Original Cold War NATO Heavily Mission Marked ZARAGOZA Spain British R.A.F. Air Force Map*
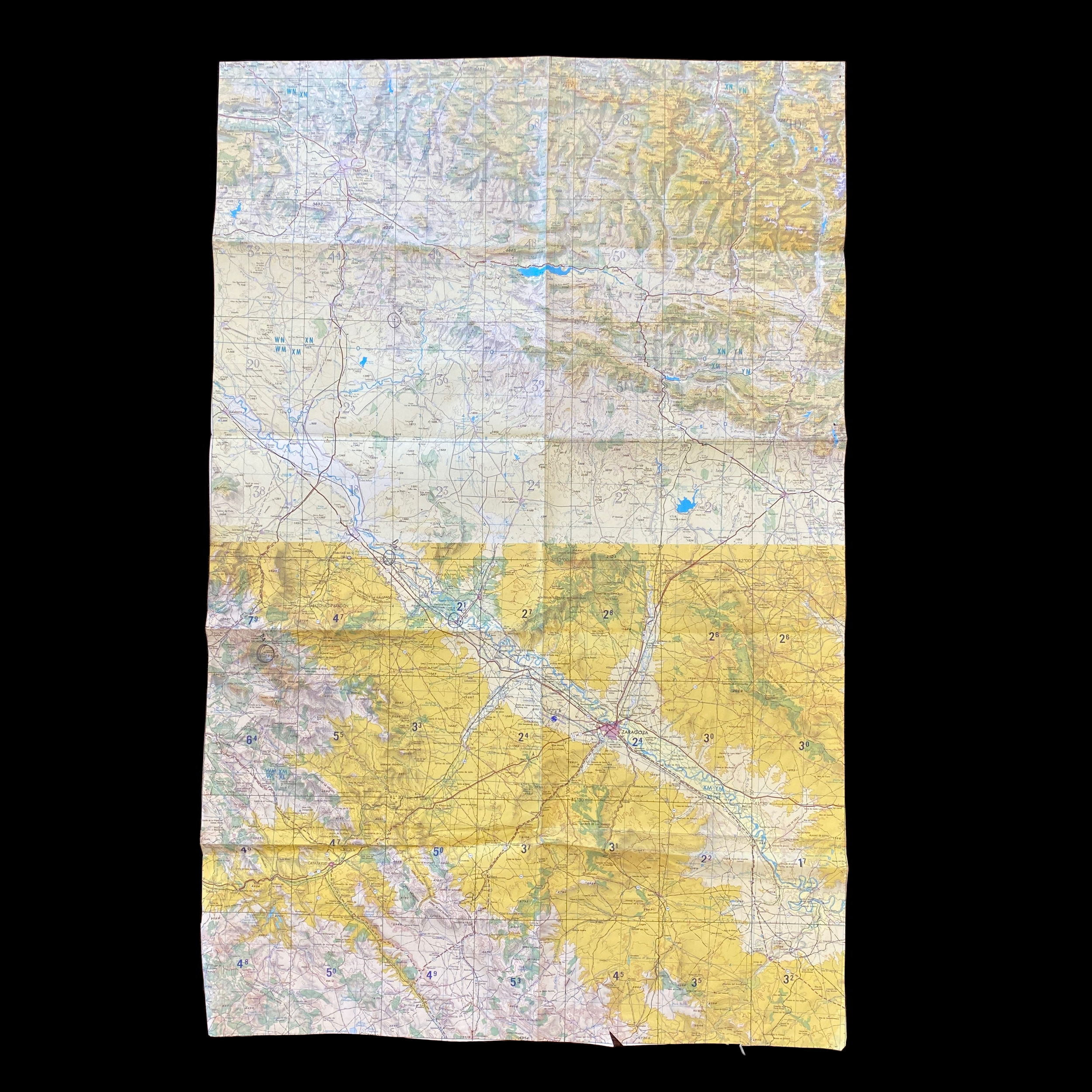


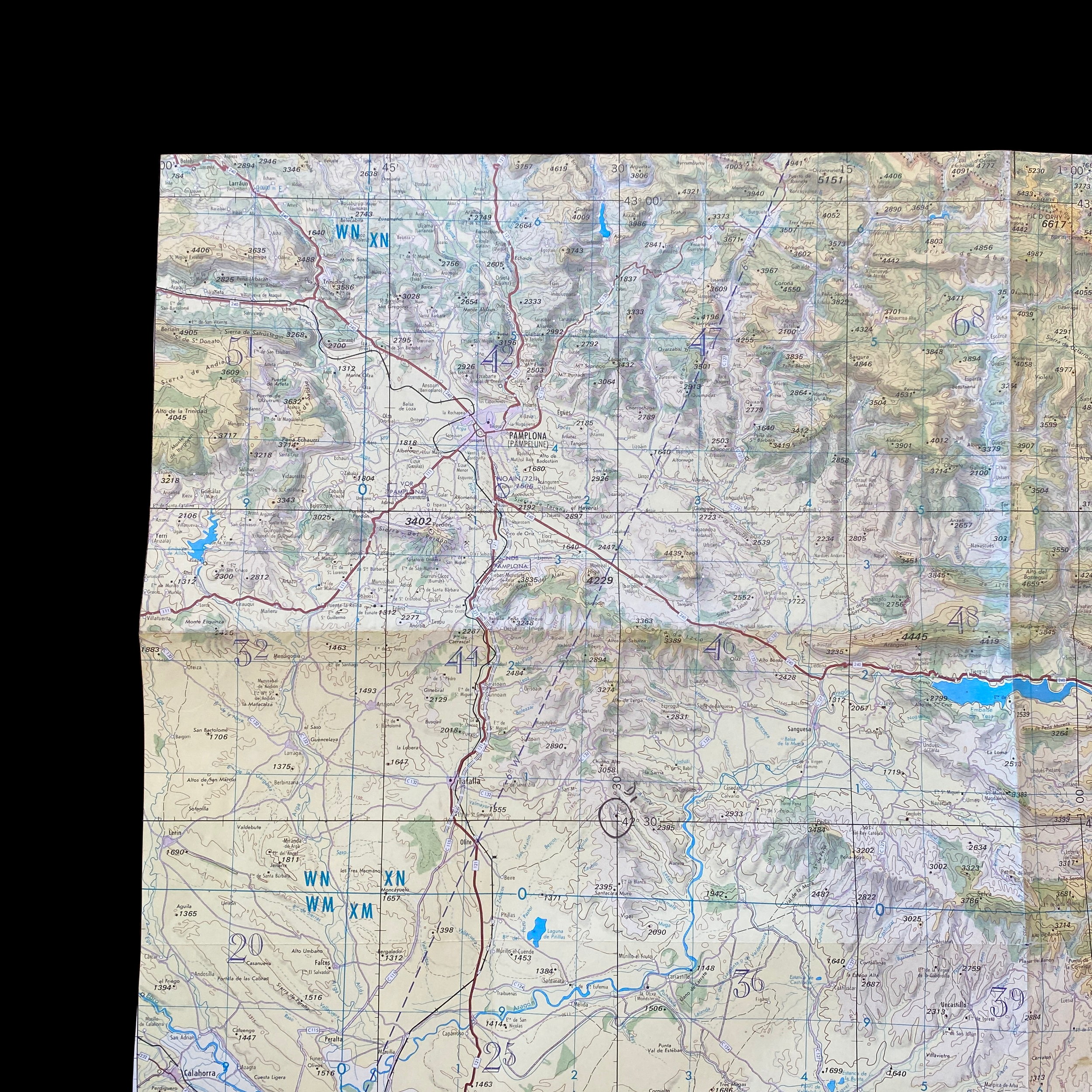








