WWII August 1945 Atomic Bomb Hiroshima (Enola Gay) Japan Map












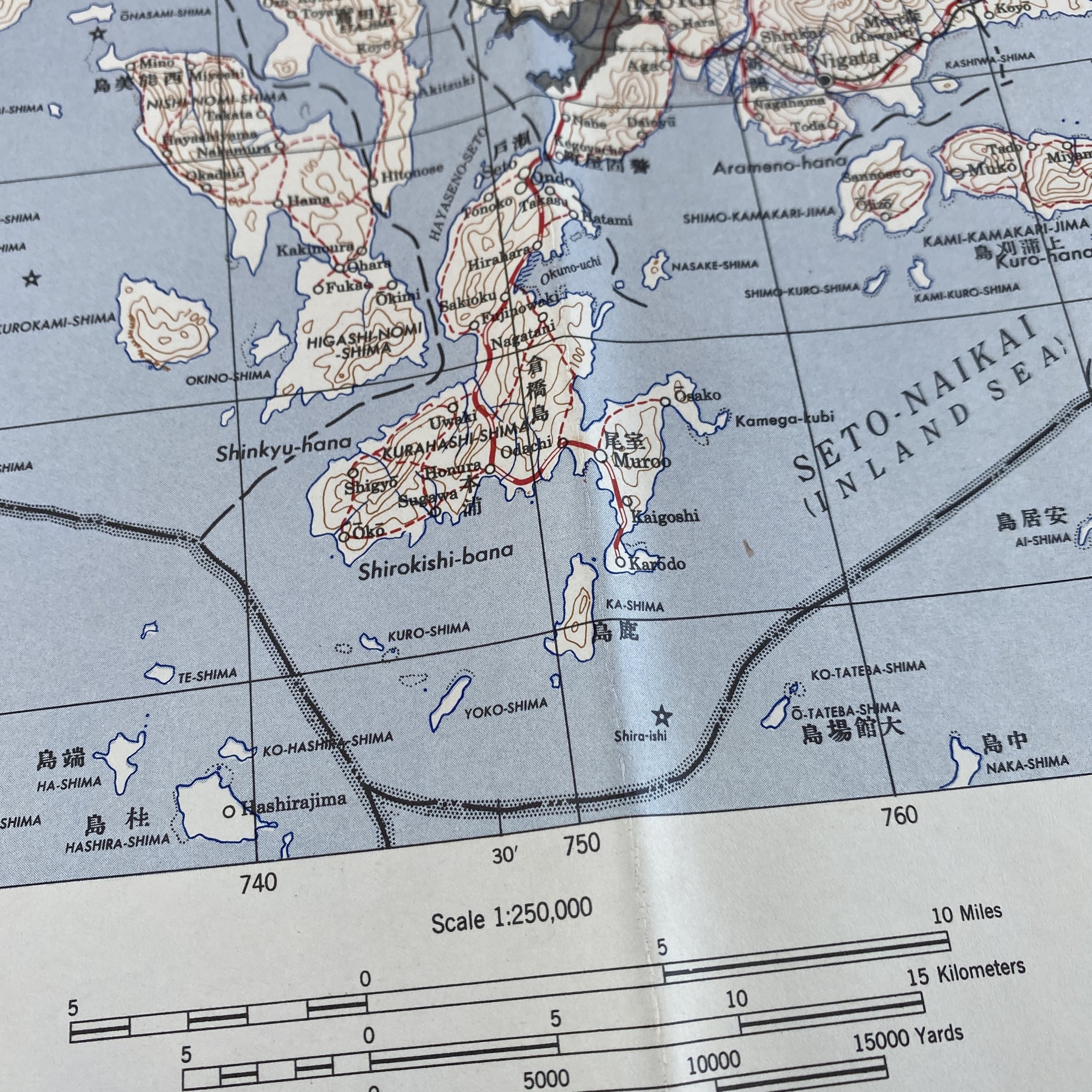
