WWII 1944 Allied MULHEIM Rhine River Germany Infantry & Armored Division Combat Map*















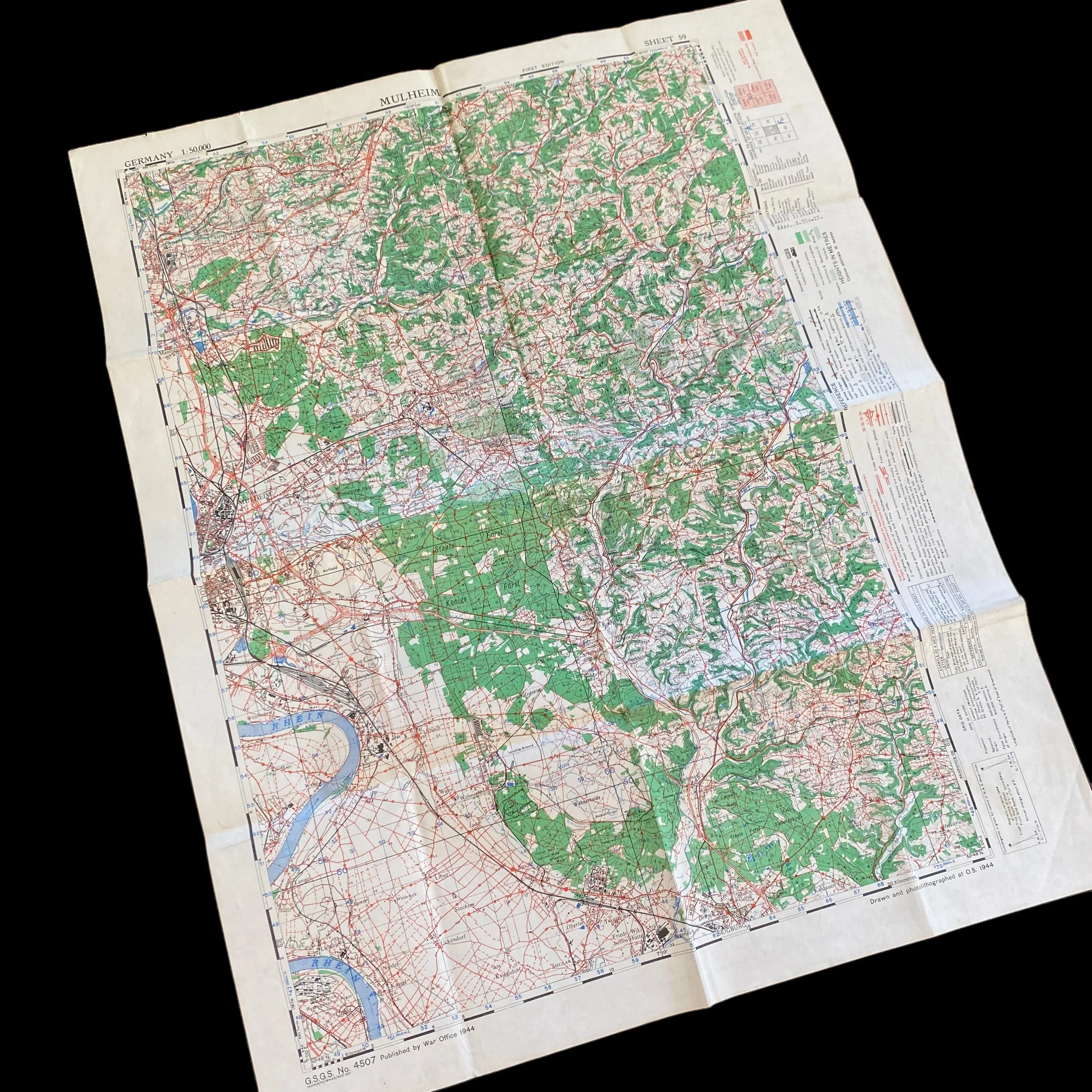





WWII 1944 Allied MULHEIM Rhine River Germany Infantry & Armored Division Combat Map*
Comes with C.O.A.