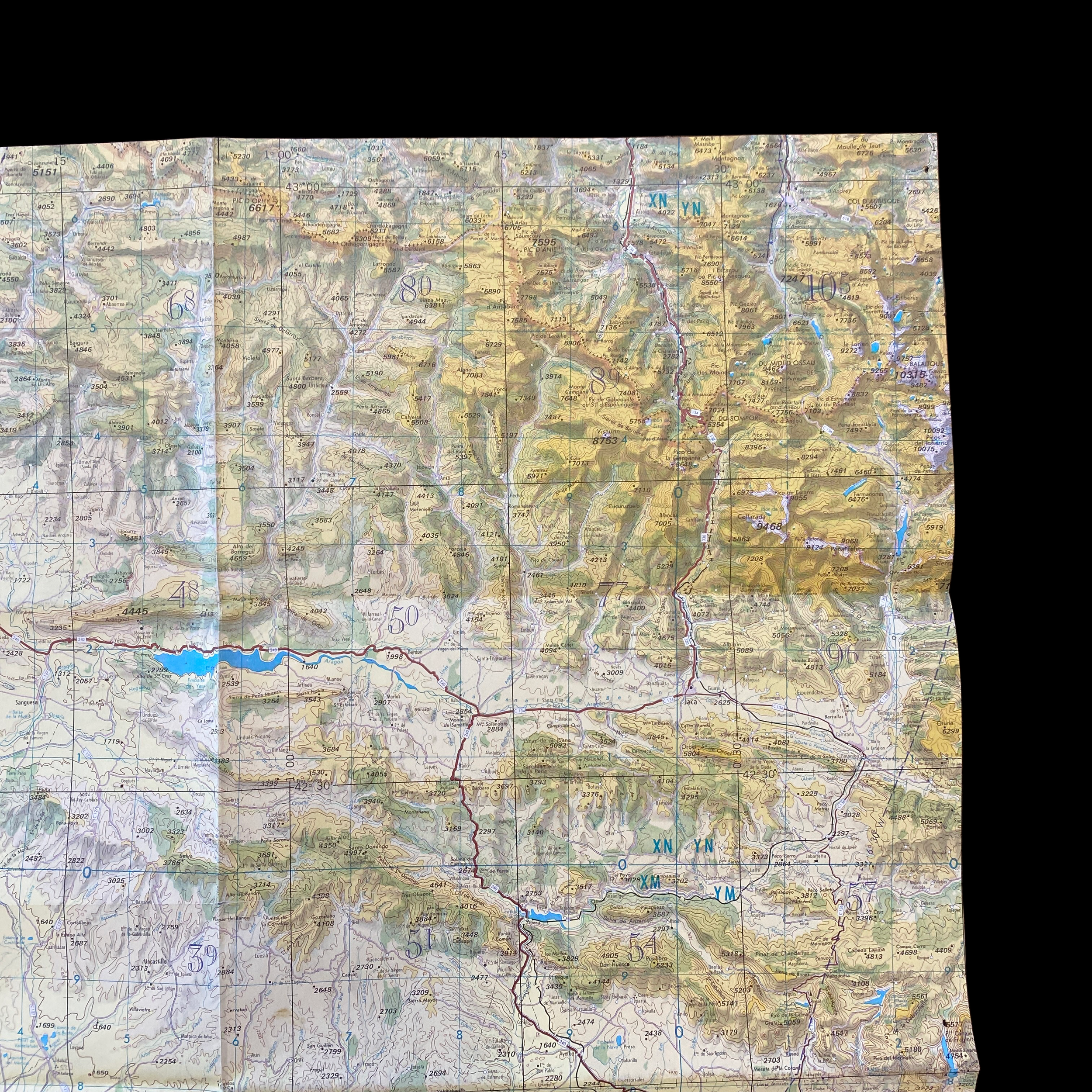
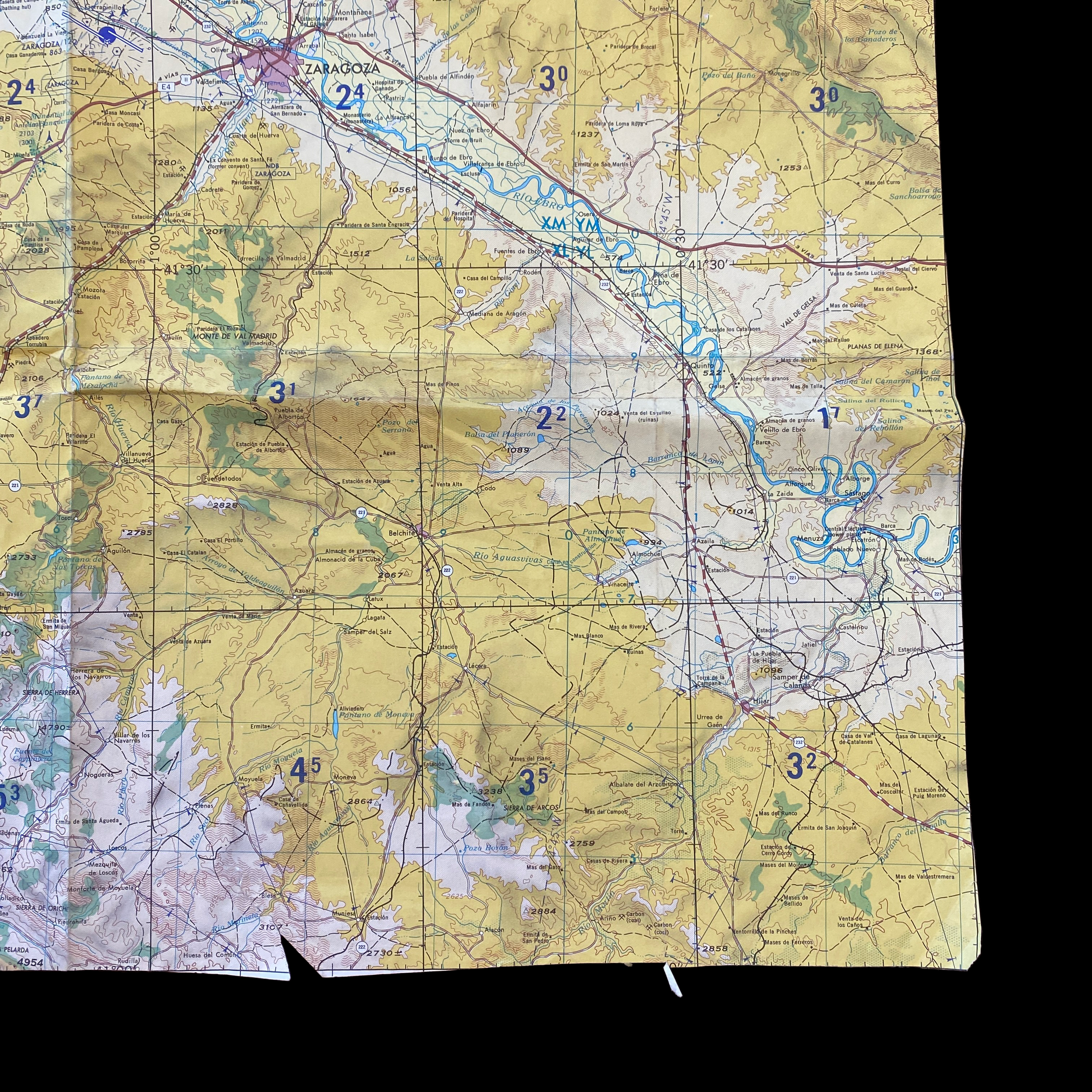
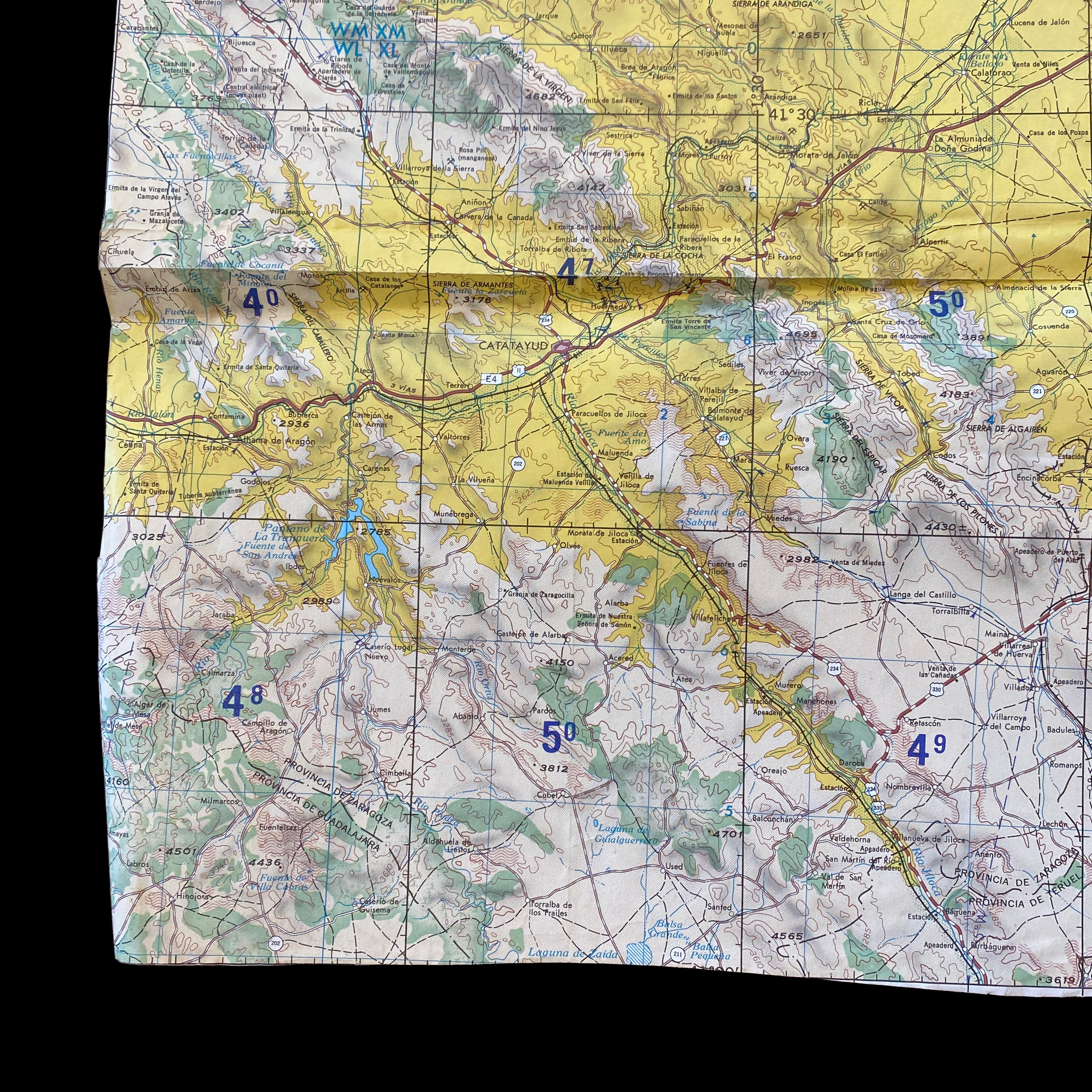