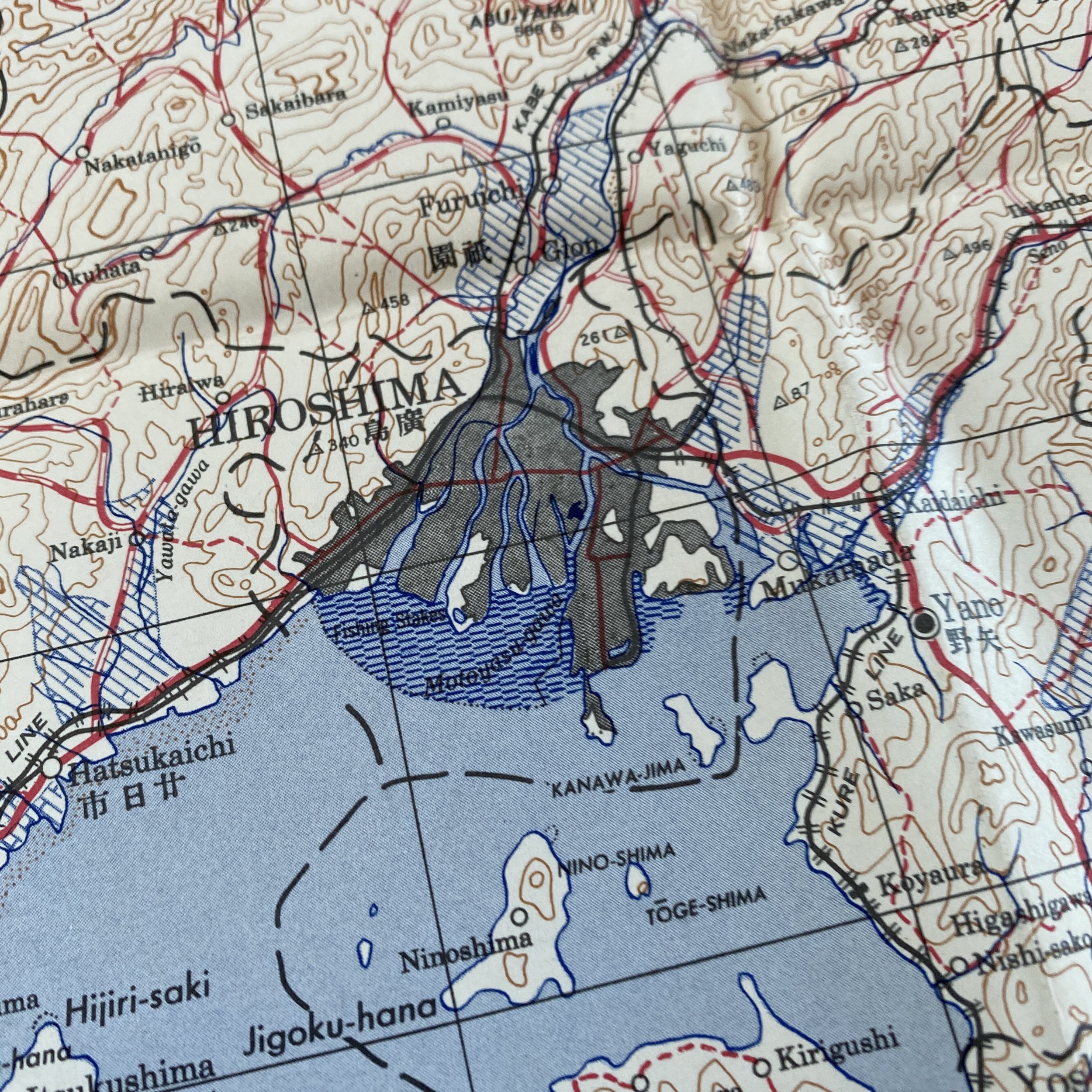
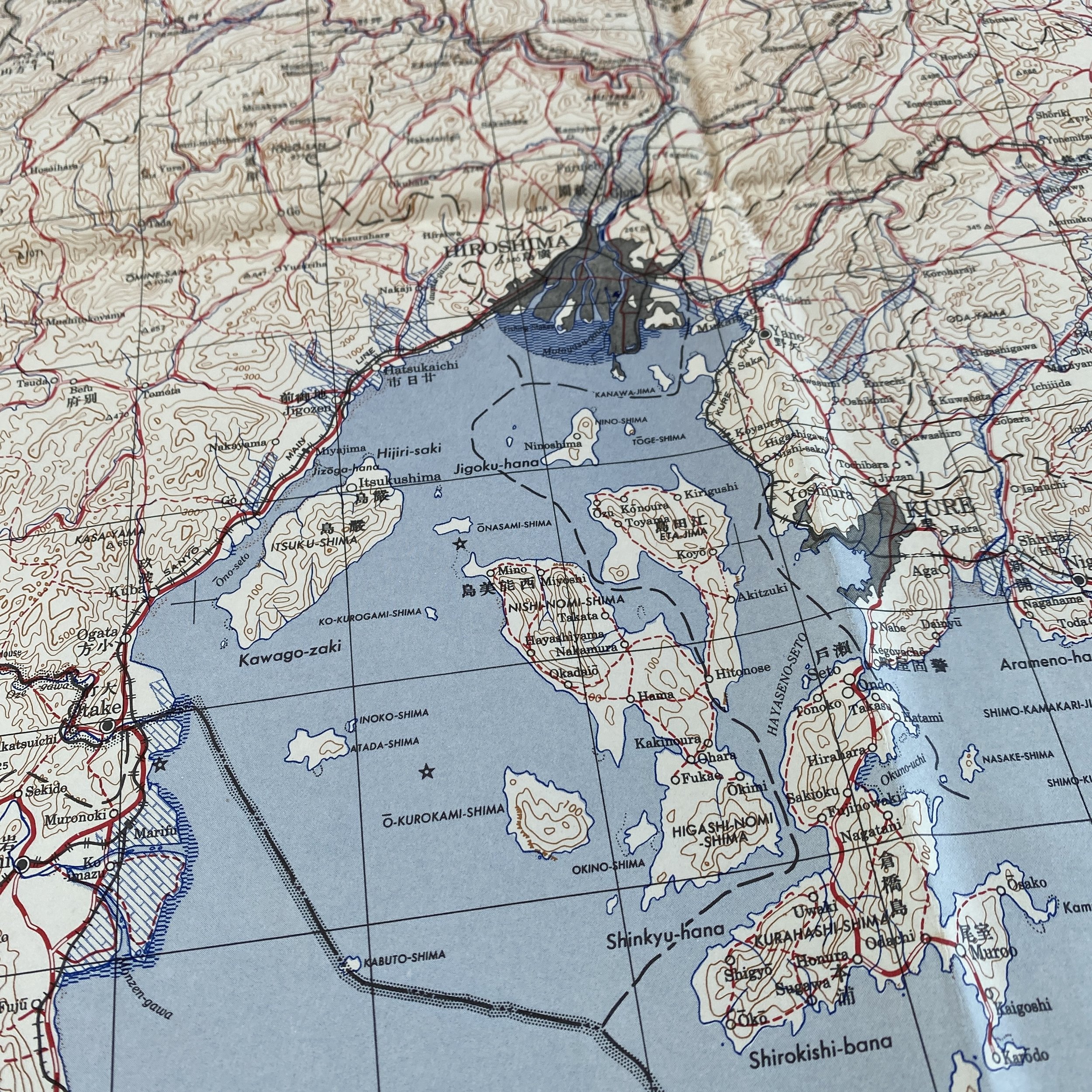
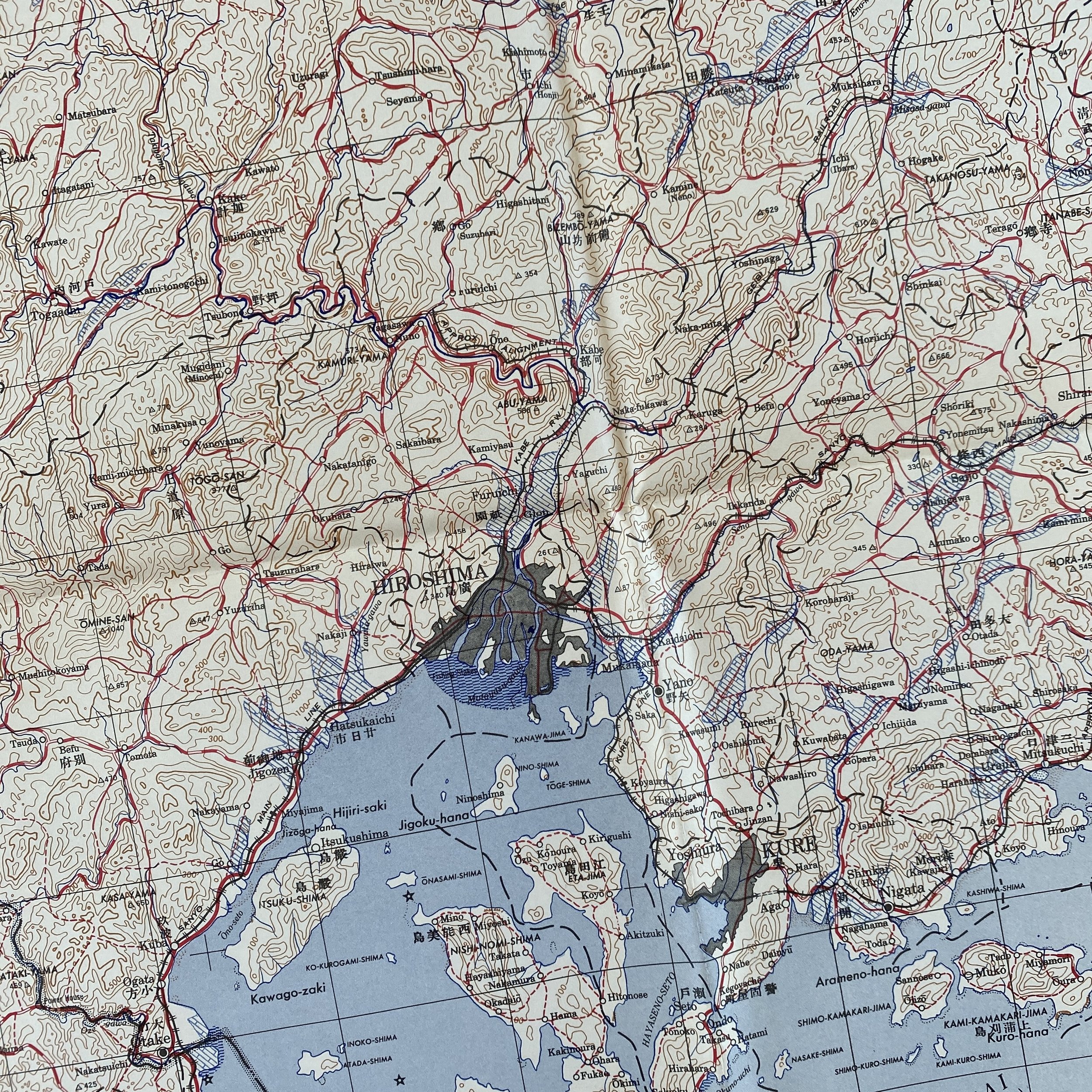
