Original 1944 WWII Nagasaki Atomic Bomb Silk Bail Out Navigation Map
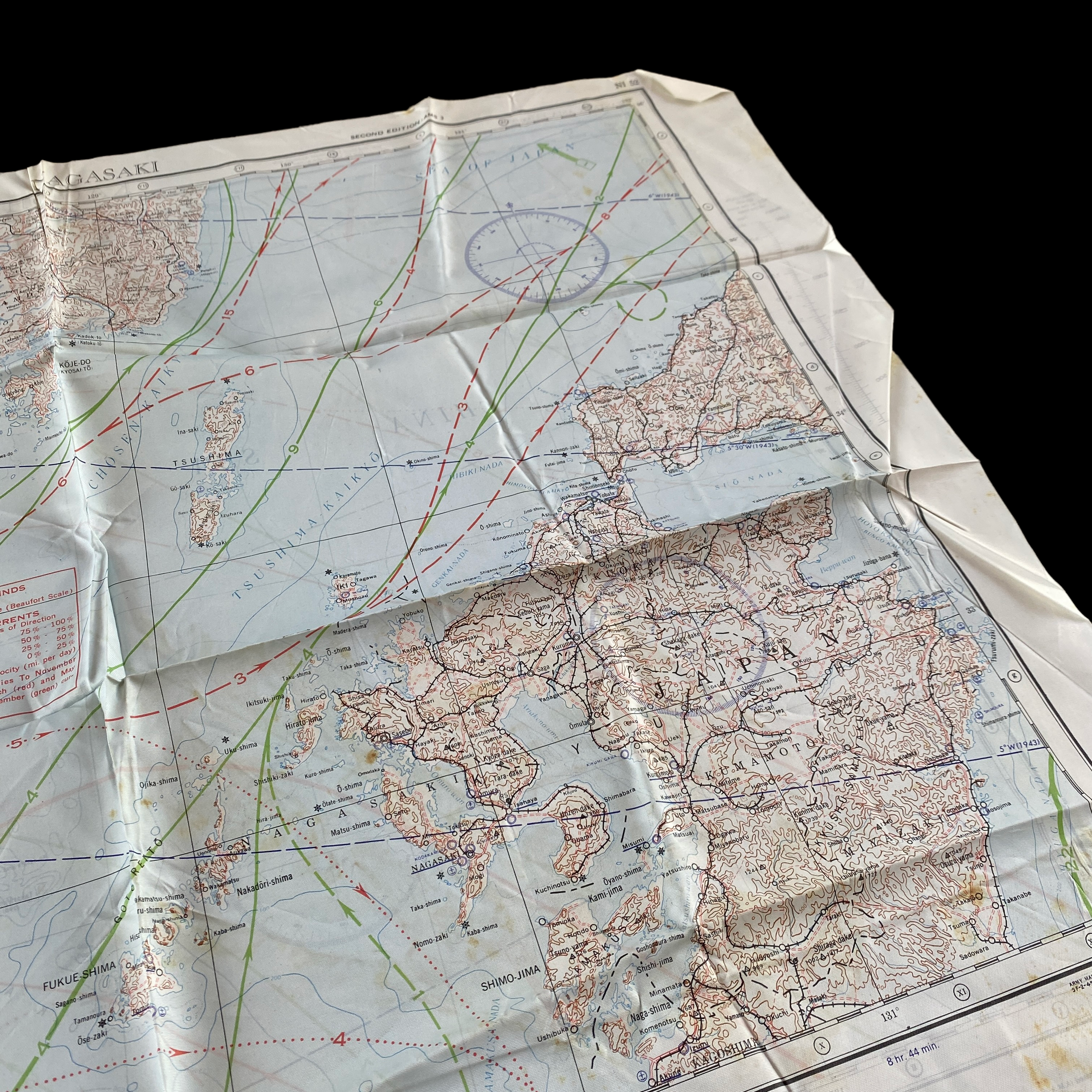