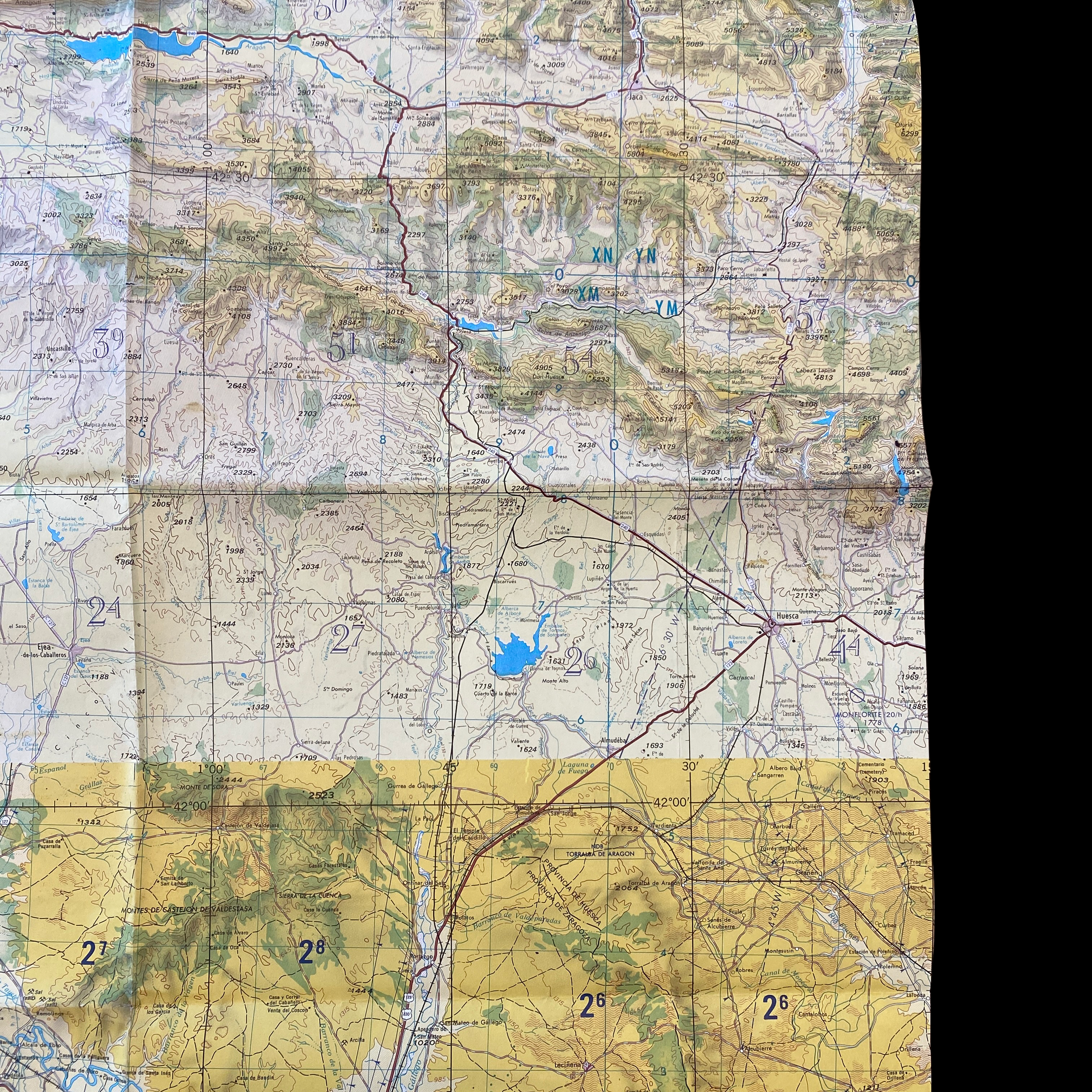
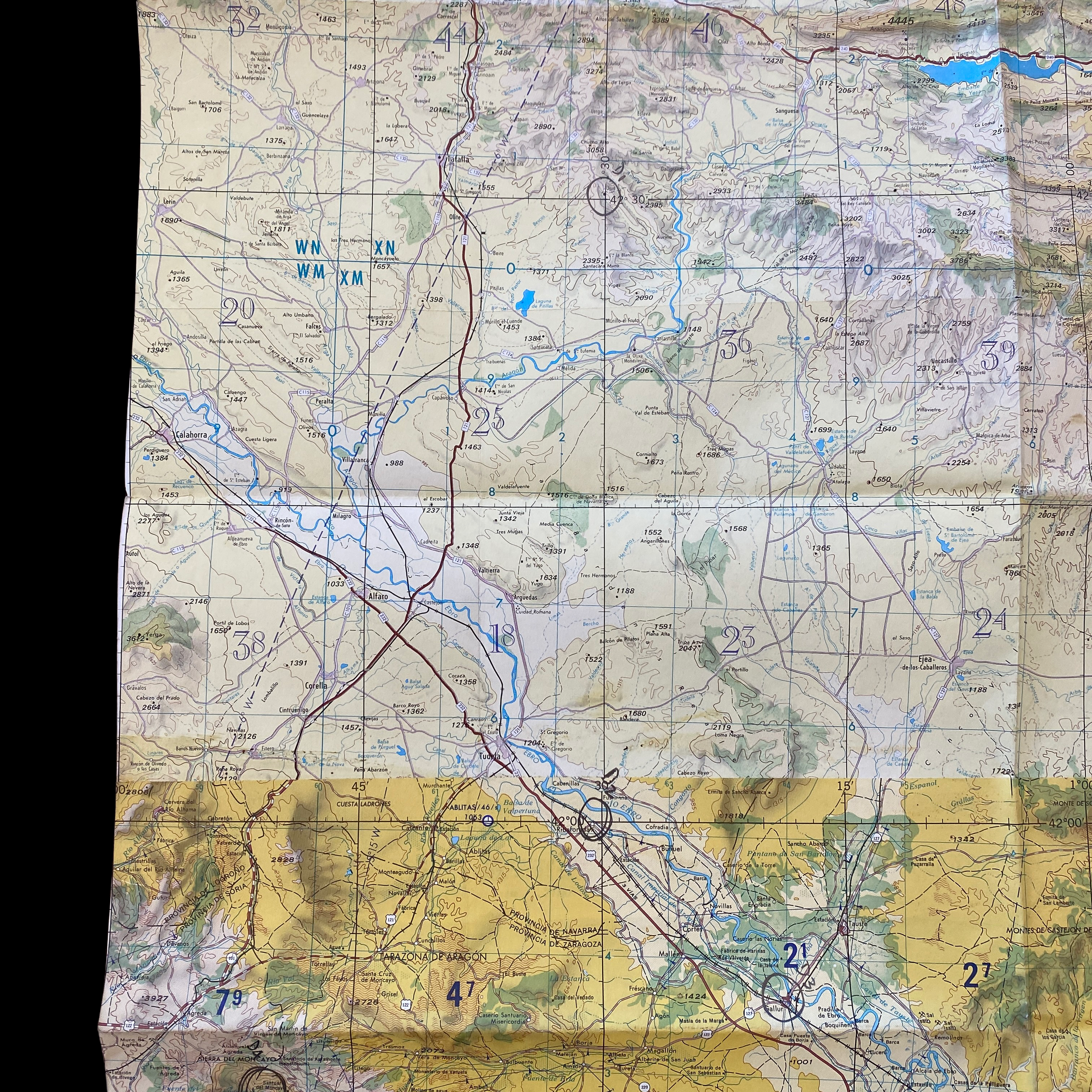
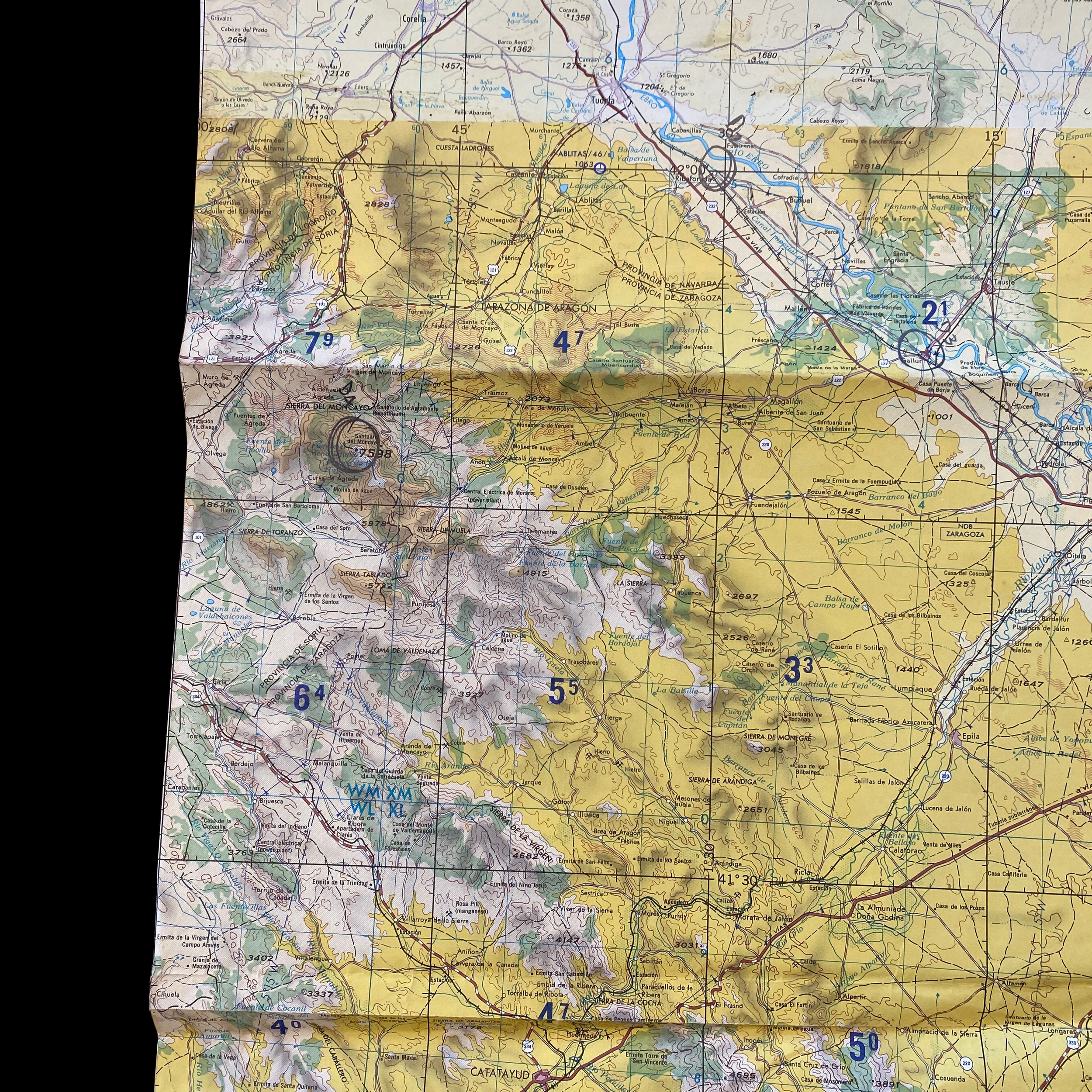
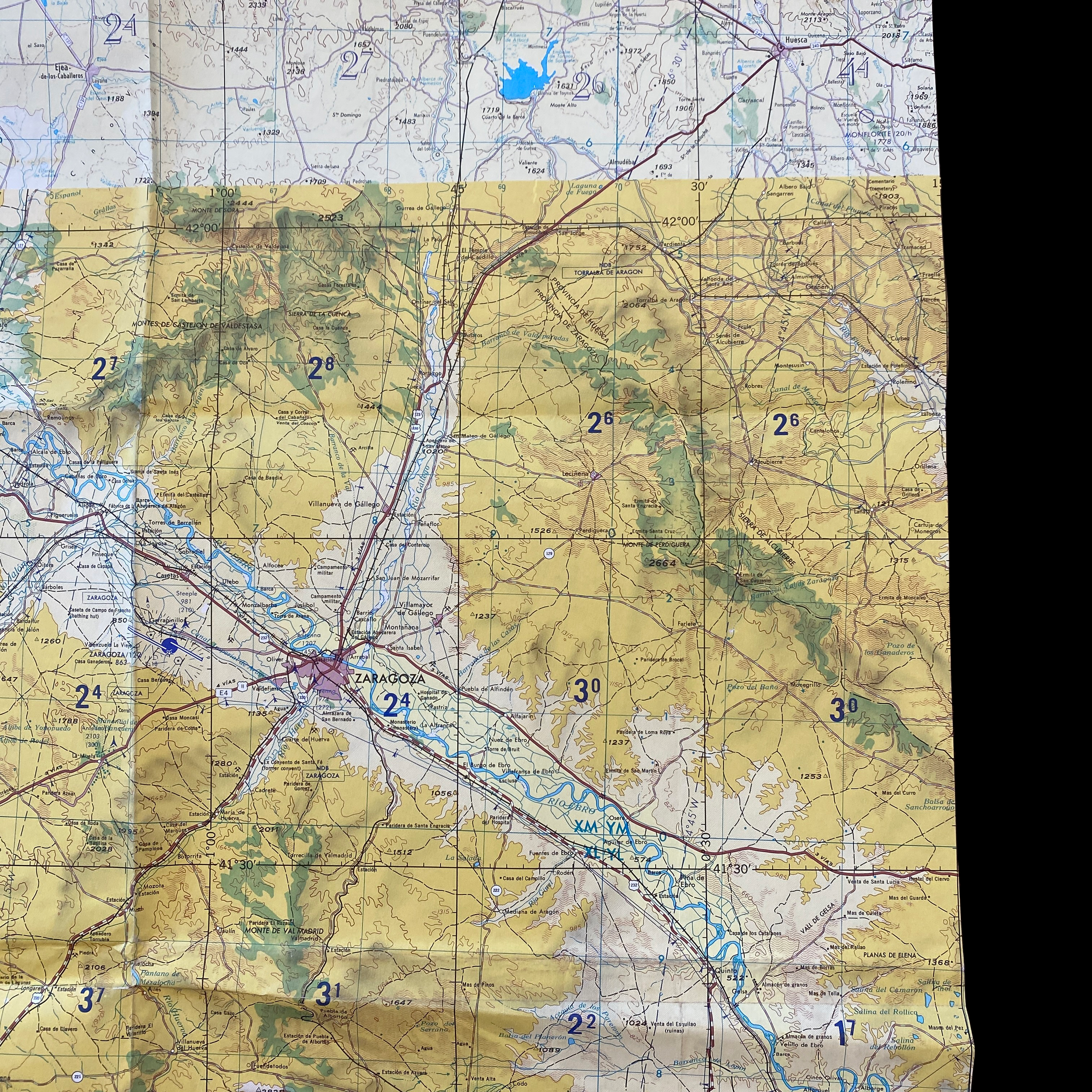
Original Cold War NATO Heavily Mission Marked ZARAGOZA Spain British R.A.F. Air Force Map*
Comes with hand-signed C.O.A. and full historical write-up
During the Cold War, Spain was a member of NATO and played a crucial role in the alliance's efforts to defend against the Soviet Union and its allies. As a result, the Royal Air Force (RAF) had a significant presence in the country. In the 1950s and 1960s, the RAF operated a number of air bases in Spain, including RAF Torrejon near Madrid and RAF Gibraltar on the southern coast. These bases were used to house fighter squadrons that were responsible for providing air defense for the region.
