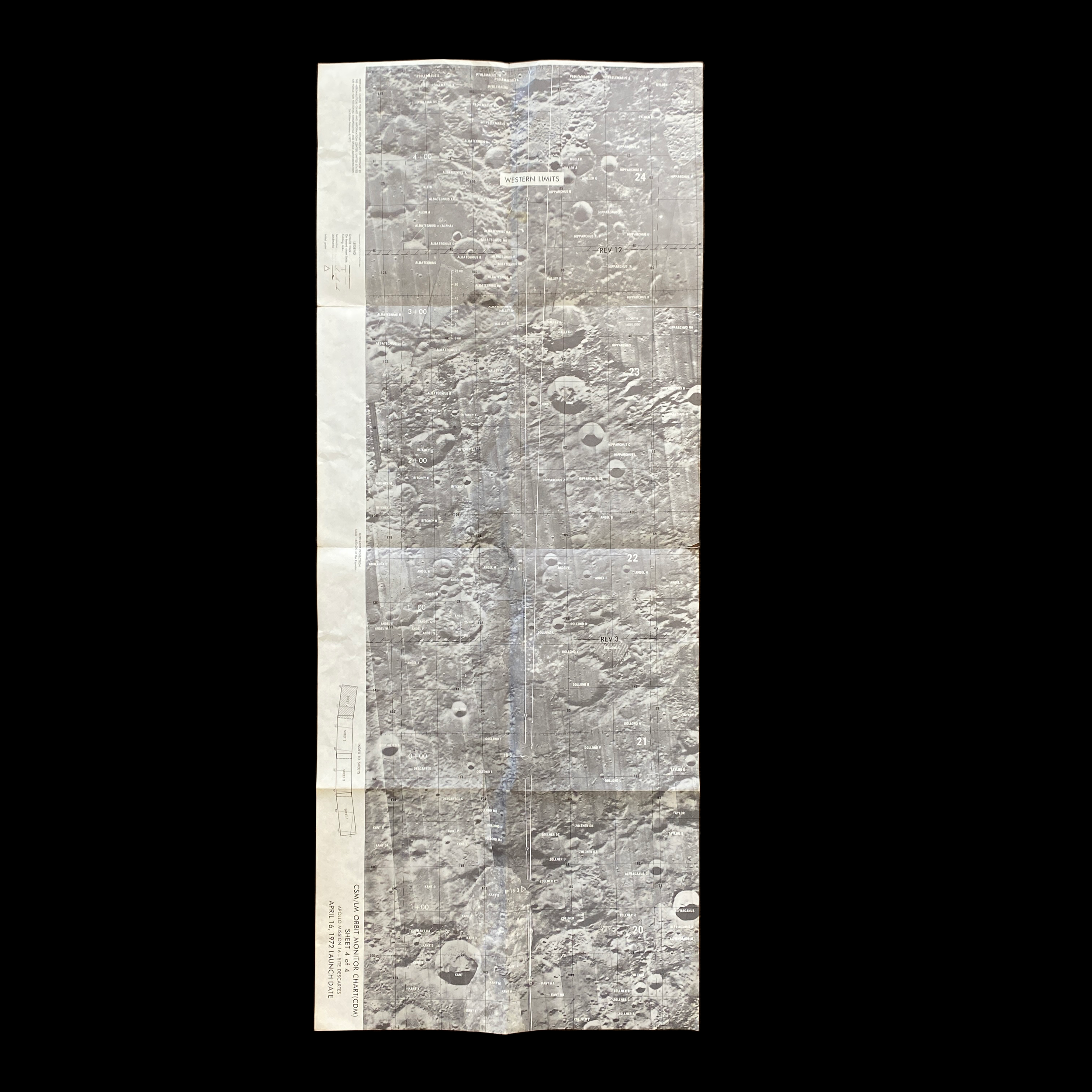
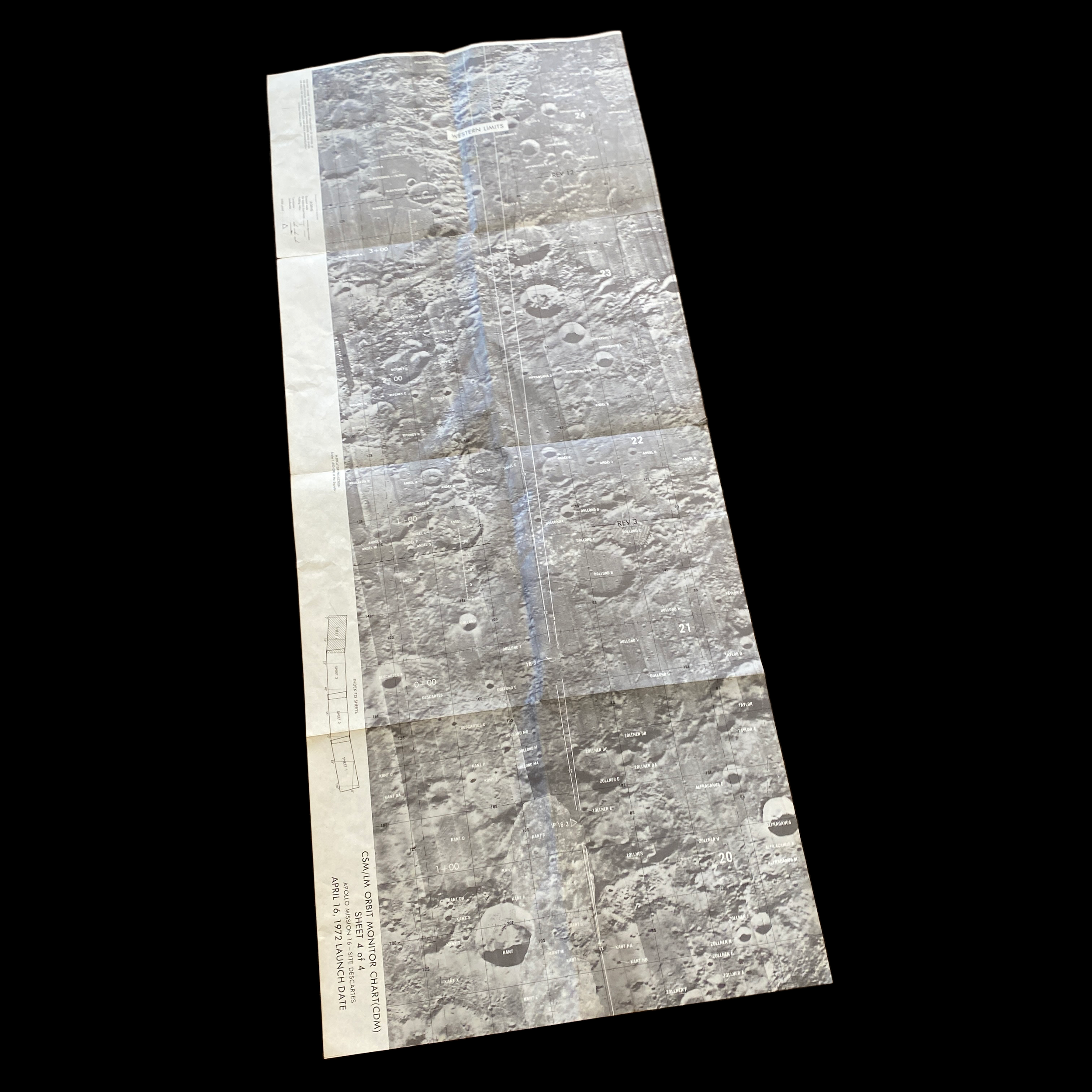
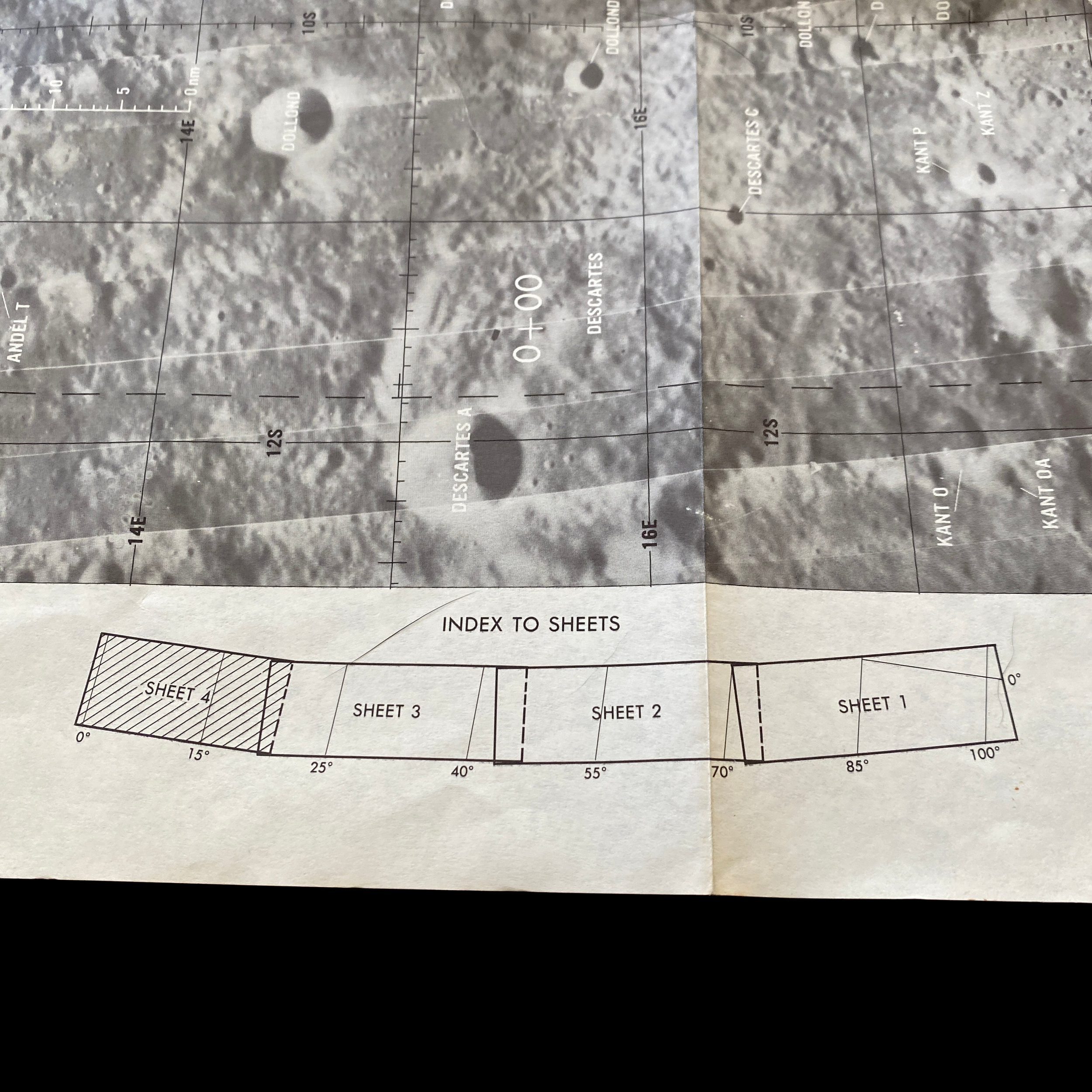
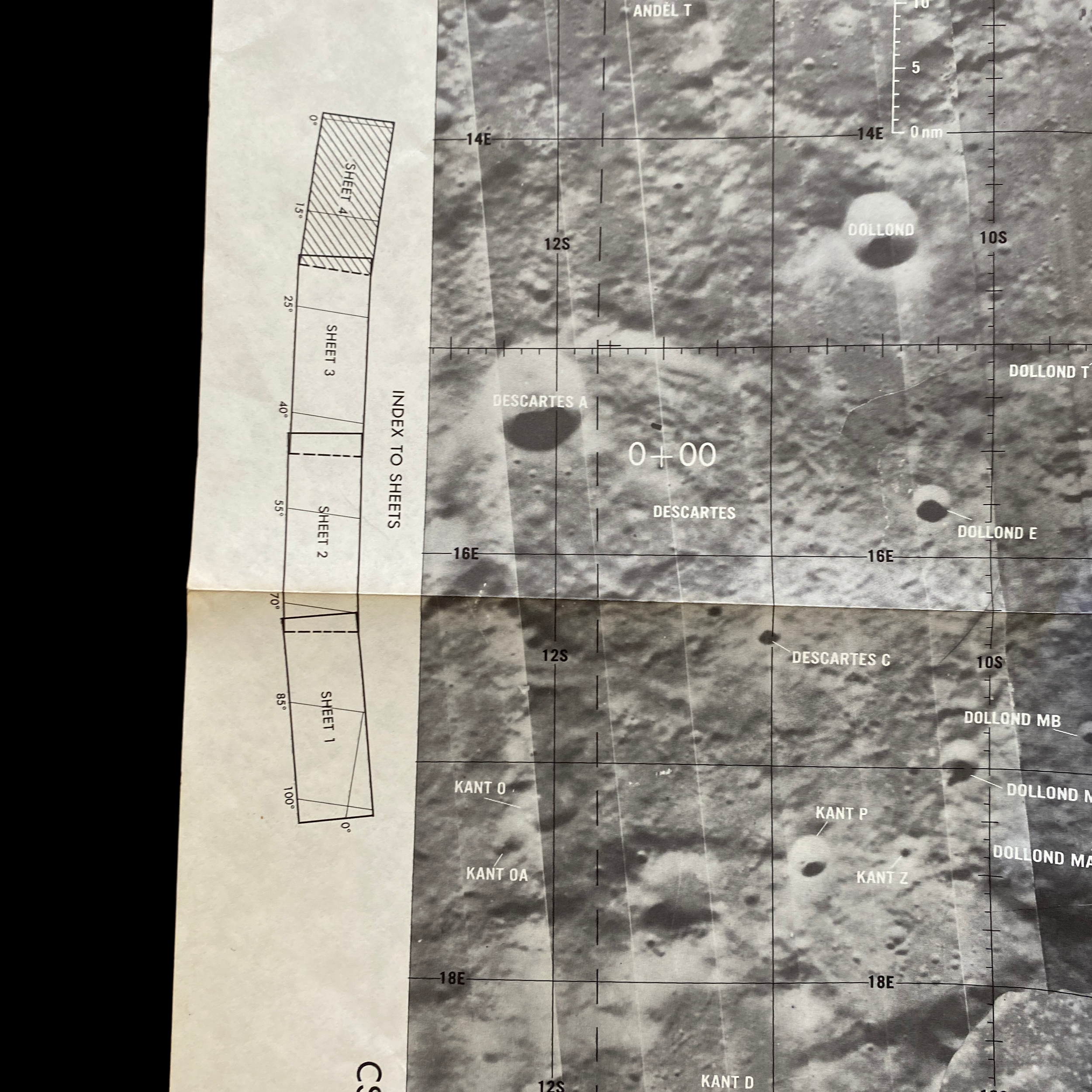
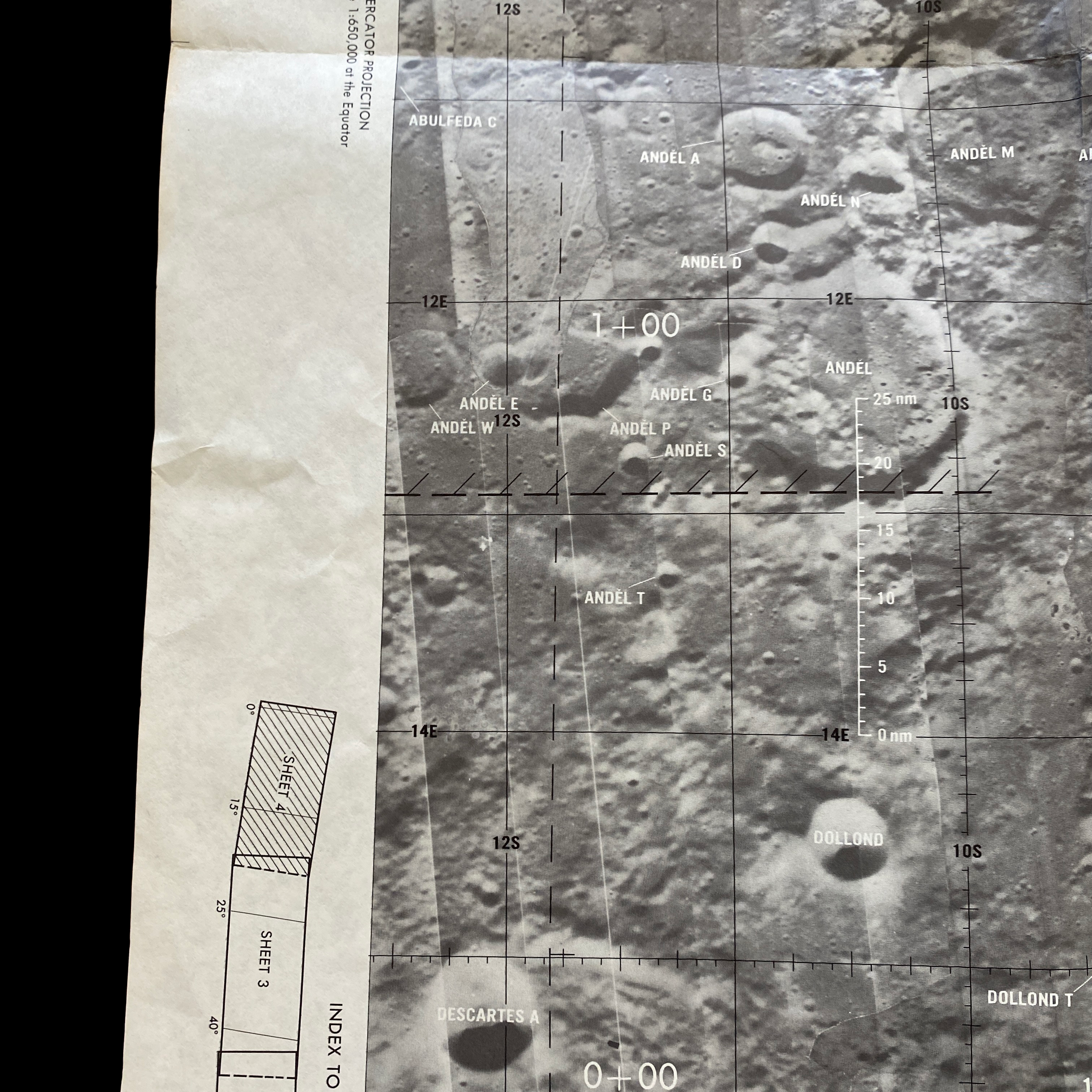
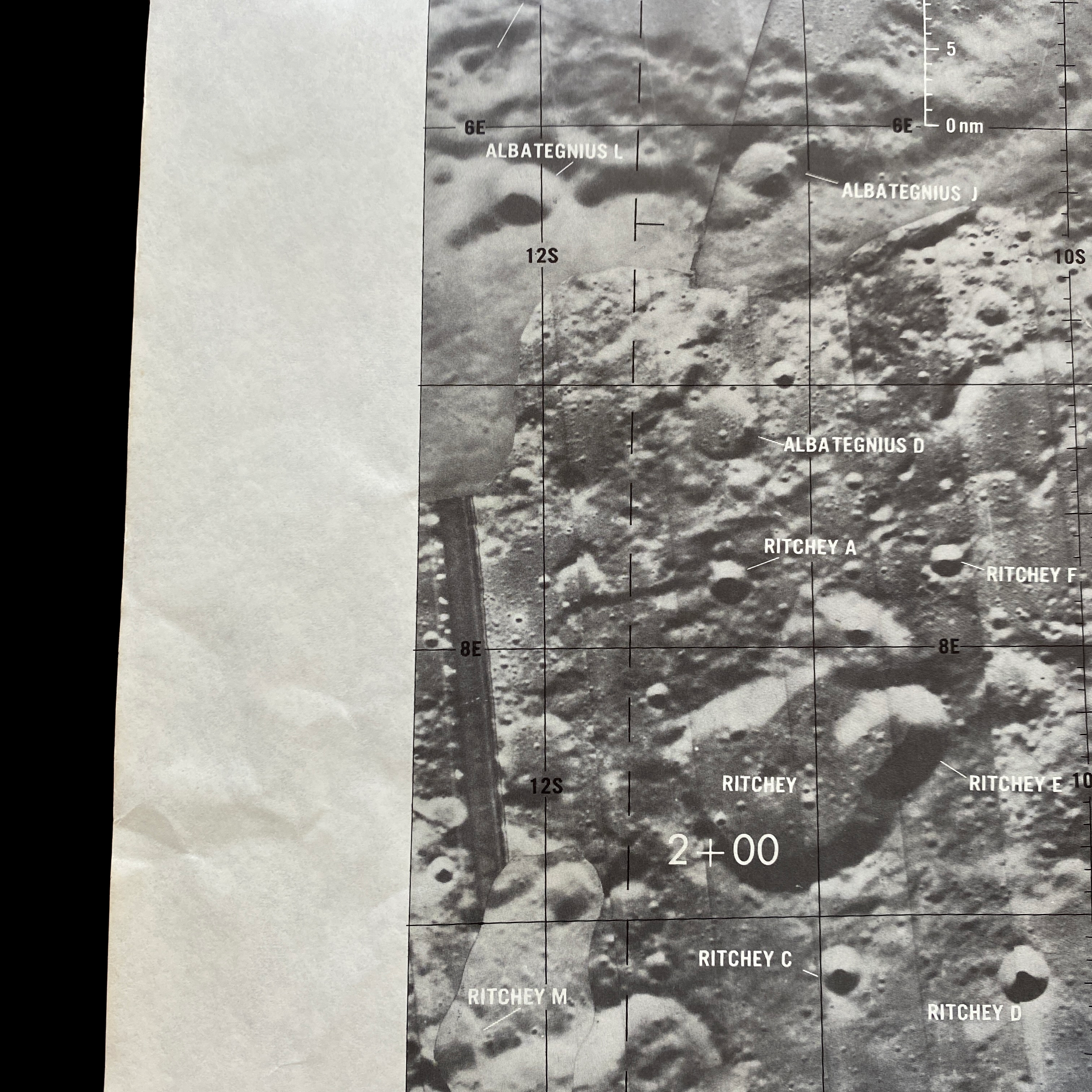
This extremely rare and museum-grade “CSM” and "LM” (LUNAR MODULE) Apollo Mission 16 lunar surface map plate is an original 1st EDITION moon landing decent map prepared under the direction of the Department of Defense by the Aeronautical Chart and Information Center, United States Air Force for National Aeronautics and Space Administration. The Lunar Module “Orbital Monitor Chart” chart covers the LM's ground track through the first complete lunar orbit before landing. This is a flight-ready article used in the lunar module Orion during its final descent to the Apollo 16 landing site in the Descartes Highlands. When folded, the crewmembers could view the lunar surface reference, showing the LM’s progress toward the landing site.