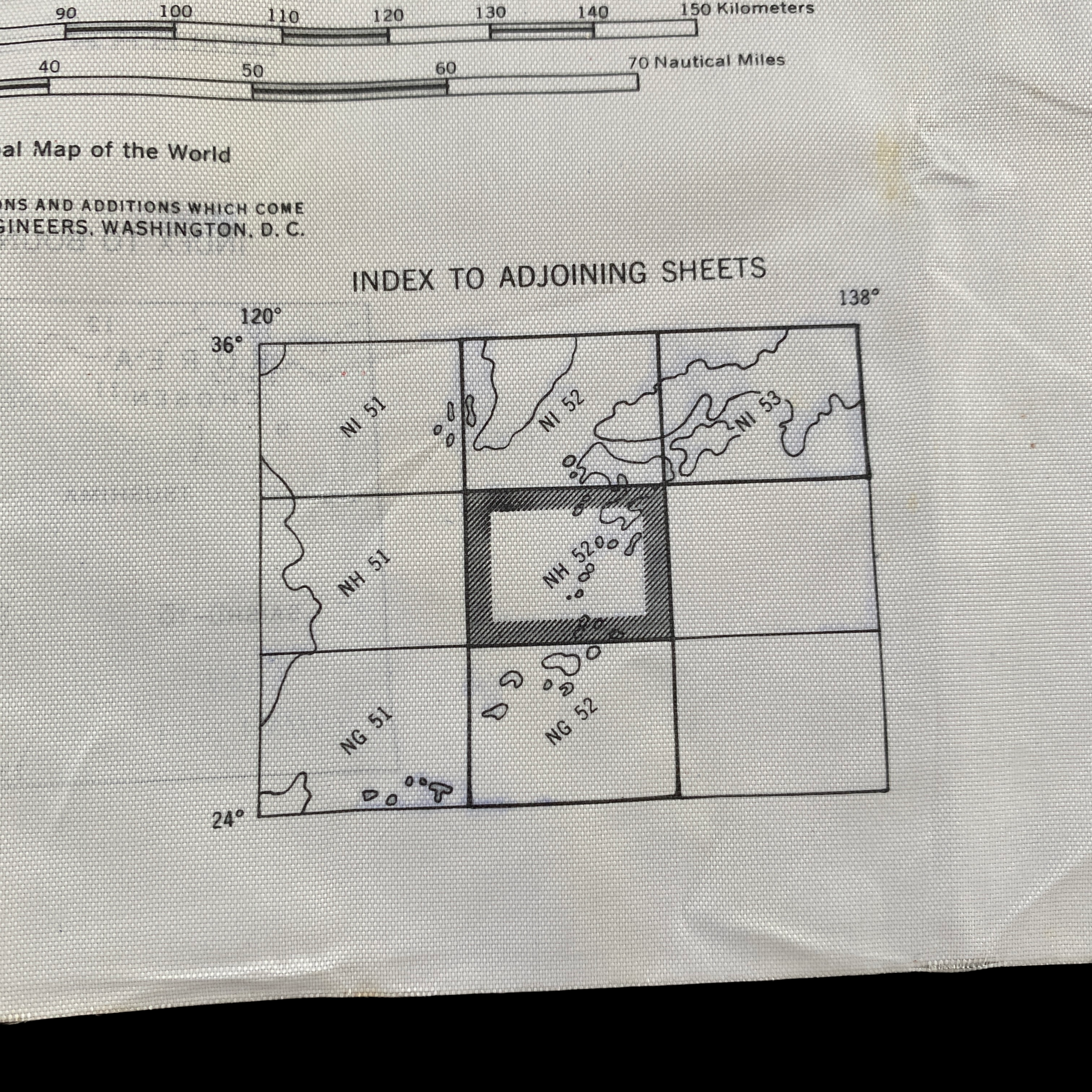
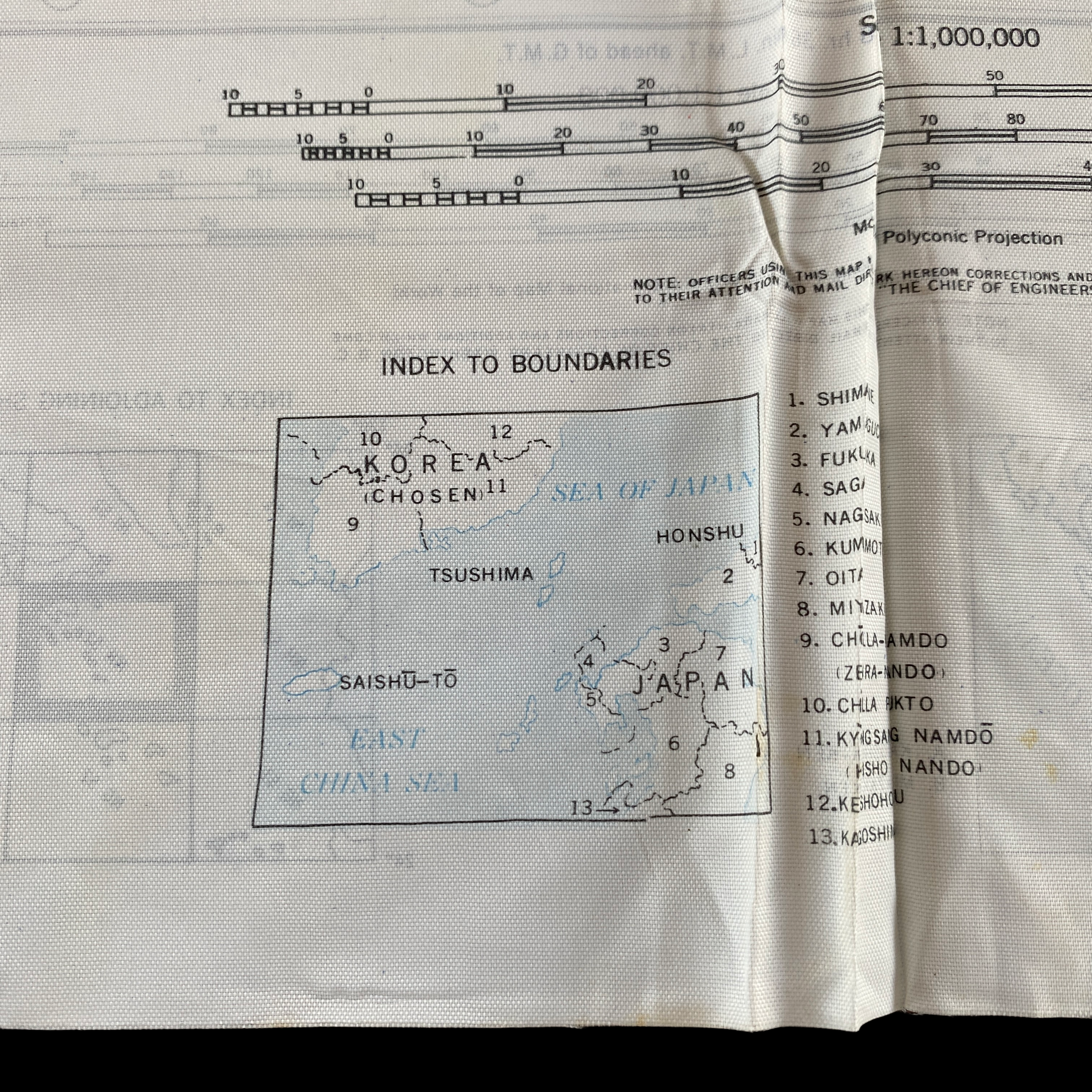