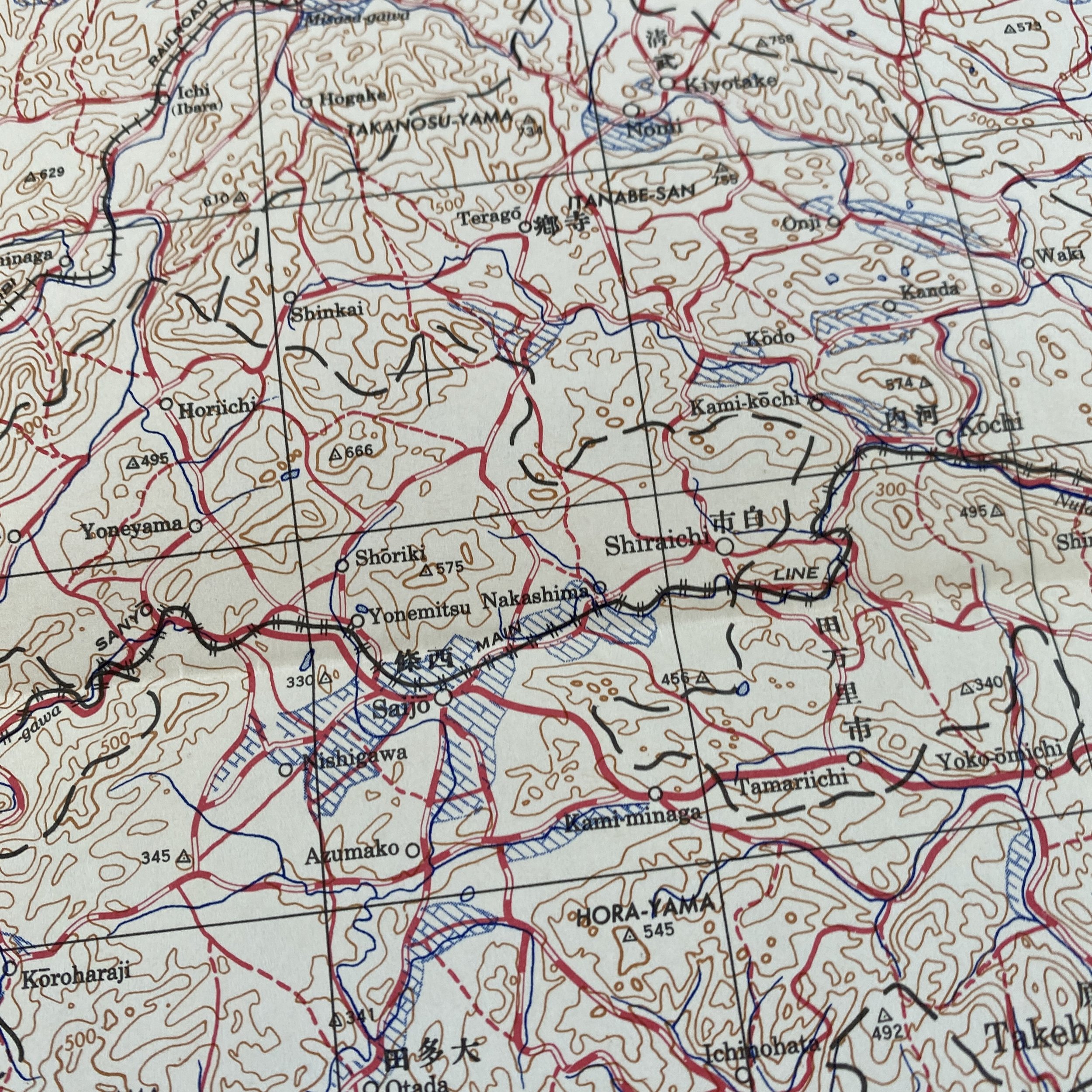
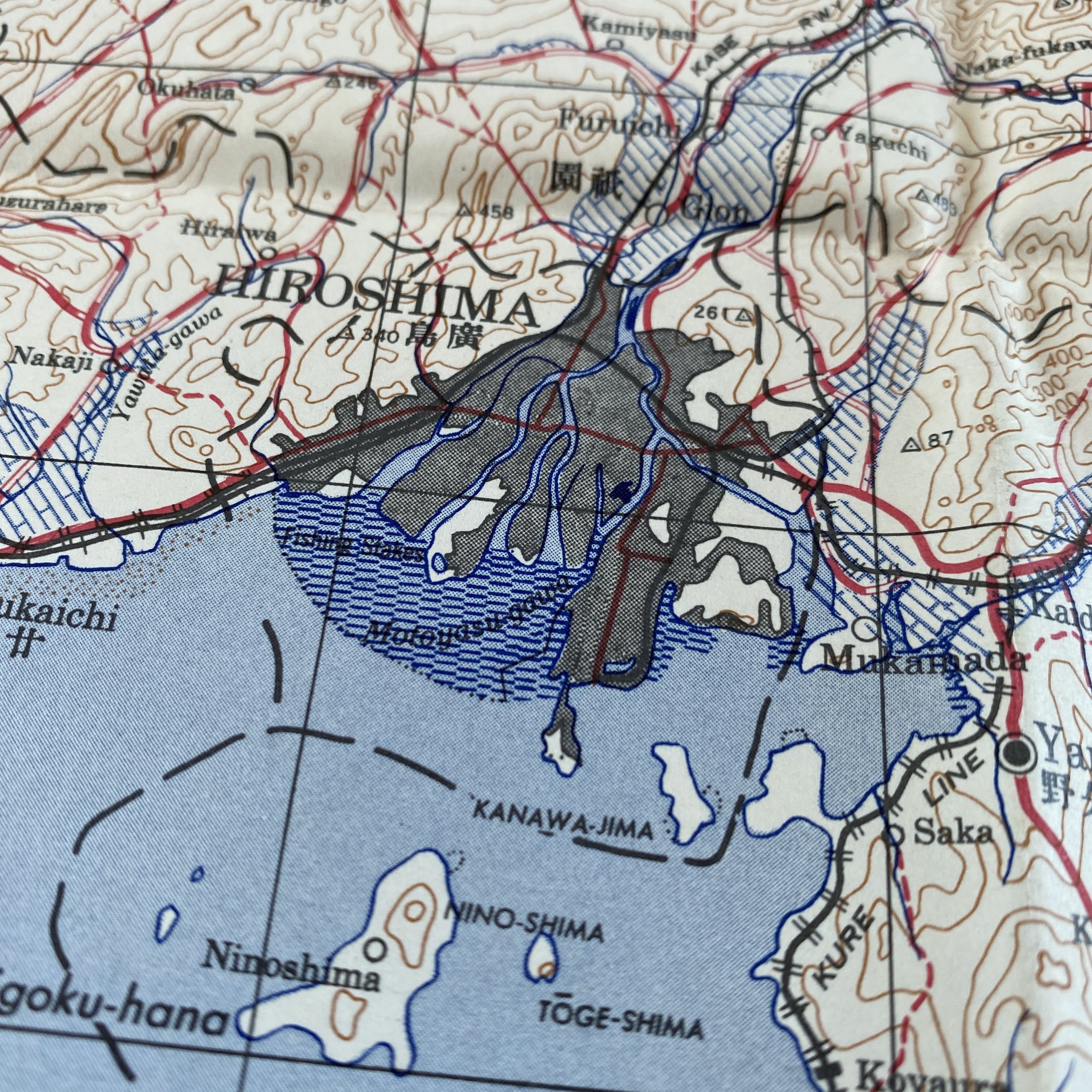