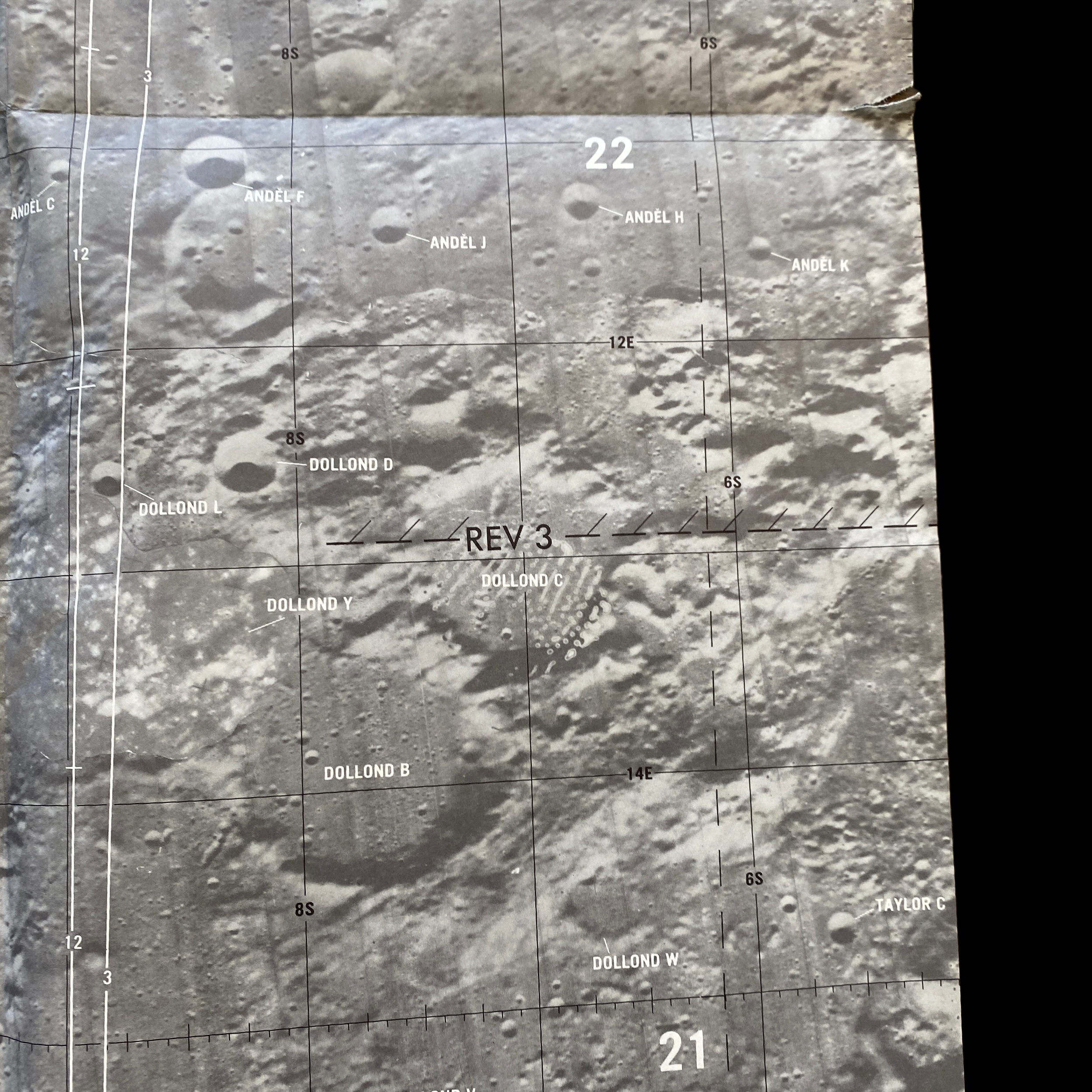
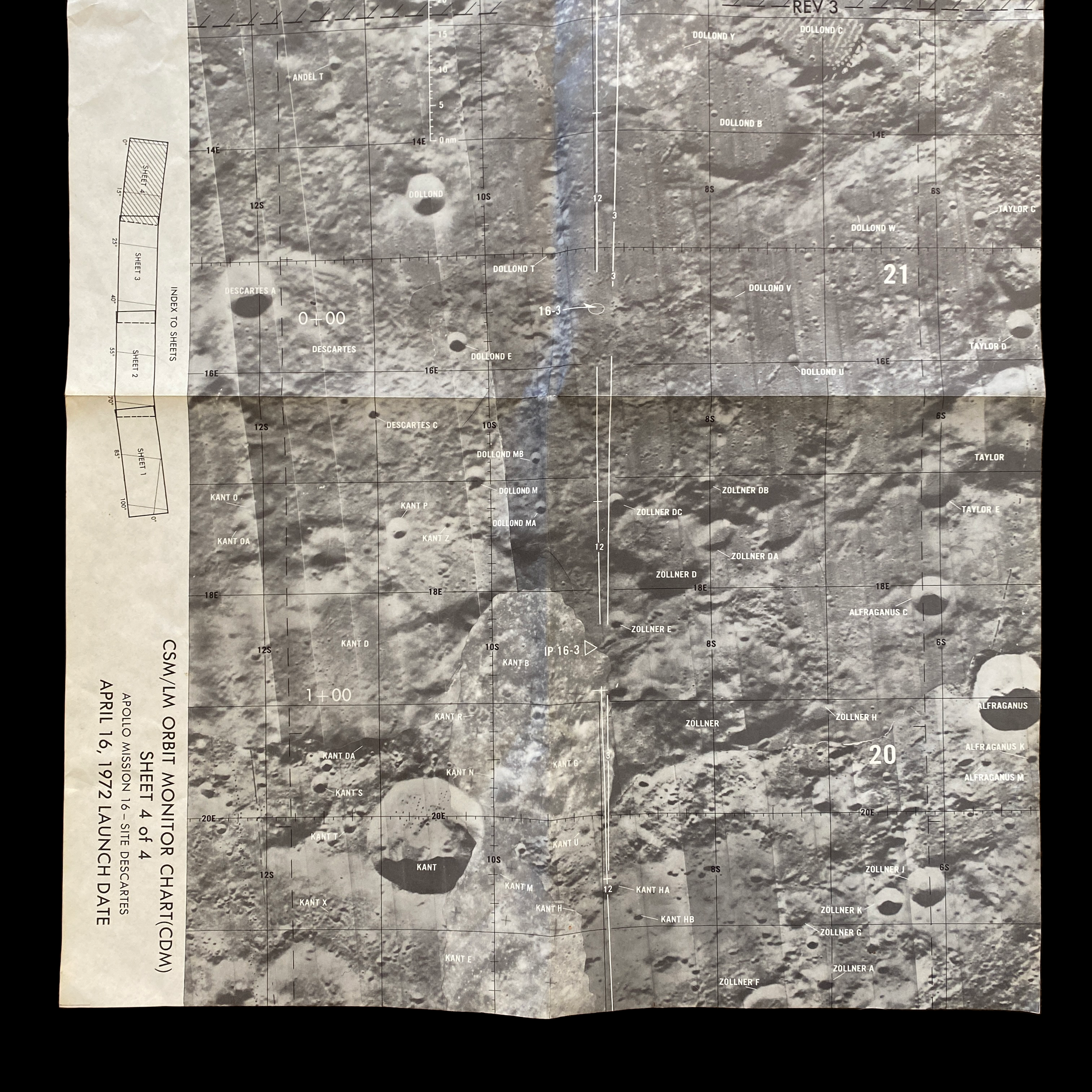
This original Apollo 16 Lunar Module Orbit Monitor Chart was used in Apollo 16 for the fifth lunar landing at Descartes. This lunar map shows a view of the lunar surface as seen during the descent, with significant landmarks labelled for quick reference. The orbital path of the lunar module, as well as time and distance scales, are overlayed on each plate in white.