The RAF's presence in Spain was not without controversy. The Spanish government, led by General Francisco Franco, was not a democracy and had a strained relationship with the UK and other Western powers. However, the threat of the Soviet Union and the importance of Spain's strategic location made it essential for the RAF to maintain a presence in the country.
This incredible and museum-grade artifact is a heavily marked and heavily used NATO Air Force map showing rare glimpses into NATO and R.A.F. operations in Spain during the Cold War. This British Royal Air Force map would have been used for air defense, air-to-ground missions, and transport and would have been of extreme importance to NATO R.A.F. pilots and navigators during NATO missions and patrols.
As the Cold War progressed, the RAF's role in Spain evolved. In the 1970s and 1980s, Spain began to transition to democracy and the country's relationship with the UK and other NATO countries improved. The RAF's air bases in Spain were used less for air defense and more for training and logistics.
Despite the changes in the international political landscape, the RAF's presence in Spain remained important to NATO's efforts to defend against the Soviet Union. The RAF's fighter squadrons were equipped with modern aircraft, such as the English Electric Lightning and the Panavia Tornado, and were ready to respond to any threat to NATO's southern flank.
Overall, the RAF's presence in Spain during the Cold War was a critical part of NATO's defense strategy and helped to deter a Soviet attack on the alliance. It also played a role in the eventual collapse of the Soviet Union and the end of the Cold War.
Cold War:
The Cold War was a period of political and military tension between the Western powers, led by the United States, and the Eastern powers, led by the Soviet Union, that lasted from the late 1940s to the early 1990s. During this time, Germany was divided into two countries: the Federal Republic of Germany (also known as West Germany) and the German Democratic Republic (also known as East Germany).
West Germany was a key member of NATO, the Western military alliance that was formed to counter the threat of the Soviet Union and the Warsaw Pact. The United States and the United Kingdom, both members of NATO, maintained a significant presence in West Germany during the Cold War, including a number of air bases. The US Air Force had bases such as Ramstein Air Base, Spangdahlem Air Base, and Rhein-Main Air Base, which were used for air defense, air-to-ground missions, and transport. The British Royal Air Force also had bases in West Germany, including RAF Gatow in Berlin and RAF Laarbruch in the western part of the country.
The air forces in West Germany played a vital role in deterring aggression from the Soviet Union and its allies, and they were also involved in a number of other operations during the Cold War. One of the most significant was the Berlin Airlift in 1948, in which the US and British air forces provided humanitarian aid to the citizens of West Berlin, who were being blockaded by the Soviet Union. The airlift was a successful demonstration of the Western powers' commitment to defending West Berlin, and it helped to prevent a potential military conflict between the East and the West.
In contrast to West Germany, East Germany was a member of the Warsaw Pact and a communist country. The East German government implemented a number of economic and social policies that were meant to improve living conditions, but many people were frustrated with the lack of freedoms and the continued presence of Soviet troops. The Berlin Wall, which separated West Berlin from East Berlin and the rest of East Germany, was erected in 1961 and remained in place until 1989. The wall was a symbol of the division between the Western world and the Eastern bloc during the Cold War.
The Cold War came to an end in the early 1990s, and in 1990, the two Germanies were reunited. The fall of the Berlin Wall and the collapse of the Soviet Union marked the end of the Cold War, and Germany has since become a unified and prosperous country, playing a key role in the European Union.
Overall, the Cold War had a significant impact on Germany, and the country's division into two rival states had far-reaching consequences for both its people and its international relations. The presence of the US and British air forces in West Germany was an important factor in deterring aggression from the East and helping to maintain peace during a volatile time in world history.