WWII 1944 Invasion of Italy U.S. Army Air Force European Theater Combat Aircraft Navigation Map














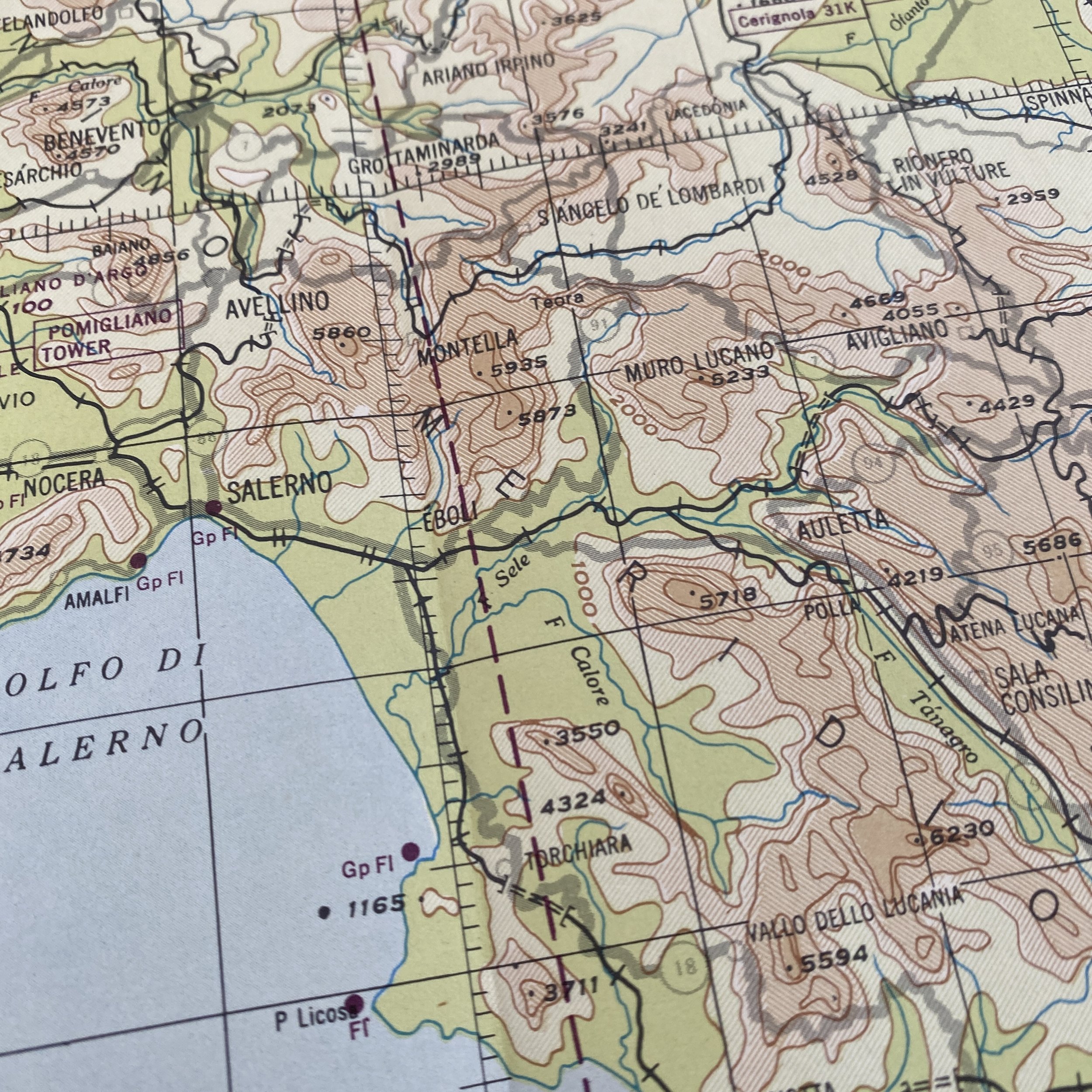






WWII 1944 Invasion of Italy U.S. Army Air Force European Theater Combat Aircraft Navigation Map
Comes with C.O.A.