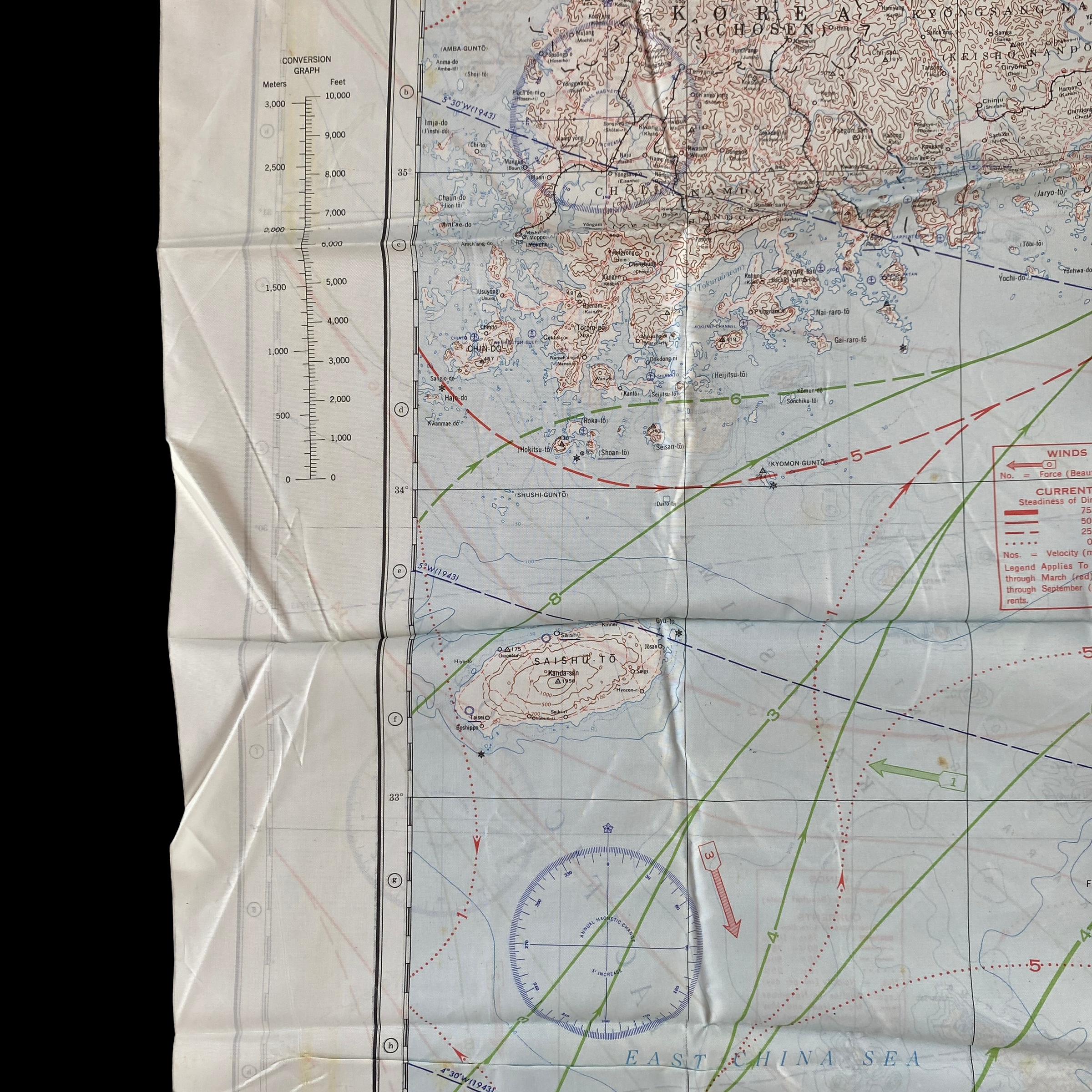



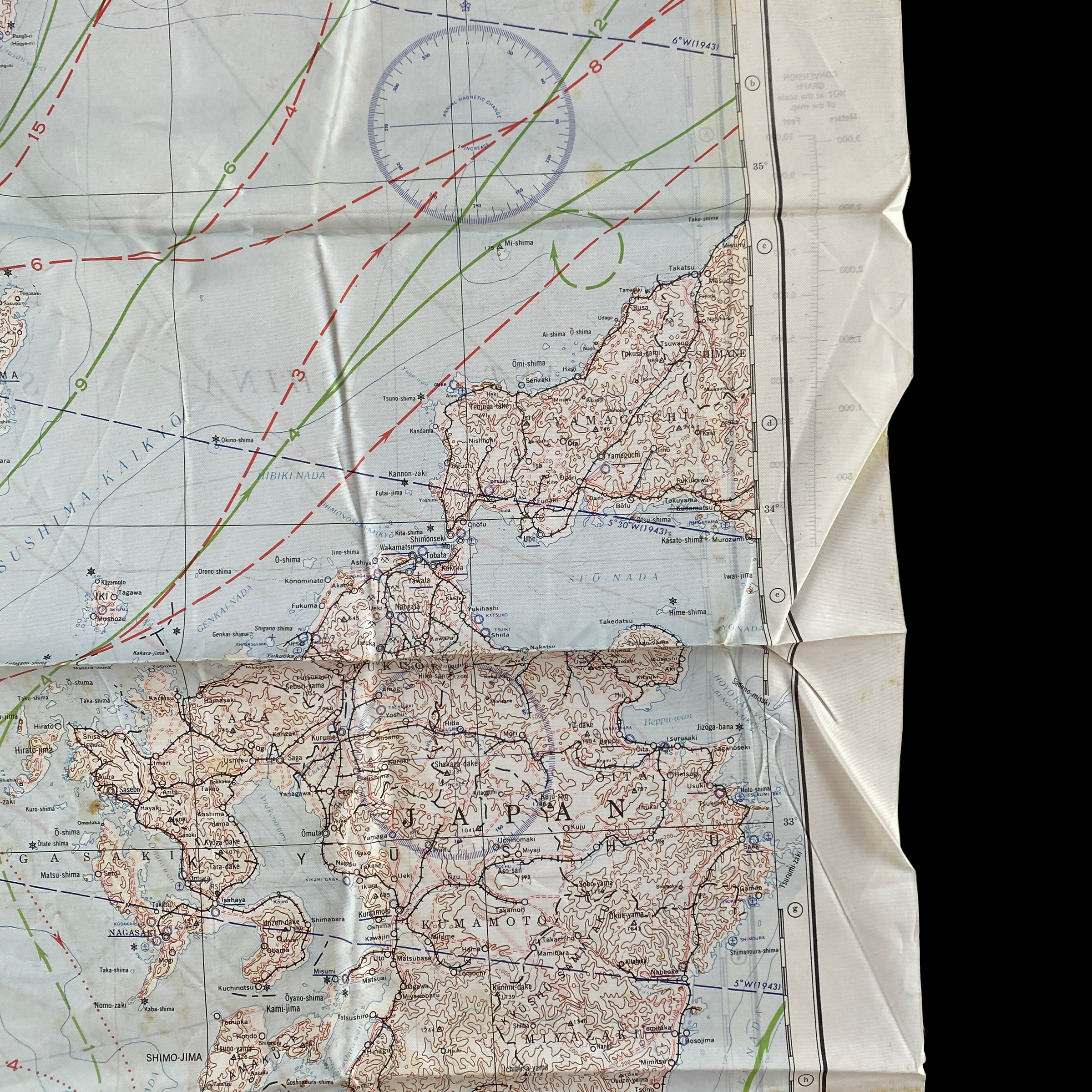

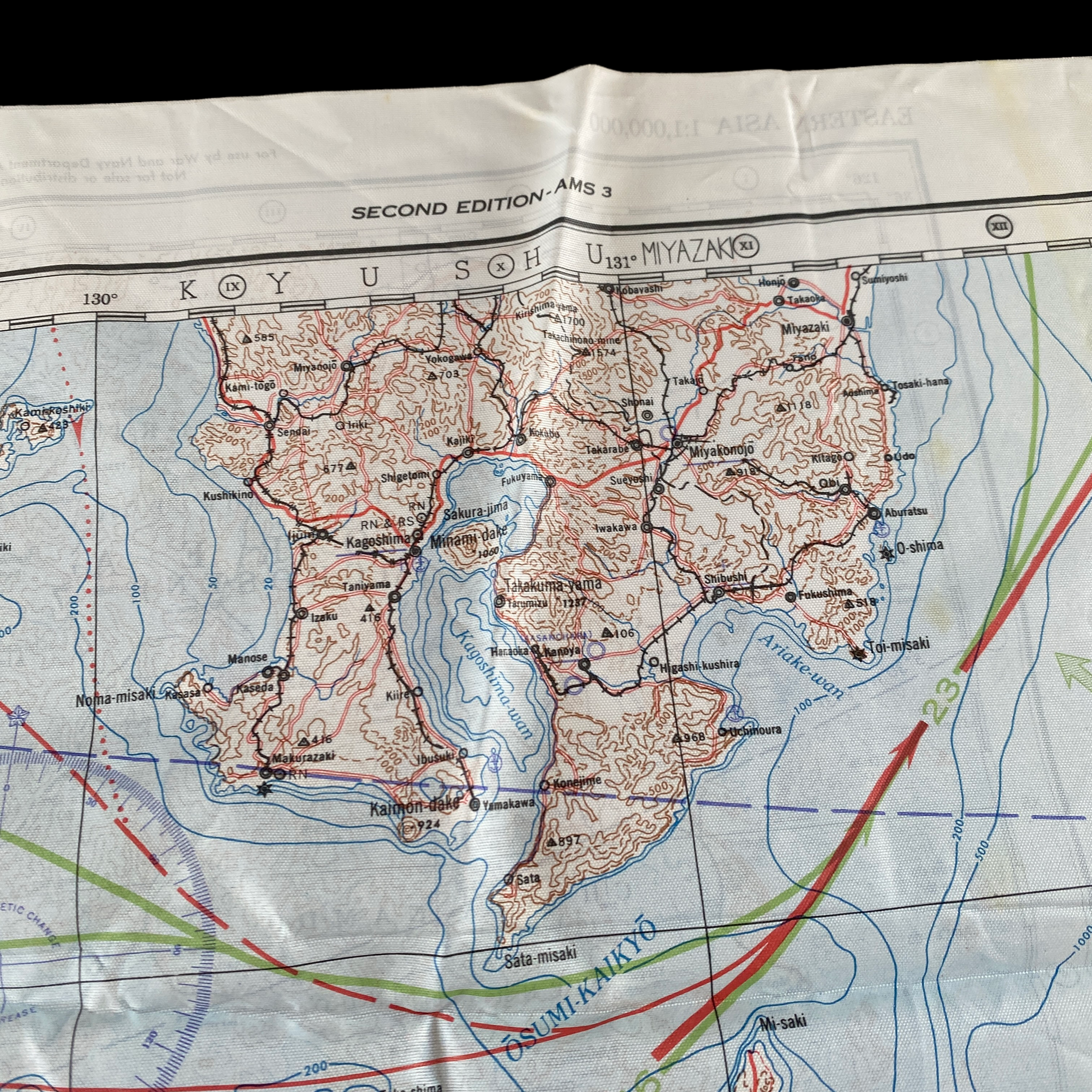
Original 1944 WWII Nagasaki Atomic Bomb Silk Bail Out Navigation Map
Comes with C.O.A.