WWII August 1945 Atomic Bomb Hiroshima (Enola Gay) Japan Map
Comes with C.O.A.
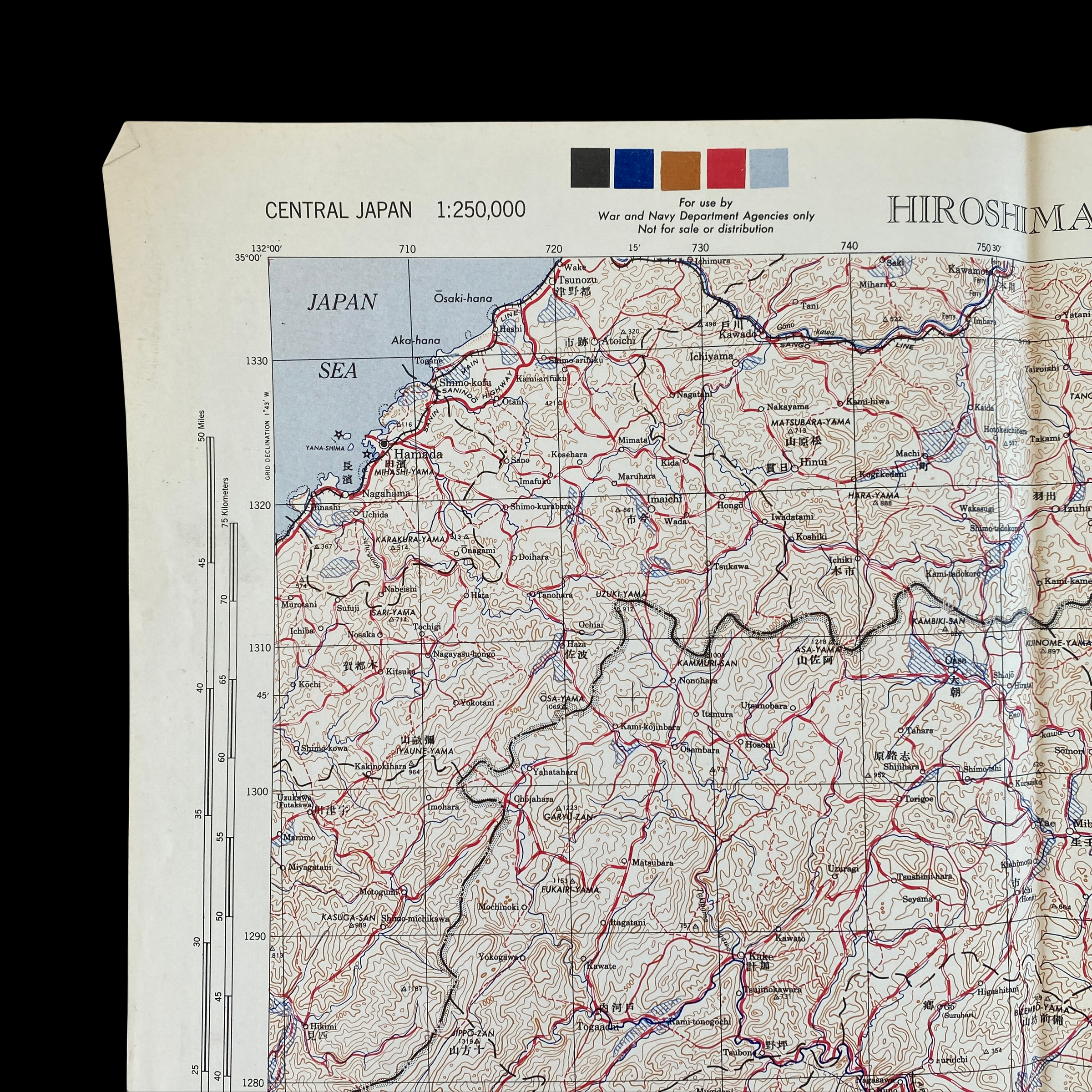