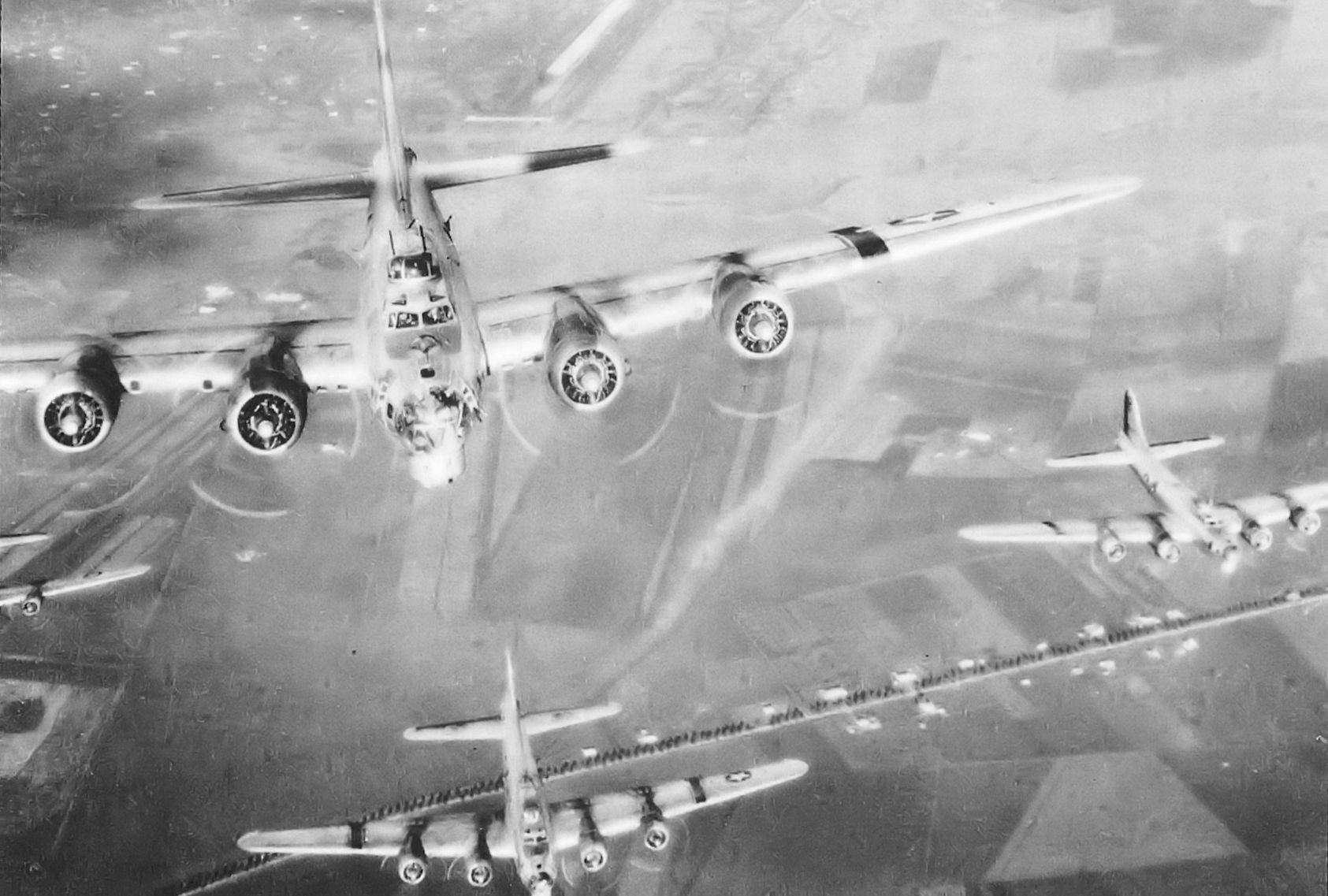
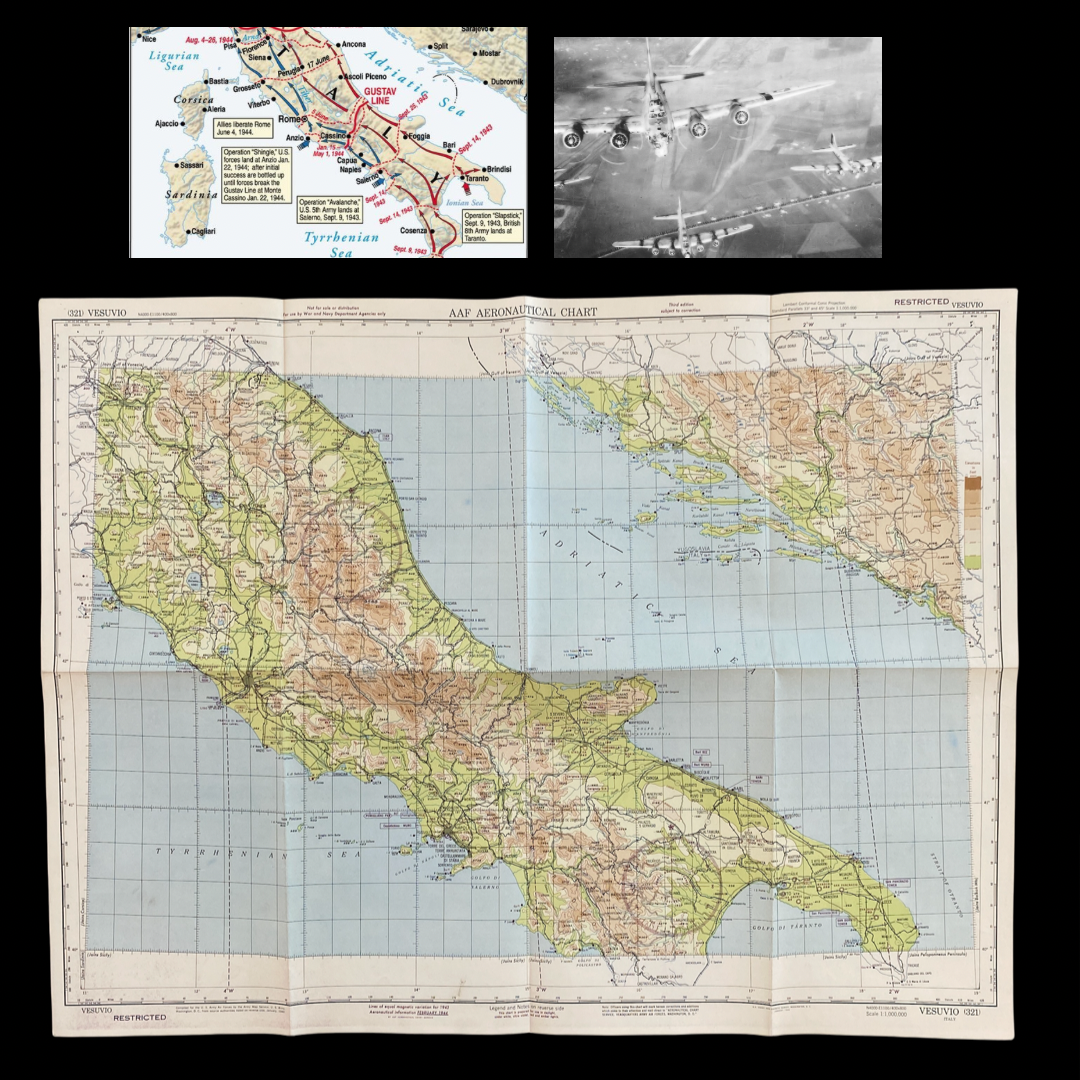
Used during the combat operations during the Allied invasion of Italy. The Allied amphibious landing on mainland Italy that took place from 3 September 1943, during the Italian campaign of World War II. The operation was undertaken by General Sir Harold Alexander's 15th Army Group (comprising General Mark W. Clark's American Fifth Army and General Bernard Montgomery's British Eighth Army) and followed the successful Allied Invasion of Sicily. The main invasion force landed around Salerno on 9 September on the western coast in Operation Avalanche, while two