*The bombing of the Japanese city of Nagasaki with the Fat Man plutonium bomb device on August 9, 1945, caused terrible human devastation and helped end World War II.
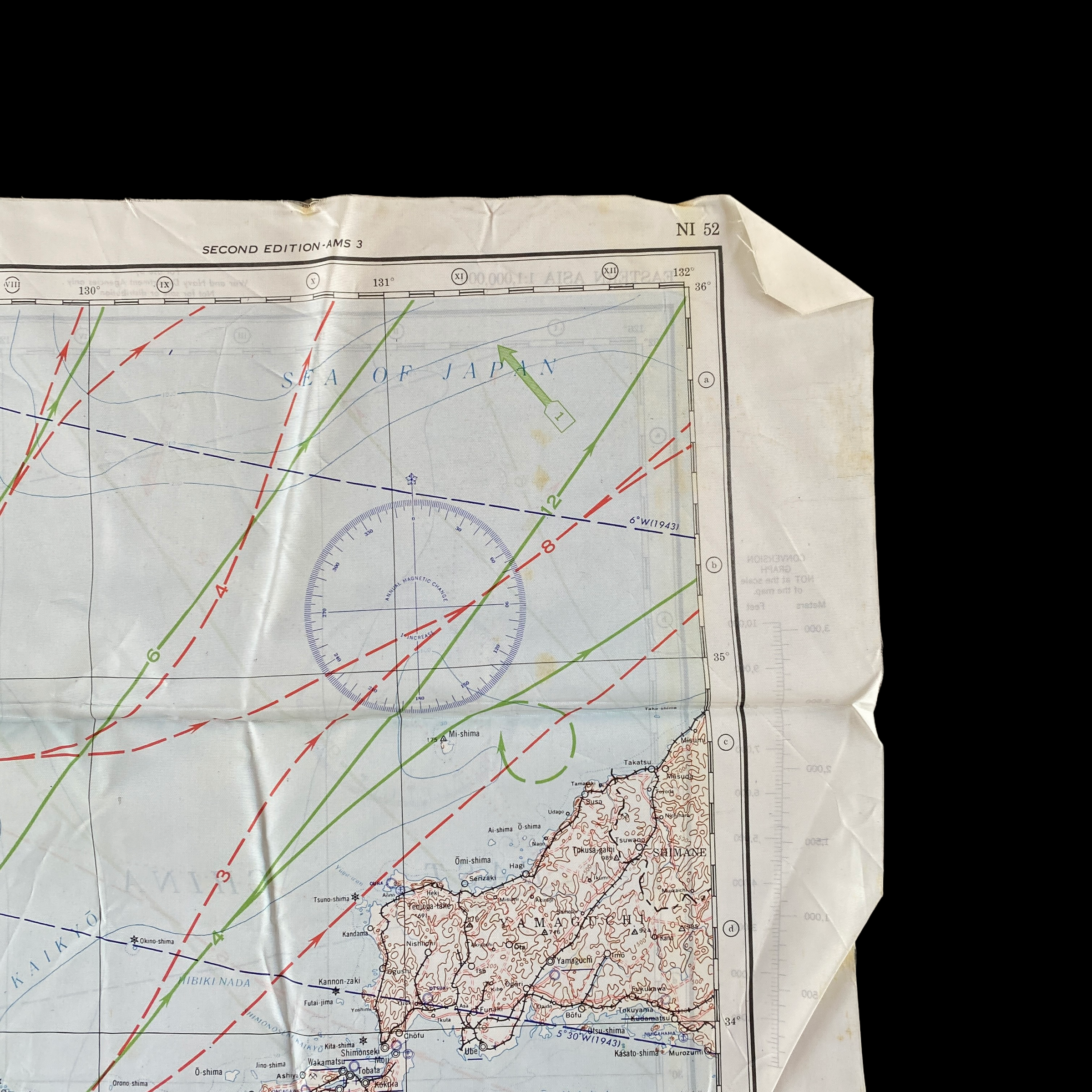
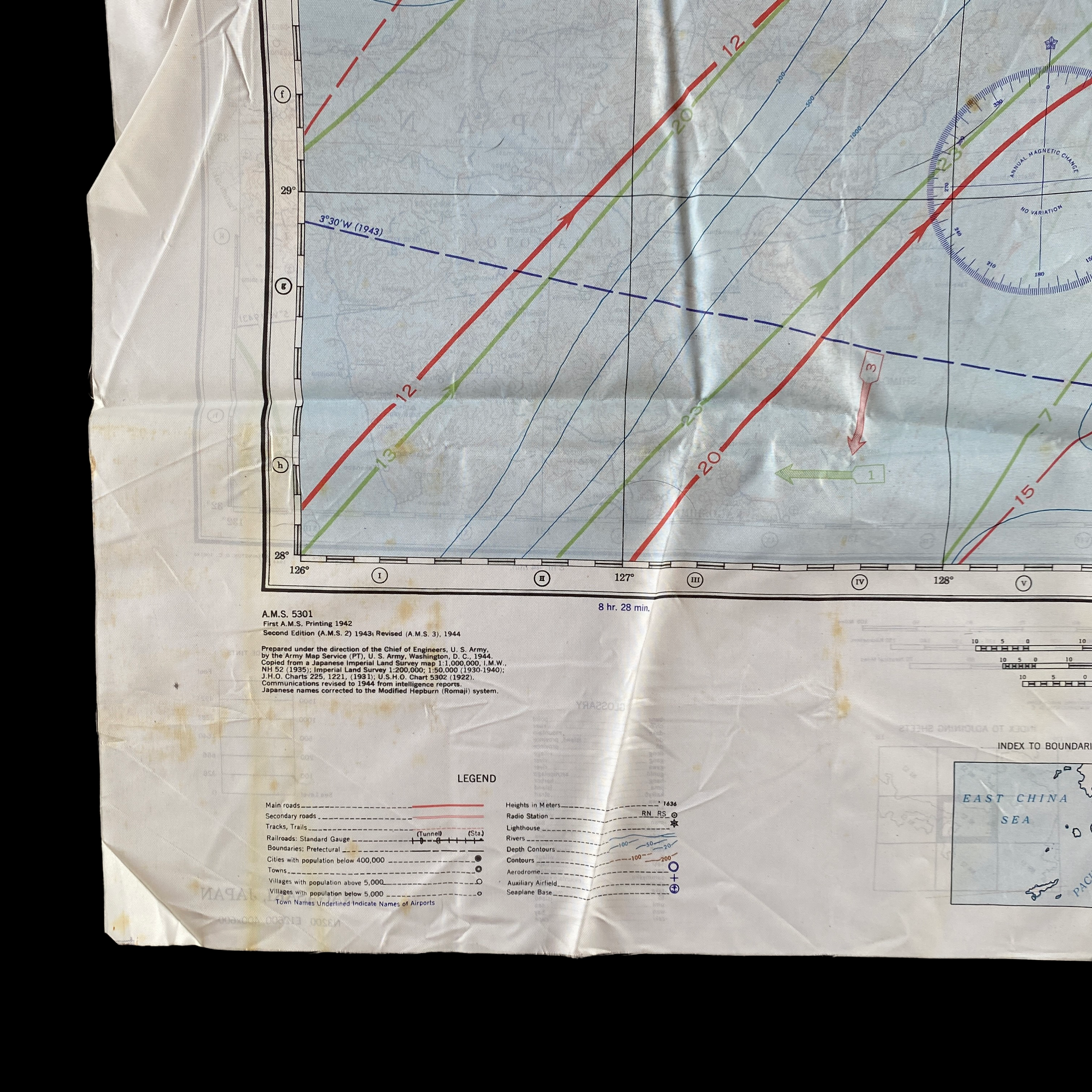
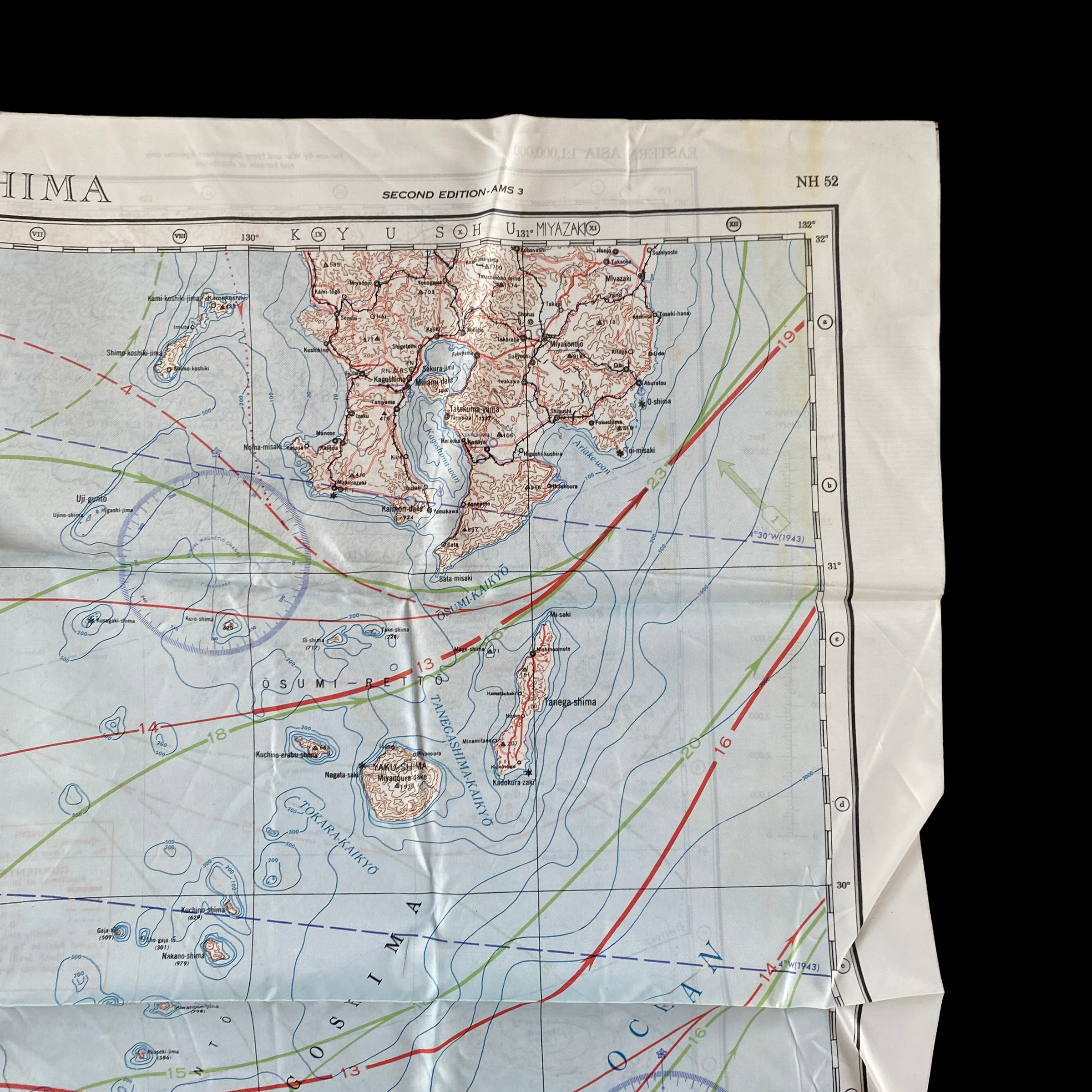
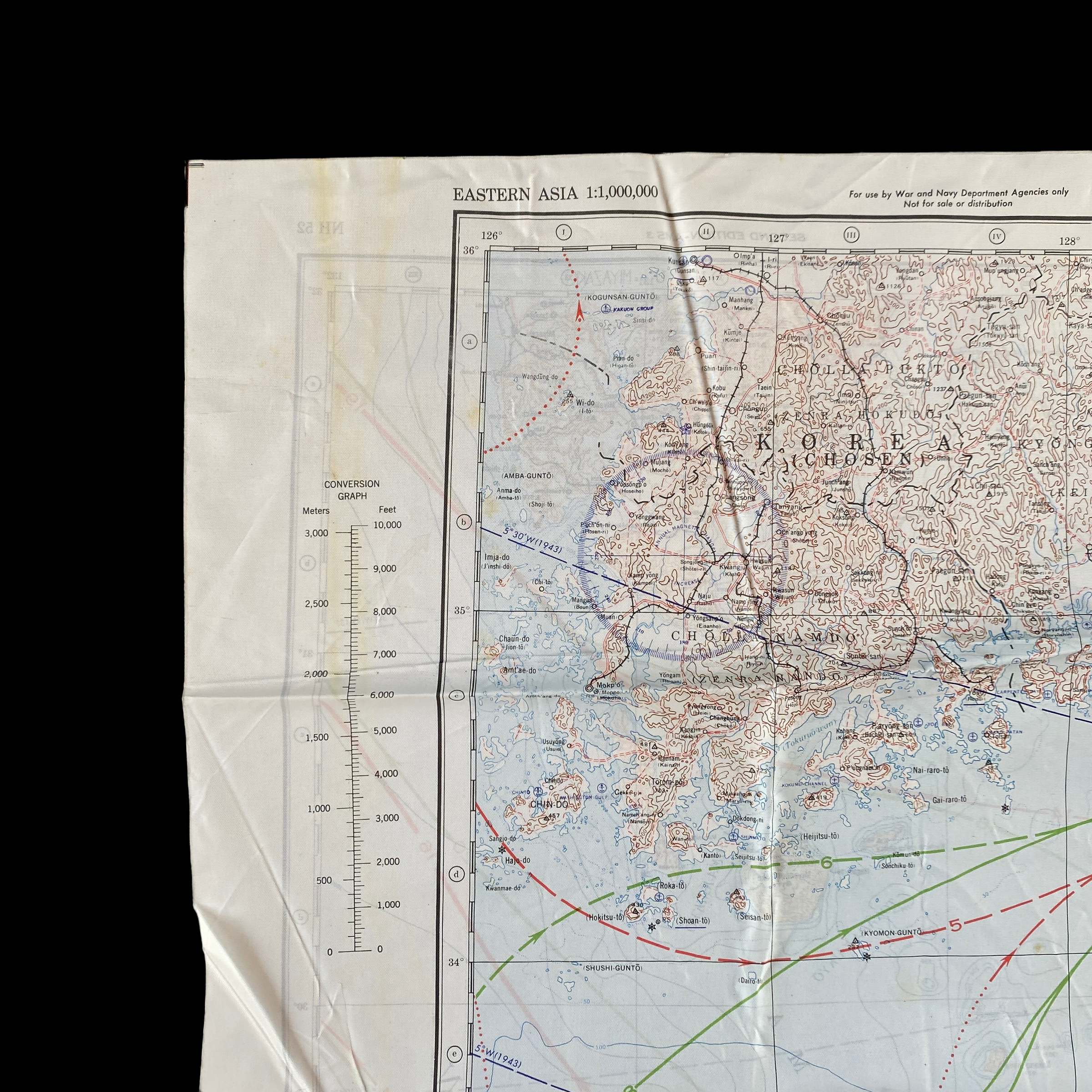
This incredible WWII double-sided silk bail out navigation map titled “NAGASAKI” is dated 1944 and shows one of the most prolific Japanese cities of WWII. Nagasaki was a port city located about 100 miles from Kokura. It was larger, with an approximate population of 263,000 people, and some major military facilities, including two Mitsubishi military factories. These cloth charts were worn as neck scarves or stuffed in the pant/jacket pockets by pilots during WWII as part of their survival gear. During WWII these silk bailout maps were produced in varying quantities by the Allied forces on thin silk (waterproof) material. The idea was that if an Allied pilot’s plane was shot down behind enemy lines they should have a map to help him find his way to safety if he escaped or evade capture.