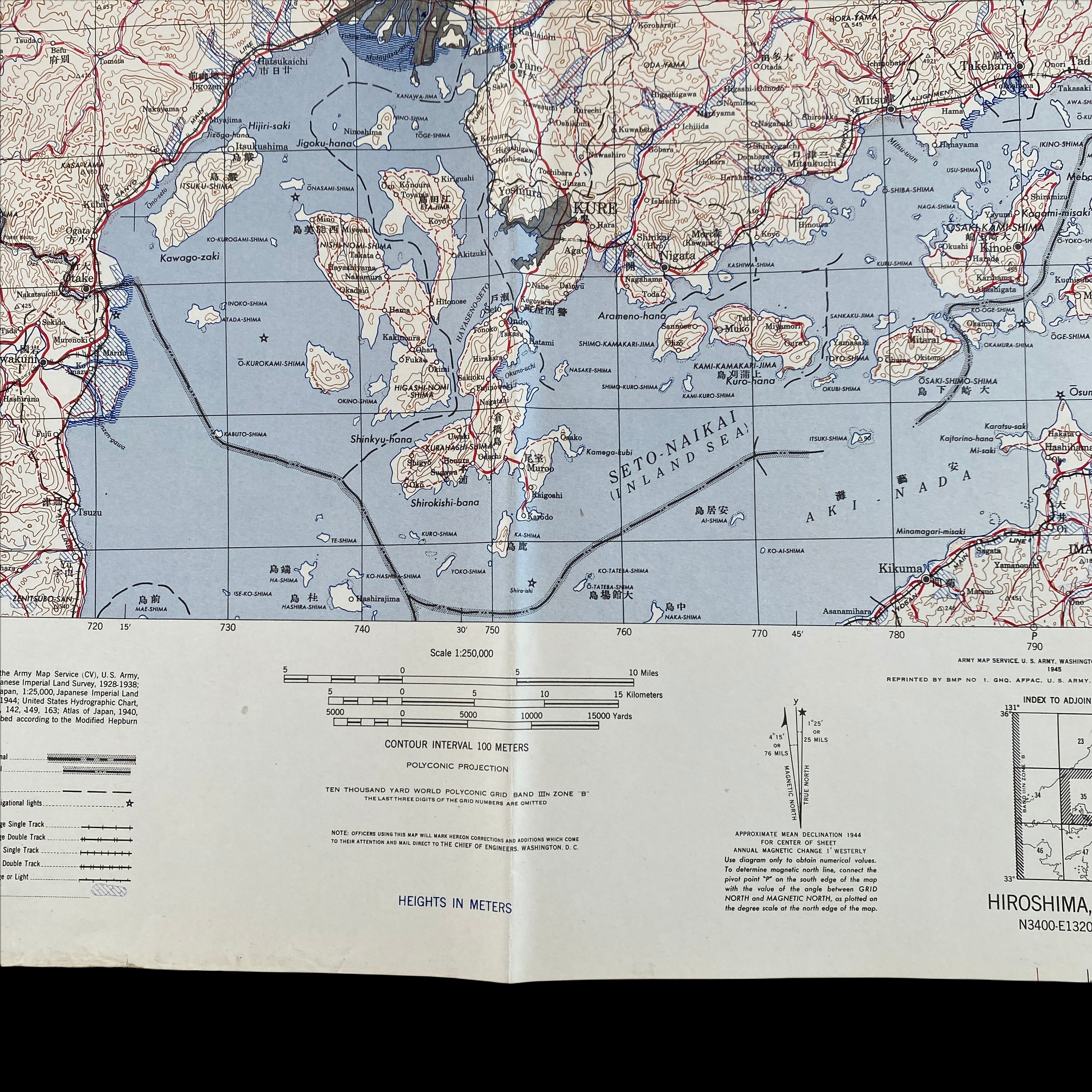
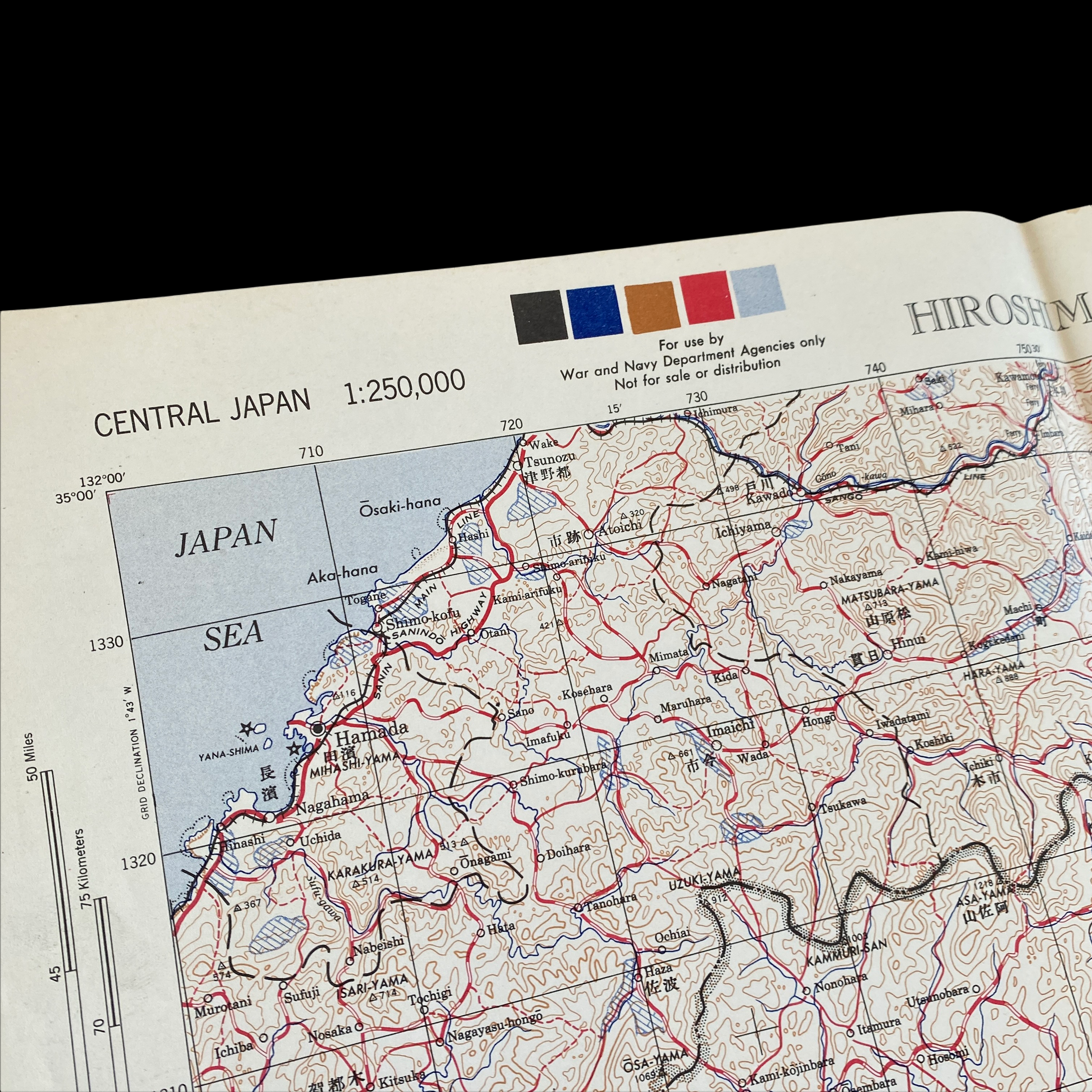
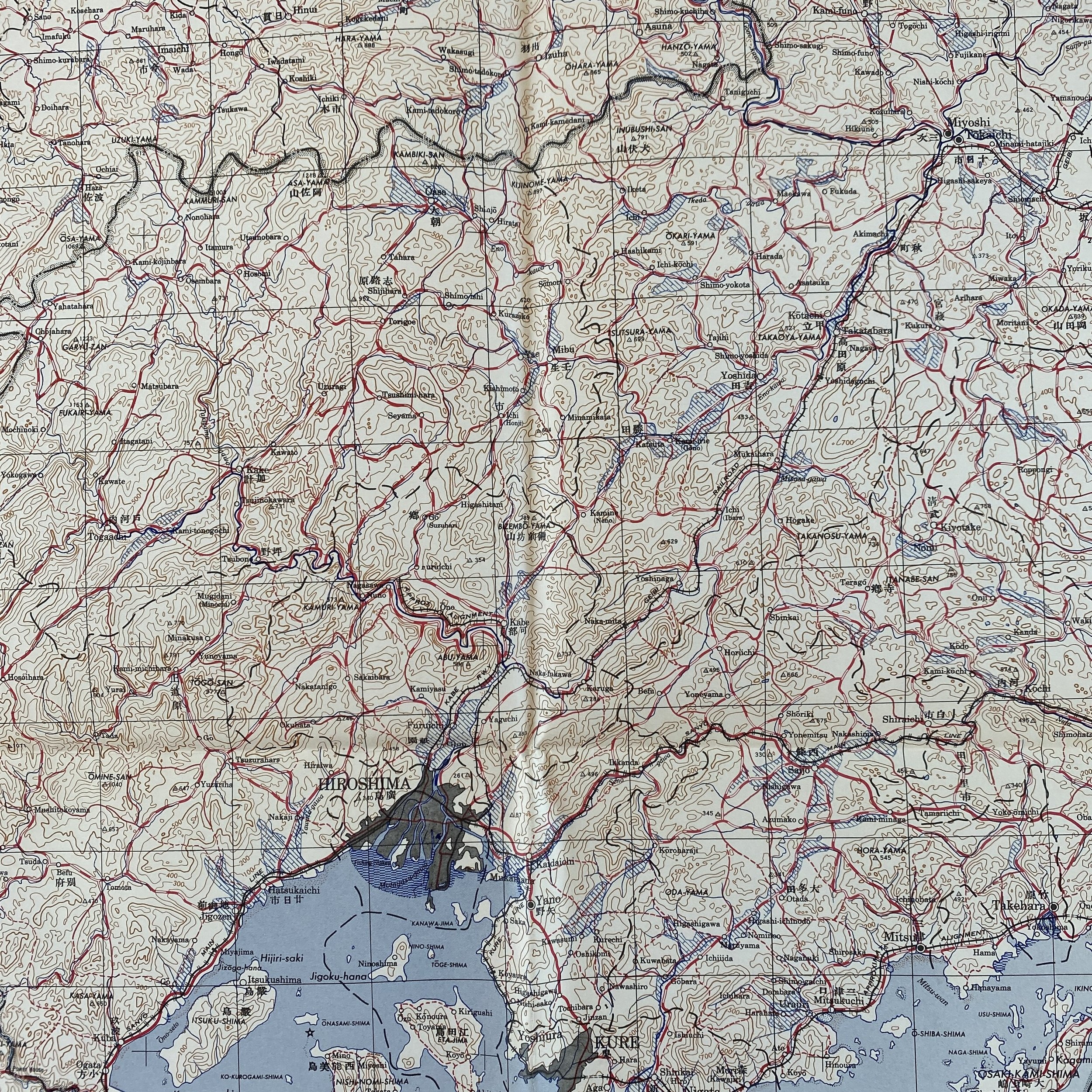