This original and museum-grade World War II Allied “MULHEIM” Rhine River map was published by the War Office in 1944 and was used during the Allied push through Germany and the advance on the Rhine River. This infantry map is updated with aerial revisions taken from previous Allied aerial reconnaissance missions in the area. This map of the Rhine River is an incredible piece of WWII history and would make an amazing addition to any WWII collection.
Mülheim is a city located in the North Rhine-Westphalia region of Germany. It was one of the many urban centers caught in the maelstrom of World War II. The Allied push towards the Rhine River was a crucial operation, as it marked the final stages of the European Theater of the war and the impending defeat of Nazi Germany.
The Allied push towards the Rhine began in earnest in 1944, after the successful D-Day landings in Normandy. This marked a turning point in the war, as the Western Allies, primarily the United States, Great Britain, and Canada, established a firm foothold on the European mainland. As the Allies continued their eastward advance, the objective became clear: reaching and crossing the Rhine River. The Rhine presented a formidable natural obstacle to their progress, as it was one of the last significant geographical barriers between them and the heartland of Nazi Germany.
Mülheim played a crucial role in this Allied push. As a city situated along the eastern bank of the Rhine, it was strategically located and would become a focal point of the impending battle. The city, like many others in the region, had suffered extensive damage from the relentless Allied bombing campaigns. This not only weakened German defenses but also demoralized the civilian population. Mülheim, like other cities in the Ruhr industrial region, was vital to the German war effort. Its industrial facilities produced essential materials and weapons for the German military. Thus, capturing Mülheim was not only about crossing the Rhine but also disrupting Germany's production capabilities.
The battle for Mülheim was part of a broader operation called Operation Grenade. This operation aimed at pushing through the heavily defended Siegfried Line, a system of German defensive fortifications, and reaching the Rhine River. The battle in and around Mülheim was fierce and intense. The German forces, well aware of the significance of the Rhine as a natural barrier, were determined to defend it vigorously. The city's infrastructure was heavily damaged, and its streets became battlegrounds.
One of the key elements of the Allied strategy was the use of combined arms. Infantry, tanks, and artillery worked in tandem to overcome the German defenses. The Battle of Mülheim saw extensive street fighting and close-quarters combat. The German defenders, often resorting to house-to-house fighting, made every attempt to halt the Allied advance.
As the Allies pushed through the Ruhr region, capturing cities like Mülheim, they disrupted the German war machine's production. Many key industries and factories were destroyed, and the logistical infrastructure was severely compromised. This not only weakened the German military but also contributed to the overall collapse of the Nazi regime.
The battle for Mülheim and the subsequent capture of the city played a crucial role in the Allied push towards the Rhine River. The Rhine marked the western boundary of Nazi Germany and was seen as the final barrier that needed to be crossed before the ultimate victory could be achieved. The capture of Mülheim and other cities in the region paved the way for the Allies to reach the Rhine.
The crossing of the Rhine River was a monumental achievement in the war. It symbolized the penetration of the heart of Nazi Germany and the impending collapse of the Third Reich. The Rhine River crossing in March 1945, particularly the famous operation known as Operation Plunder, involved an enormous coordinated effort by the Allies. The capture of key cities like Mülheim provided valuable bridgeheads and staging points for the river crossing.
The battle for Mülheim was not without its costs. Both sides suffered casualties, and the city itself bore the scars of war for years to come. However, the victory was essential in securing the western bank of the Rhine, a critical stepping stone in the final stages of the war.
In conclusion, Mülheim, a city in western Germany, played a significant role in the Allied push towards the Rhine River during World War II. This push was a crucial phase in the war, marking the final stages of the European Theater and the impending defeat of Nazi Germany. The battle for Mülheim was fierce, and its capture disrupted the German war effort by crippling its industrial capacity in the Ruhr region. The subsequent crossing of the Rhine River was a momentous achievement, bringing the Allies closer to victory. Mülheim, like many other cities, witnessed the ravages of war, but its role in history is a testament to the determination and sacrifice of those who fought for a better world.