This silk map of NAGASAKI would have been similar to the exact bail out maps that would have been distributed to the aircraft that participated in the infamous second A-bomb on Nagasaki on August 9, 1945.
On August 6, 1945, during World War II (1939-45), an American B-29 bomber dropped the world’s first deployed atomic bomb over the Japanese city of Hiroshima. The explosion immediately killed an estimated 80,000 people; tens of thousands more would later die of radiation exposure. Three days later, a second B-29 dropped another A-bomb on Nagasaki, killing an estimated 40,000 people. Japan’s Emperor Hirohito announced his country’s unconditional surrender in World War II in a radio address on August 15, citing the devastating power of “a new and most cruel bomb.”
Bockscar, sometimes called Bock's Car, is the name of the United States Army Air Forces B-29 bomber that dropped a Fat Man nuclear weapon over the Japanese city of Nagasaki during World War II in the second – and last – nuclear attack in history.
The Bombing of Nagasaki, August 9, 1945:
The Target Committee appointed by President Harry Truman to decide which Japanese cities would receive the Little Boy and Fat Man atomic bombings did not place Nagasaki among their top two choices. Instead they identified Kokura as the second target after Hiroshima. In Kokura, a city of 130,000 people on the island of Kyushu, the Japanese operated one of their biggest ordnance factories, manufacturing among other things chemical weapons. The Americans knew all this, but strangely had not targeted the city yet in their conventional bombing campaign. That was one of the reasons the Target Committee thought it would be a good option after Hiroshima.
The third choice, Nagasaki was a port city located about 100 miles from Kokura. It was larger, with an approximate population of 263,000 people, and some major military facilities, including two Mitsubishi military factories. Nagasaki also was an important port city. Like Kokura and Hiroshima, it had not suffered much thus far from American conventional bombing.
After the bombing of Hiroshima on August 6, workers on Tinian island labored intensely to put the finishing touches on the Fat Man bomb and prepare it for use. This was a plutonium implosion device of far greater complexity than the Little Boy bomb used at Hiroshima, which used uranium-235 in a fairly conventional explosive mechanism. The scientists and ordnance experts at Los Alamos had agonized for years over how to use plutonium in an atomic weapon, and Fat Man was the result.
The decision to use Fat Man just days after the explosion of Little Boy at Hiroshima was based on two calculations: the always-changeable Japanese weather—the appearance of a typhoon or other major weather event could force deployment to be postponed for weeks—and the belief that two bombings following in quick succession would convince the Japanese that the Americans had plenty of atomic devices and were ready to keep using them until Japan finally surrendered. Reports of approaching bad weather convinced the Americans to drop the next bomb on August 9.
Clouds also obscured visibility over Nagasaki, and Maj. Sweeney, running out of fuel, prepared to turn back toward Okinawa. At the last second a hole opened in the clouds, however, and Bombardier Capt. Kermit K. Beahan announced that he could see his target. And so Fat Man began its journey, detonating over Nagasaki at 11:02 a.m. local time.
Fat Man detonated at an altitude of 1,650 feet over Nagasaki with a yield of 21 kilotons, about 40 percent more powerful than Little Boy had been. It did so almost directly above the Mitsubishi factories that were the city’s primary targets, rather than over the residential and business districts further south. Tens of thousands of civilians, especially children, had already been evacuated from the city. The series of hills bracing Nagasaki also somewhat confined the initial blast and restricted the damage.
Still, the impact was devastating, particularly because people had heard the all-clear after an earlier aircraft raid warning, and had left their shelters. Everything within a mile of ground zero was annihilated. Fourteen thousand homes burst into flames. People close to the blast were vaporized; those unlucky enough to be just outside that radius received horrific burns and, there and further out, radiation poisoning that would eventually kill them. Although estimates vary, perhaps 40,000 people were killed by the initial detonation. By the beginning of 1946, 30,000 more people were dead. And within the next five years, well over 100,000 deaths were directly attributable to the bombing of Nagasaki on August 9, 1945.