This wide-angle areal lunar image shows the area around the anticipated Apollo 16 landing site. The image covers a vast area in detail, spanning over 12 lunar longitudinal degrees and four lunar latitudinal degrees, but the large size of the image allows for ample detail.
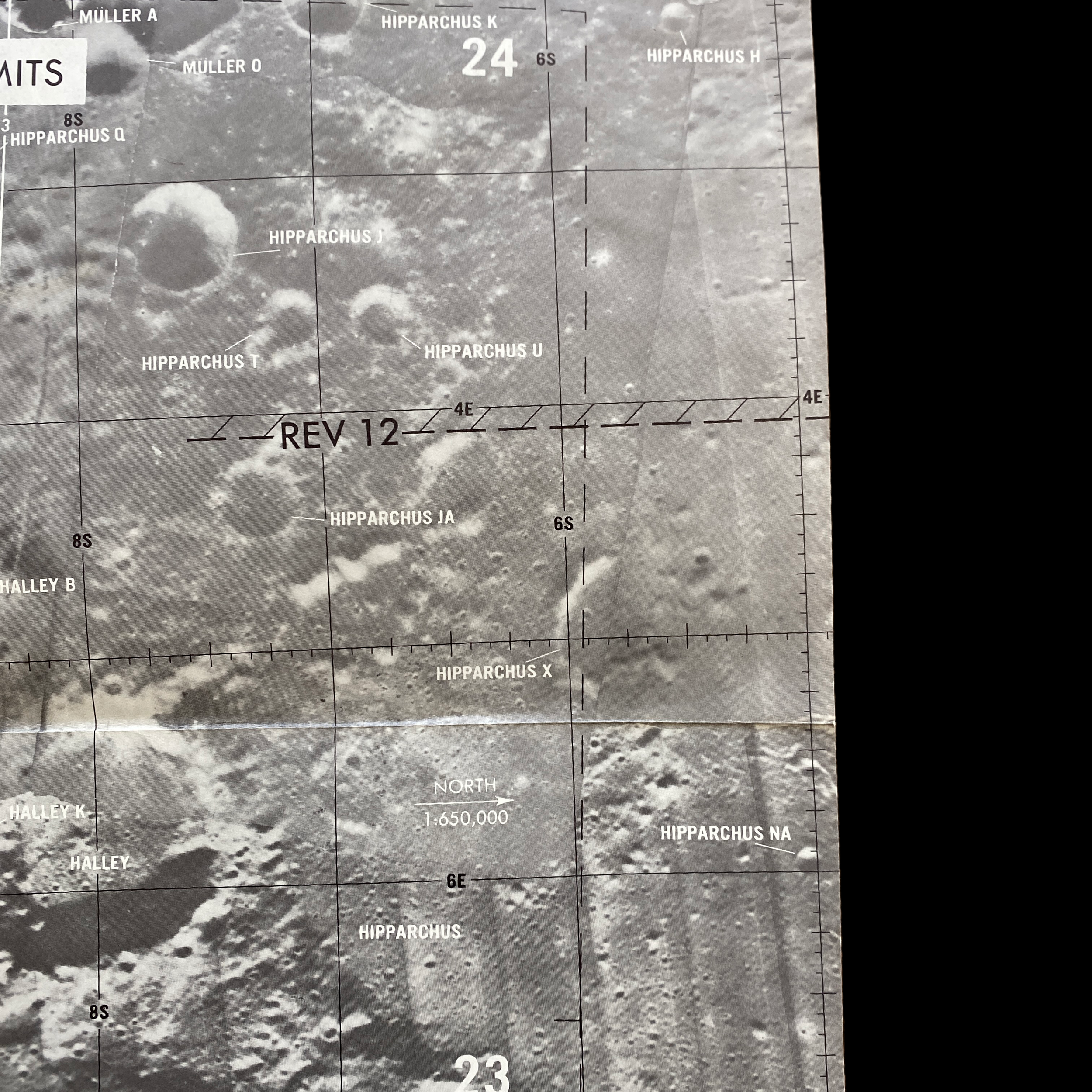
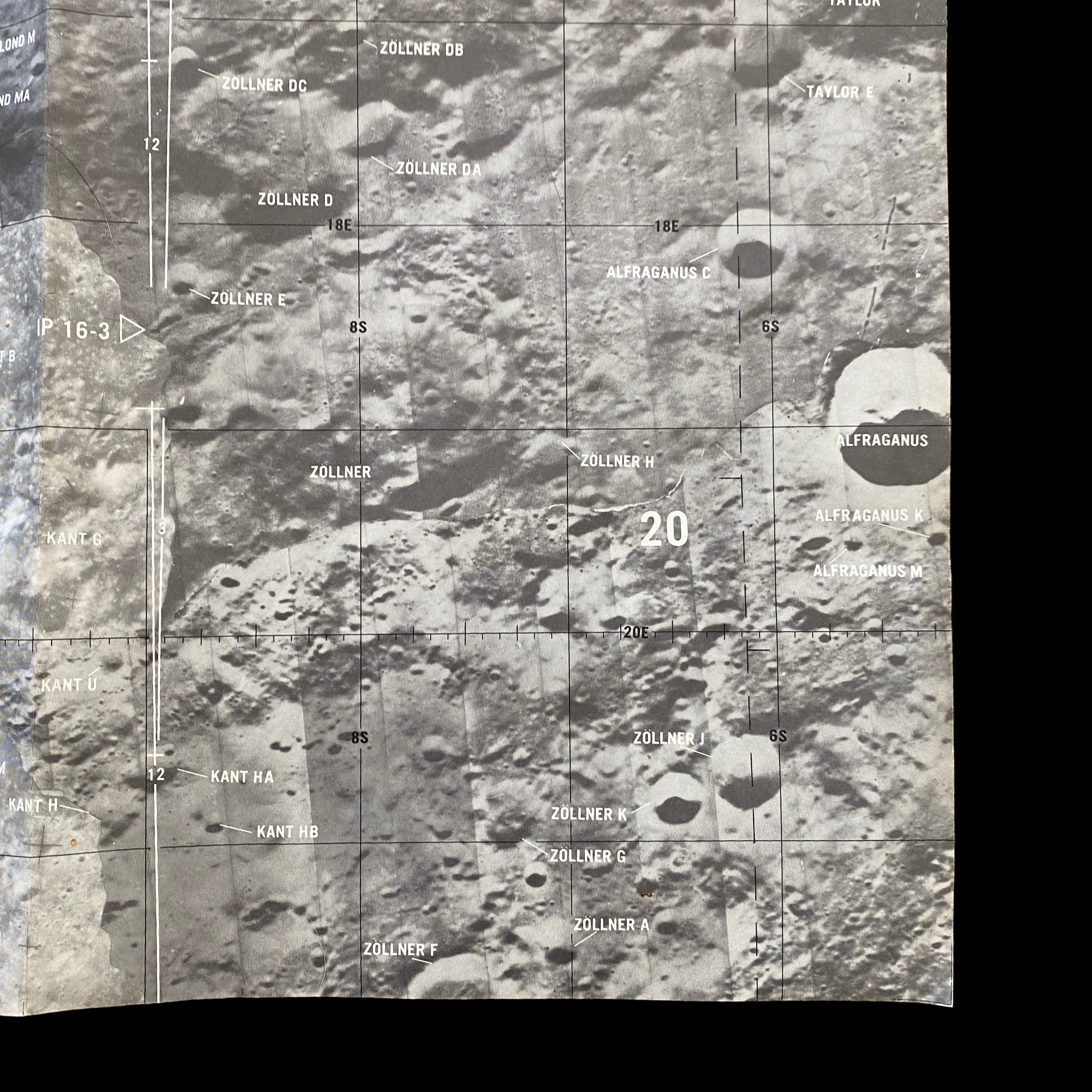
This lunar moon map shows the rugged region immediately to the West of the Apollo 16 landing site at Descartes-Cayley. This mission map features craters Ritchey, Hind, and Hipparchus' minor craters. This lunar chart shows Halley (bottom, black), with Albategnius dominating the left side and Hipparchus dominating the right side. The bottom edge of Müller can be seen at the top of the map. This Apollo 16 map features a large swath of Smyth's Sea, with crater Haldane dominating the center of the plate, the top half of Runge (near bottom center), with Talbot above.
Apollo 16:
Apollo 16 was the fifth mission in the Apollo program of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) to land astronauts on the moon. Launched on April 16, 1972, this mission was the first of the "J" missions, which were longer and more scientifically oriented than the earlier missions.
The Apollo 16 crew consisted of commander John W. Young, lunar module pilot Charles M. Duke, Jr., and command module pilot Thomas K. Mattingly II. The mission's main objective was to explore the Descartes Highlands, a mountainous region in the moon's southern hemisphere, and to conduct a series of experiments to gather information about the moon's geology, environment, and natural resources.
During their three-day stay on the moon, the astronauts explored the Descartes Highlands and conducted a number of experiments and surveys. They deployed scientific instruments and tools, including a Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) that allowed them to cover more ground than any previous mission. They also collected a variety of rock and soil samples that provided valuable information about the moon's composition and history.
One of the most memorable moments of the Apollo 16 mission was when Duke left a plaque on the moon that read, "Here Men From the Planet Earth First Set Foot Upon the Moon. July 1969 A.D. We Came in Peace For All Mankind." This plaque not only marked the achievements of the Apollo program, but also symbolized the spirit of exploration and discovery that drives humanity forward.
The Apollo 16 mission was also notable for the first use of a scientific instrument known as the Lunar Sounder Experiment, which was designed to map the moon's subsurface structure. The experiment provided new insights into the moon's internal structure and helped to confirm the presence of ice in some of the moon's craters.
In conclusion, the Apollo 16 mission was a major milestone in the exploration of the moon and our understanding of its geology, environment, and resources. The mission's scientific achievements and technological innovations continue to inspire and inform space exploration today. It remains a testament to the human spirit of discovery and a reminder of the infinite possibilities of scientific progress.