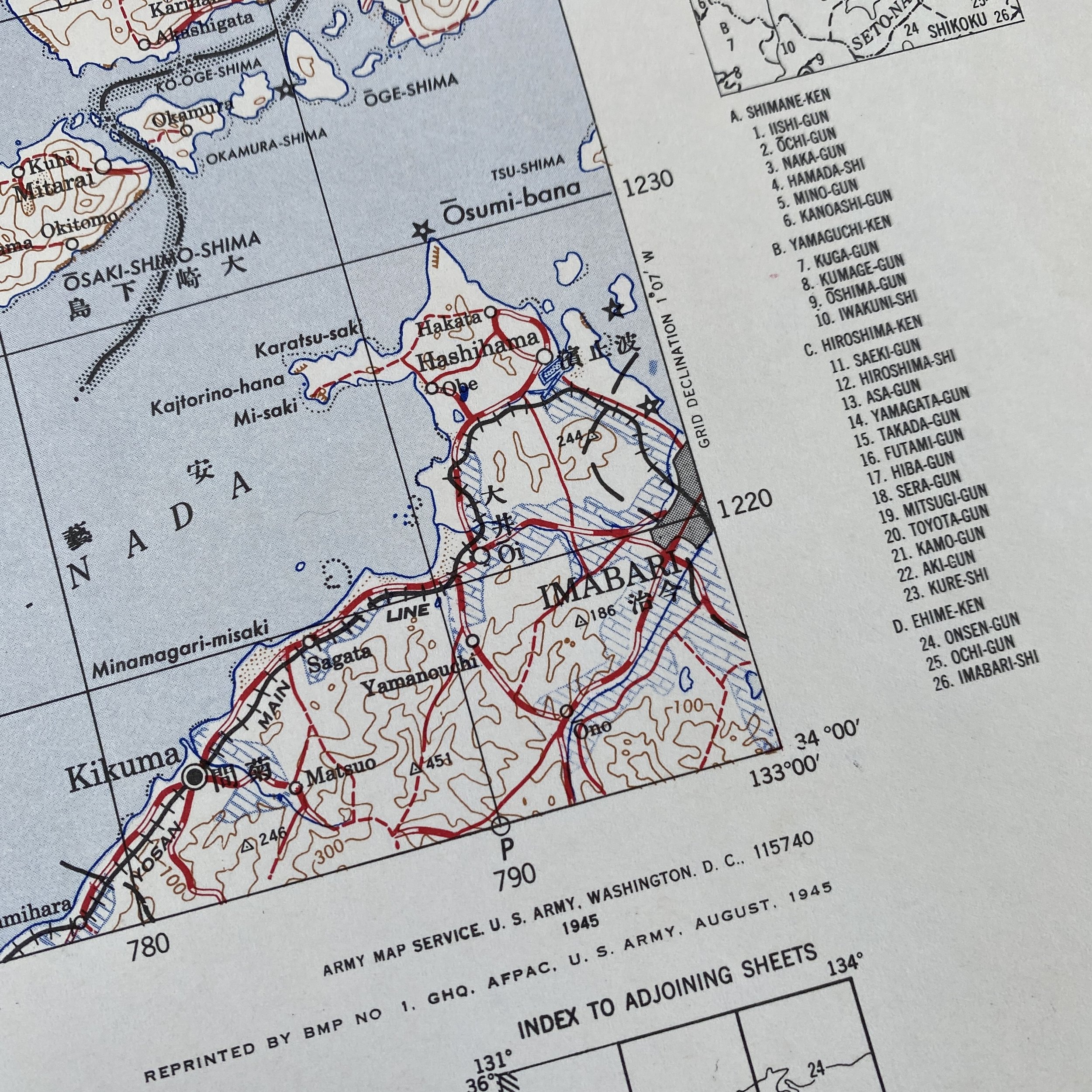
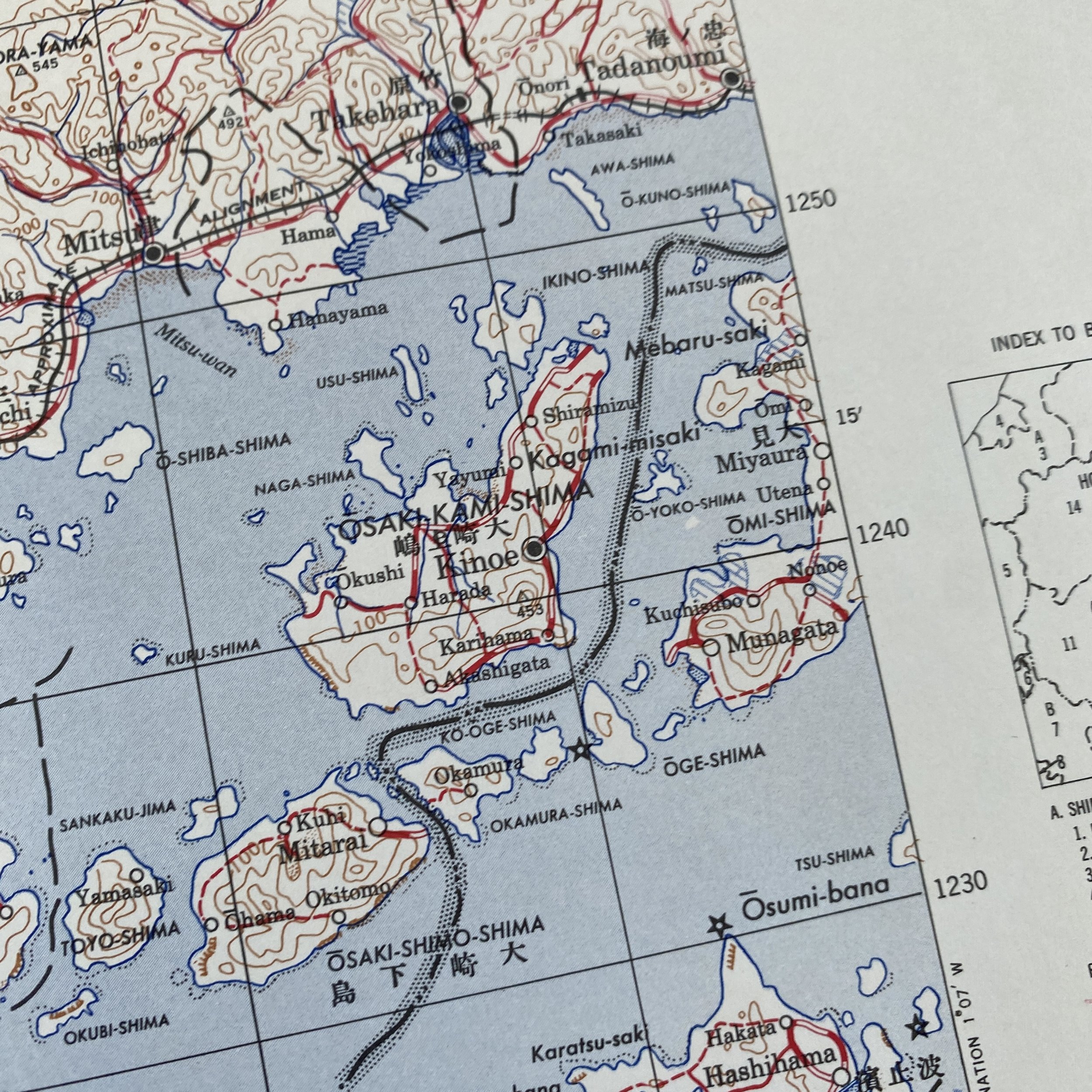
*This incredible WWII map titled “HIROSHIMA” is dated August 1945 (the same month the first atomic bomb was dropped on Hiroshima).