supporting operations took place in Calabria (Operation Baytown) and Taranto (Operation Slapstick).
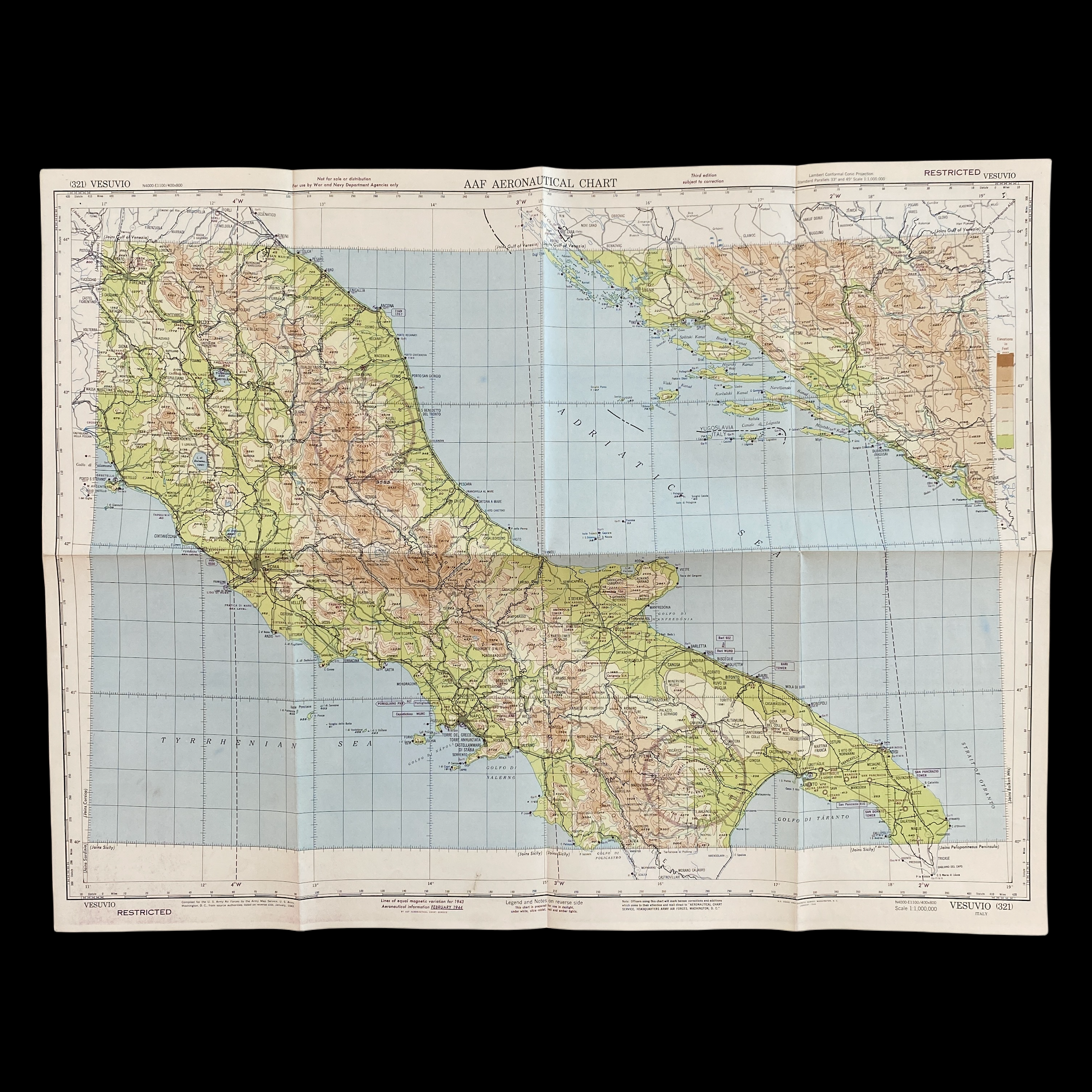
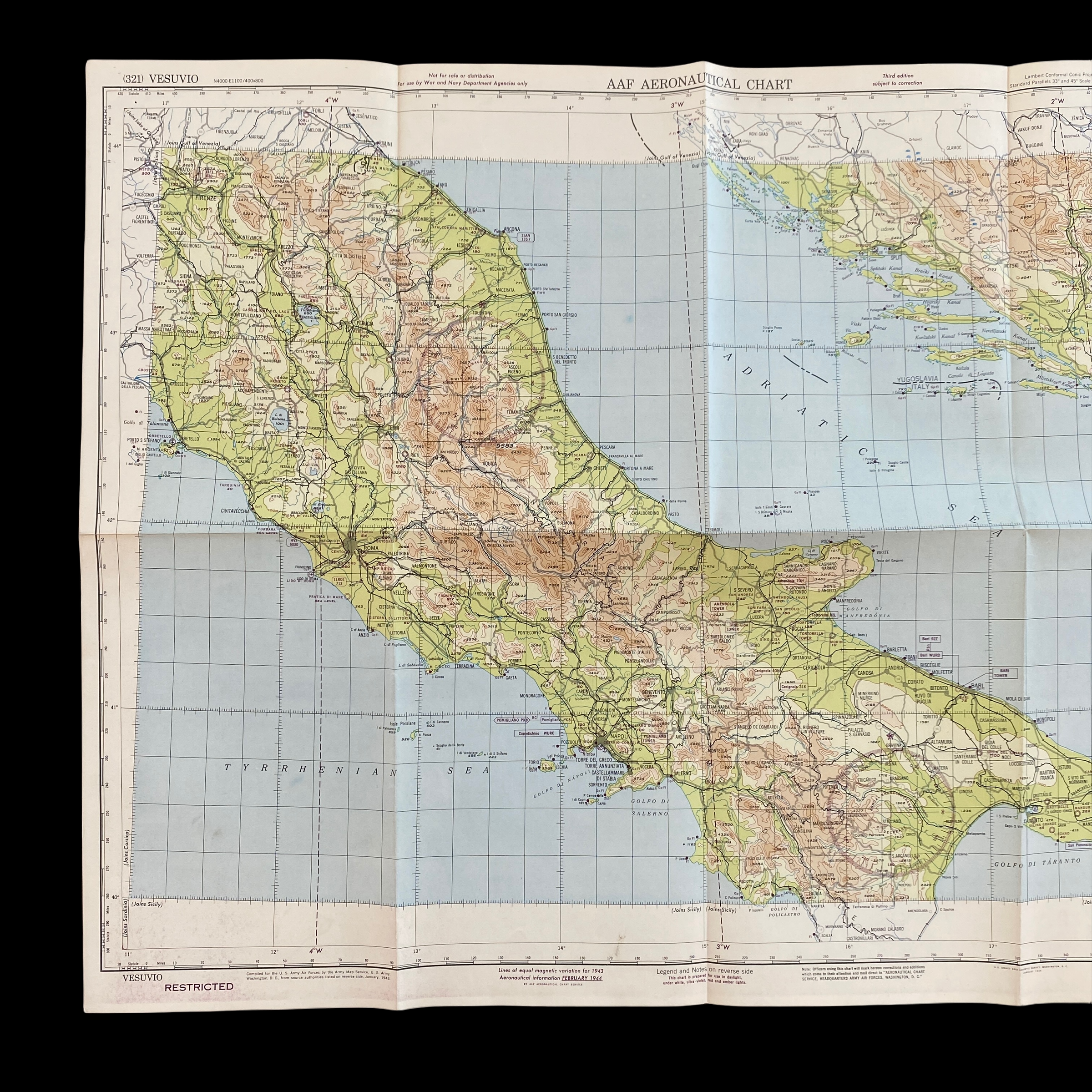
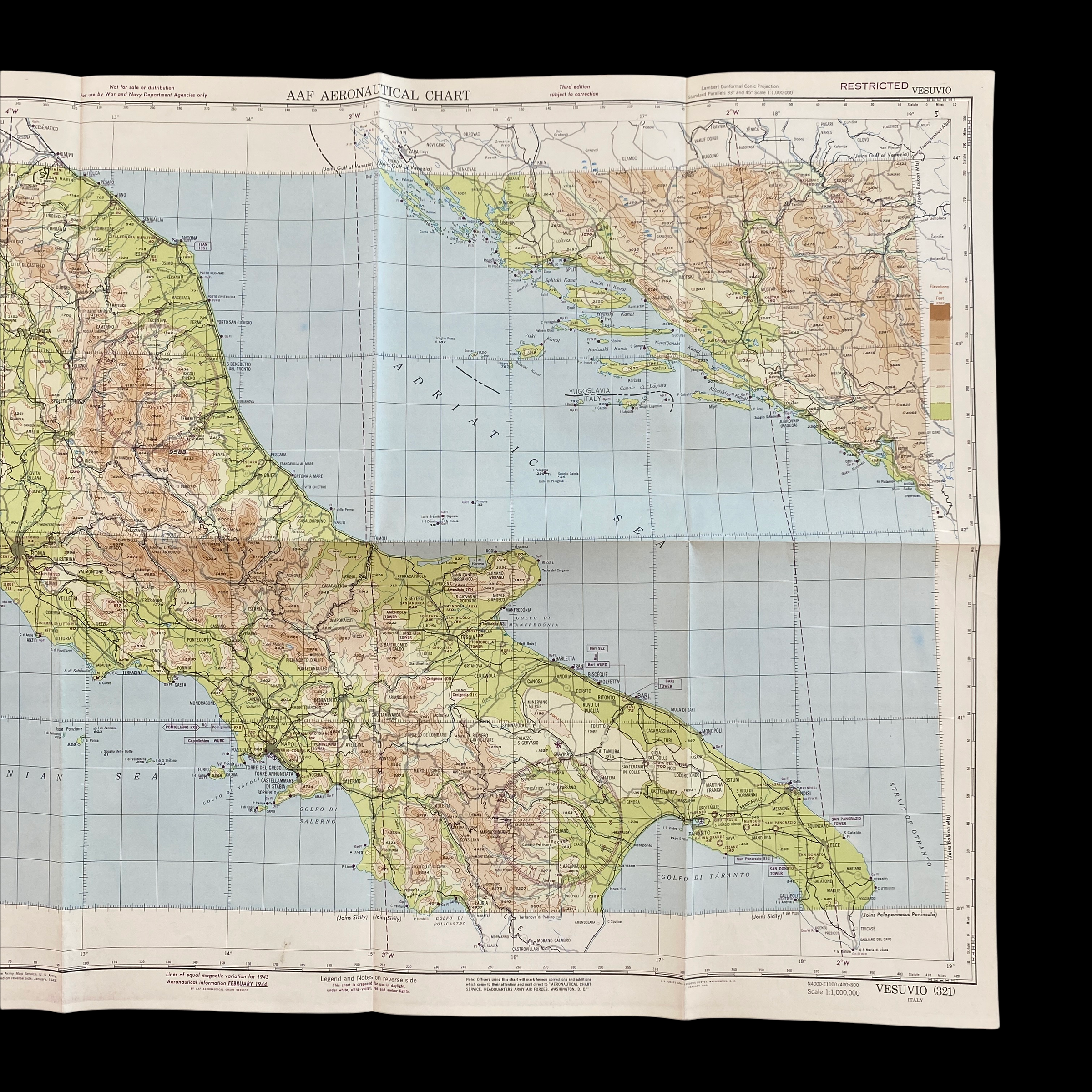
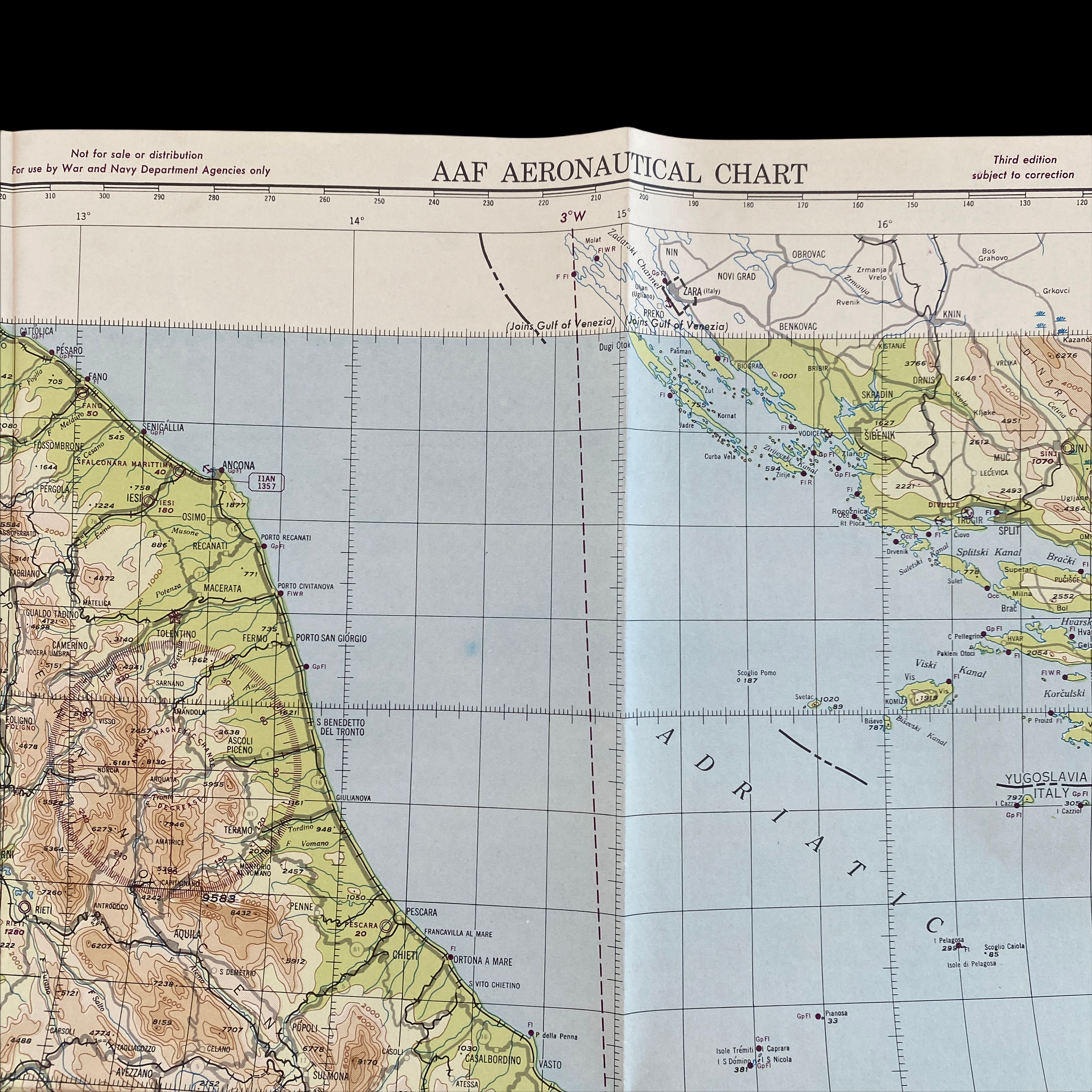
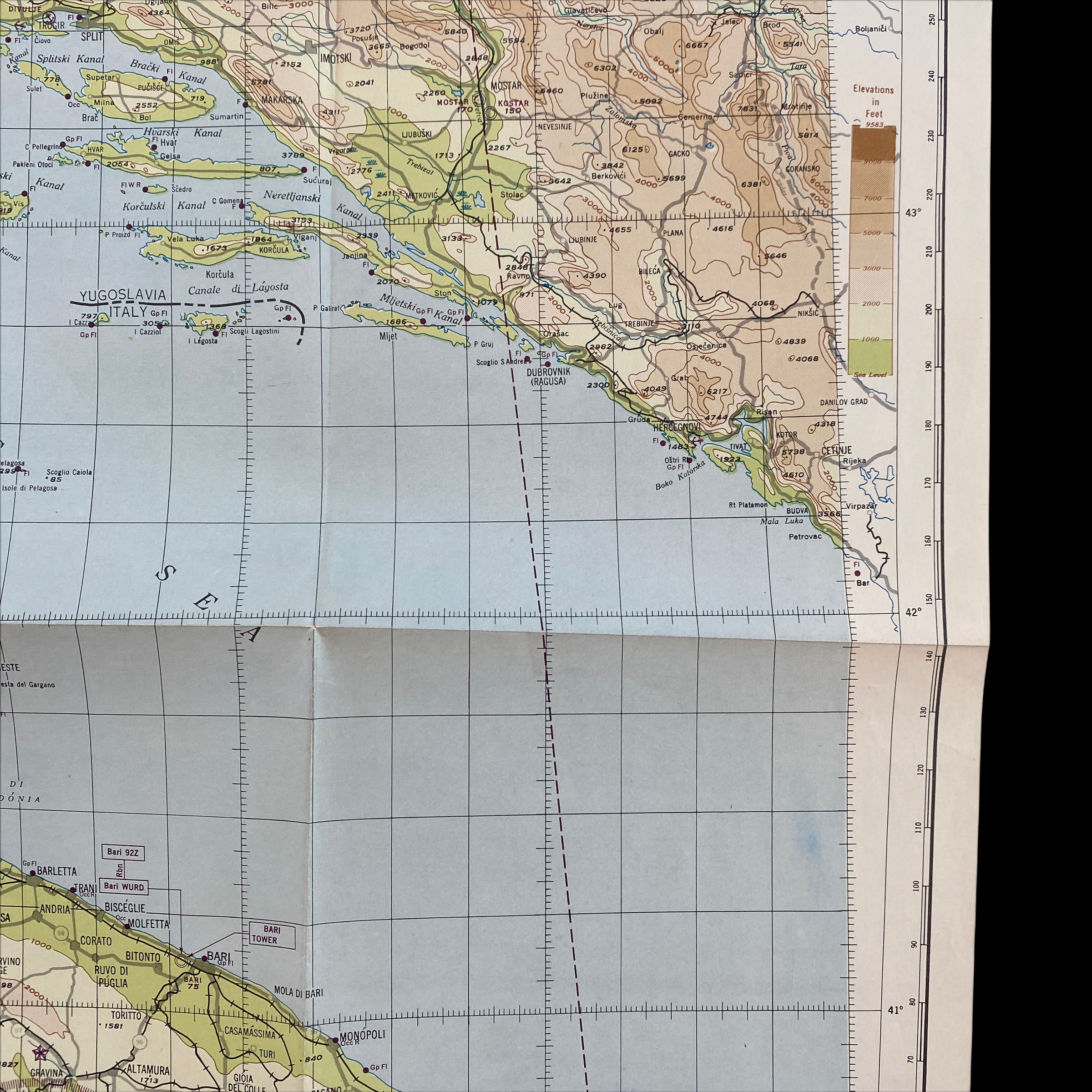
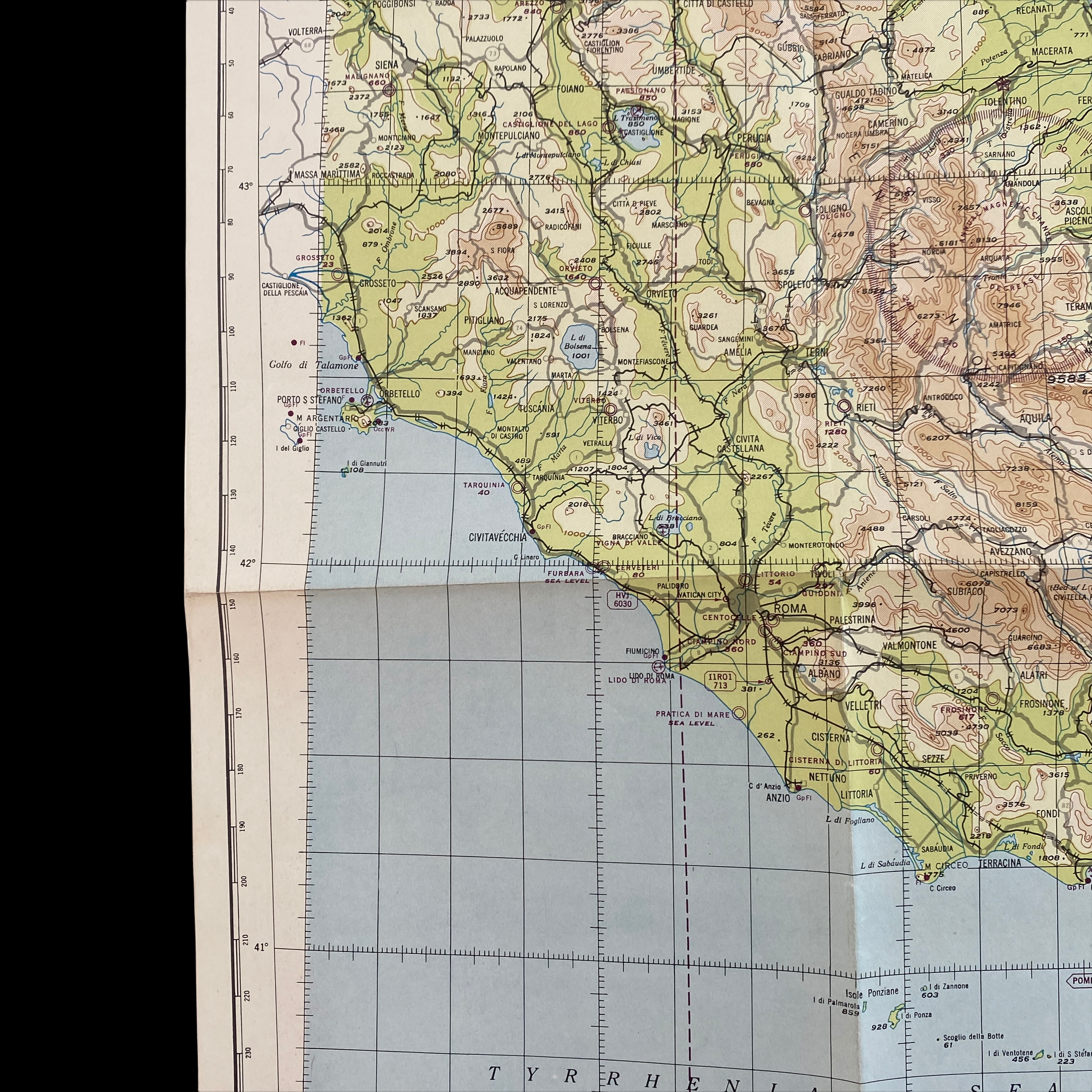
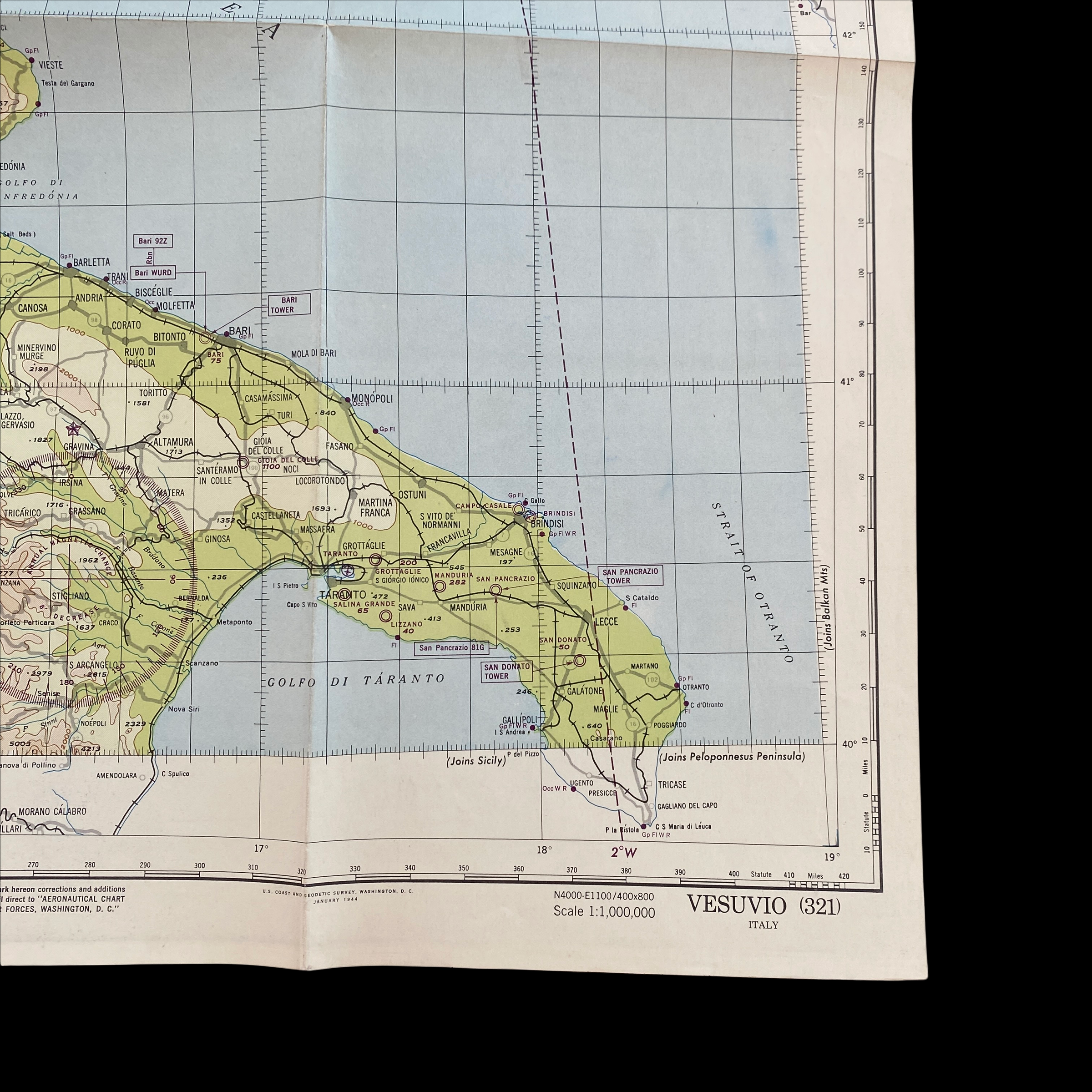
Dated 1944 and titled "VESUVIO - ITALY” this incredible double-sided ‘THIRD EDITION’ Aeronautical Chart was used for aerial navigation of the U.S. Army Air Force during WWII. Prepared under the direction of the Commanding General of the Army Air Force this map is