Apollo 16 and Casper “CSM”:
The Apollo 16 (AS-511) space vehicle was launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, KSC, at 12:54 p.m. EST April 16, with a crew of astronauts John W. Young, Thomas K. Mattingly II, and Charles M. Duke, Jr. After insertion into an earth parking orbit for spacecraft system checks, the spacecraft and the S-IVB stage were placed on a trajectory to the moon at 3:28 p.m. CSM transposition and docking with the LM were achieved, although a number of minor anomalies were noted.One anomaly, an auxiliary propulsion system leak on the S-IVB stage, produced an unpredictable thrust and prevented a final S-IVB targeting maneuver after separation from the CSM. Tracking of the S-IVB ended at 4:04 p.m. EST April 17, when the instrument unit's signal was lost. The stage hit the lunar surface at 4:02 p.m. April 19, 260 kilometers northeast of the target point. The impact was detected by the seismometers left on the moon by the Apollo 12, 14, and 15 missions.Spacecraft operations were near normal during the coast to the moon. Unexplained light-colored particles from the LM were investigated and identified as shredded thermal paint. Other activities during the translunar coast included a cislunar navigation exercise, ultraviolet photography of the earth and moon, an electrophoresis demonstration, and an investigation of the visual light-flash phenomenon noted on previous flights. Astronaut Duke counted 70 white, instantaneous light flashes that left no after-glow.Apollo 16 entered a lunar orbit of 314 by 107.7 kilometers at 3:22 p.m. April 19. After separation of LM-11 Orion from CSM 112 Casper, a CSM active rendezvous kept the two vehicles close together while an anomaly discovered on the service propulsion system was evaluated. Tests and analyses showed the redundant system to be still safe and usable if required. The vehicles were again separated and the mission continued on a revised timeline because of the 5 3/4-hour delay.The lunar module landed with Duke and Young in the moon's Descartes region, about 230 meters northwest of the planned target area at 9:23 p.m. EST April 20. A sleep period was scheduled before EVA.The first extravehicular activity began at 11:59 a.m. April 21, after the eight-hour rest period. Television coverage of surface activity was delayed until the lunar roving vehicle systems were activated, because the steerable antenna on the lunar module could not be used. The lunar surface experiments packages were deployed, but accidental breaking of the electronics cable rendered the heat flow experiment inoperable. After completing activities at the experiments site, the crew drove the lunar roving vehicle west to Flag Crater, where they performed the planned tasks. The inbound traverse route was just slightly south of the outbound route, and the next stop was Spook Crater. The crew then returned via the experiment station to the lunar module and deployed the solar wind composition experiment. The duration of the extravehicular activity was 7 hours 11 minutes. The distance traveled by the lunar roving vehicle was 4.2 kilometers. The crew collected 20 kilograms of samples.The second extravehicular traverse, which began at 11:33 a.m. April 22, was south-southeast to a mare-sampling area near the Cinco Craters on Stone Mountain. The crew then drove in a northwesterly direction, making stops near Stubby and Wreck Craters. The last leg of the traverse was north to the experiments station and the lunar module. The second extravehicular activity lasted 7 hours 23 minutes. The distance traveled by the lunar roving vehicle was 11.1 kilometers.Four stations were deleted from the third extravehicular traverse, which began 30 minutes early at 10:27 a.m. April 23 to allow extra time. The first stop was North Ray Crater, where "House Rock" on the rim of the crater was sampled. The crew then drove southeast to "Shadow Rock." The return route to the LM retraced the outbound route. The third extravehicular activity lasted 5 hours 40 minutes, and the lunar roving vehicle traveled 11.4 kilometers.Lunar surface activities outside the LM totaled 20 hours 15 minutes for the mission. The total distance traveled in the lunar roving vehicle was 26.7 kilometers. The crew remained on the lunar surface 71 hours 02 minutes and collected 96.6 kilograms of lunar samples.While the lunar module crew was on the surface, Mattingly, orbiting the moon in the CSM, was obtaining photographs, measuring physical properties of the moon and deep space, and making visual observations. Essentially the same complement of instruments was used to gather data as was used on the Apollo 15 mission, but different areas of the lunar surface were flown over and more comprehensive deep space measurements were made, providing scientific data that could be used to validate findings from Apollo 15 as well as add to the total store of knowledge of the moon and its atmosphere, the solar system, and galactic space.The LM lifted off from the moon at 8:26 p.m. EST April 23, rendezvoused with the CSM, and docked with it in orbit. Young and Duke transferred to the CSM with samples, film, and equipment, and the LM was jettisoned the next day. LM attitude control was lost at jettison; therefore a deorbit maneuver was not possible and the LM remained in lunar orbit, with an estimated orbital lifetime of about one year.The particles and fields subsatellite was launched into lunar orbit and normal system operation was noted. However, the spacecraft orbital shaping maneuver was not performed before ejection and the subsatellite was placed in a non-optimum orbit that resulted in a much shorter lifetime than the planned year. Loss of all subsatellite tracking and telemetry data on the 425th revolution (May 29) indicated that the subsatellite had hit the lunar surface.The mass spectrometer deployment boom stalled during a retract cycle and was jettisoned before transearth injection. The second plane-change maneuver and some orbital science photography were deleted so that transearth injection could be performed about 24 hours earlier than originally planned.Activities during the transearth coast phase of the mission included photography for a contamination study for the Skylab program and completion of the visual light-flash-phenomenon investigation that had been partially accomplished during translunar coast. A 1-hour 24-minute transearth extravehicular activity was conducted by command module pilot Mattingly to retrieve the film cassettes from the scientific instrument module cameras, inspect the equipment, and expose a microbial-response experiment to the space environment. Two midcourse corrections were made on the return flight to achieve the desired entry interface conditions.Entry and landing were normal, completing a 265-hour 51-minute mission. The command module was viewed on television while dropping on the drogue parachutes, and continuous coverage was provided through crew recovery. Splashdown was at 2:44 p.m. EST April 27 in mid-Pacific, 5 kilometers from the recovery ship U.S.S. Ticonderoga. All primary mission objectives had been achieved.Official NASA Account of the Mission from Where No Man Has Gone Before: A History of Apollo Lunar Exploration Missions, by W. David Compton, published as NASA SP-4214 in the NASA History Series, 1989.Apollo 16 blasted off from Kennedy Space Center at 12:54 p.m. Eastern Standard Time on April 16, 1972. Command module Casper and lunar module Orion arrived in lunar orbit three days later. All systems functioned well until Orion separated from the command module; a malfunctioning component in the main propulsion system caused Houston to delay the lunar module's descent for nearly six hours while it was checked out. When Mission Control was satisfied, Orion fired its descent engine and landed easily on the plain at Descartes at 9:33 p.m. EST on April 20.In the next 71 hours mission commander John Young and lunar module pilot Charles Duke laid out the surface instruments and conducted three traverses in their lunar rover, covering in all some 27 kilometers (nearly 17 miles). While they were busy on the surface, Ken Mattingly in Casper was occupied with operating the instruments in the service module. The only serious mishap on the surface occurred when Young tripped over the cable to the heat-flow sensors, pulling it loose from the central station and incapacitating the experiment.Young and Duke finished their exploration, loaded the 96 kilograms (210 pounds) of samples they had collected into Orion , and rejoined Mattingly in lunar orbit on April 23. They released the moon-orbiting subsatellite, but because of recurring problems with the service propulsion system, the spacecraft was not in the optimum orbit for the satellite. As a result, the satellite crashed into the moon after only five weeks. During the four-day return flight they conducted additional experiments with electrophoresis, a technique that offered advantages for separating certain biological preparations that could not be efficiently done in a gravity field. A normal landing in the Pacific, north of Christmas Island, completed the mission On April 27.