On August 6, 1945, an American B-29 bomber dropped the world’s first deployed atomic bomb over the Japanese city of Hiroshima. The explosion immediately killed an estimated 80,000 people; tens of thousands more would later die of radiation exposure. The United States detonated two nuclear weapons over the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki on 6 and 9 August 1945, respectively. The two bombings killed between 129,000 and 226,000 people, most of whom were civilians, and remain the only use of nuclear weapons in armed conflict.
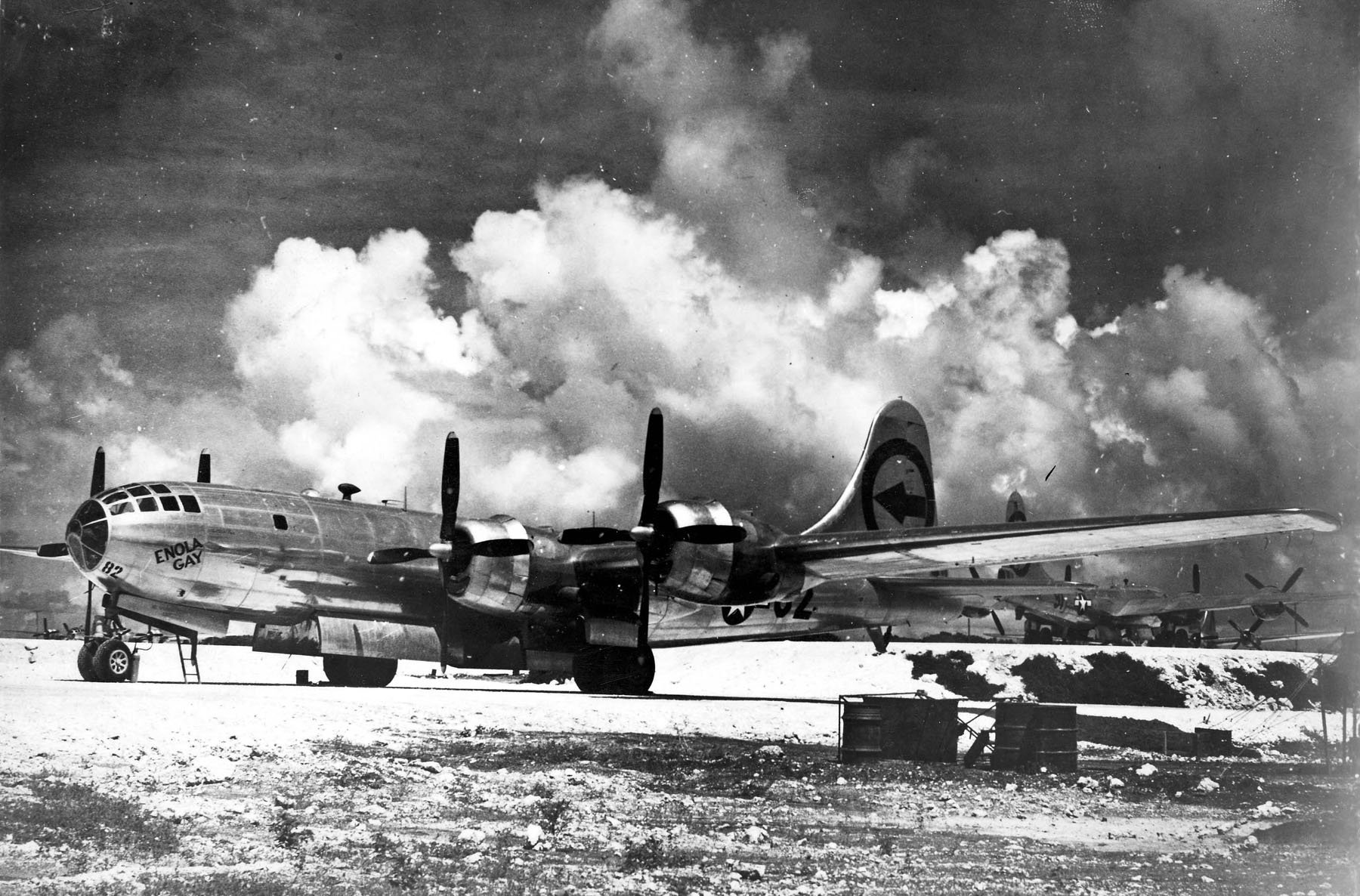
Printed in 1945 this incredible ‘SECOND EDITION AMS-2’ WWII Pacific Theater map was complied and updated using intelligence reports and updated aerial photography. This map would have been used for planning strategic aerial raid attacks and is very similar to maps used on the morning of August 6, 1945 as the American B-29 bomber Enola Gay dropped an atomic bomb on the Japanese city of Hiroshima.
'Little Boy' and 'Fat Man' Are Dropped:
Hiroshima, a manufacturing center of some 350,000 people located about 500 miles from Tokyo, was selected as the first target. After arriving at the U.S. base on the Pacific island of Tinian, the more than 9,000-pound uranium-235 bomb was loaded aboard a modified B-29 bomber christened Enola Gay (after the mother of its pilot, Colonel Paul Tibbets). The plane dropped the bomb—known as “Little Boy”—by parachute at 8:15 in the morning, and it exploded 2,000 feet above Hiroshima in a blast equal to 12-15,000 tons of TNT, destroying five square miles of the city.
Hiroshima’s devastation failed to elicit immediate Japanese surrender, however, and on August 9 Major Charles Sweeney flew another B-29 bomber, Bockscar, from Tinian. Thick clouds over the primary target, the city of Kokura, drove Sweeney to a secondary target, Nagasaki, where the plutonium bomb “Fat Man” was dropped at 11:02 that morning. More powerful than the one used at Hiroshima, the bomb weighed nearly 10,000 pounds and was built to produce a 22-kiloton blast. The topography of Nagasaki, which was nestled in narrow valleys between mountains, reduced the bomb’s effect, limiting the destruction to 2.6 square miles.
The aftermath of the Bombing:
At noon on August 15, 1945 (Japanese time), Emperor Hirohito announced his country’s surrender in a radio broadcast. The news spread quickly, and “Victory in Japan” or “V-J Day” celebrations broke out across the United States and other Allied nations. The formal surrender agreement was signed on September 2, aboard the U.S. battleship Missouri, anchored in Tokyo Bay.
Because of the extent of the devastation and chaos—including the fact that much of the two cities' infrastructure was wiped out—the exact death tolls from the bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki remain unknown. However, it's estimated roughly 70,000 to 135,000 people died in Hiroshima and 60,000 to 80,000 people died in Nagasaki, both from acute exposure to the blasts and from long-term side effects of radiation.