marked ‘RESTRICTED’ while being used in the theater of operation as it contains sensitive information wartime information such as Allied air radio frequencies, vital defense areas, and the location of military facilities. While participating in combat operation missions this map would have been used for the navigation to aerial bombardment targets, aerial reconnaissance, strike attacks, search and rescue missions, transport operations, etc.
Allied Invasion of Mainland Italy:
The British 8th Army under Field Marshal Bernard L. Montgomery begins the Allied invasion of the Italian peninsula, crossing the Strait of Messina from Sicily and landing at Calabria–the “toe” of Italy. On the day of the landing, the Italian government secretly agreed to the Allies’ terms for surrender, but no public announcement was made until September 8.
Italian dictator Benito Mussolini envisioned building Fascist Italy into a new Roman Empire, but a string of military defeats in World War II effectively made his regime a puppet of its stronger Axis partner, Germany. By the spring of 1943, opposition groups in Italy were uniting to overthrow Mussolini and make peace with the Allies, but a strong German military presence in Italy threatened to resist any such action.
On July 10, 1943, the Allies began their invasion of Axis-controlled Europe with landings on the island of Sicily, off mainland Italy. Encountering little resistance from demoralized Sicilian troops, Montgomery’s 8th Army came ashore on the southeast part of the island, while the U.S. 7th Army, under General George S. Patton, landed on Sicily’s south coast. Within three days, 150,000 Allied troops were ashore. On August 17, Patton arrived in Messina before Montgomery, completing the Allied conquest of Sicily and winning the so-called Race to Messina.
In Rome, the Allied conquest of Sicily, a region of the kingdom of Italy since 1860, led to the collapse of Mussolini’s government. Early in the morning of July 25, he was forced to resign by the Fascist Grand Council and was arrested later that day. On July 26, Marshal Pietro Badoglio assumed control of the Italian government. The new government promptly entered into secret negotiations with the Allies, despite the presence of numerous German troops in Italy.
On September 3, Montgomery’s 8th Army began its invasion of the Italian mainland and the Italian government agreed to surrender to the Allies. By the terms of the agreement, the Italians would be treated with leniency if they aided the Allies in expelling the Germans from Italy. Later that month, Mussolini was rescued from a prison in the Abruzzo Mountains by German commandos and was installed as leader of a Nazi puppet state in northern Italy.
In October, the Badoglio government declared war on Germany, but the Allied advance up through Italy proved to be a slow and costly affair. Rome fell in June 1944, at which point a stalemate ensued as British and American forces threw most of their resources into the Normandy invasion. In April 1945, a new major offensive began, and on April 28 Mussolini was captured by Italian partisans and summarily executed. German forces in Italy surrendered on May 1, and six days later all of Germany surrendered.