WWII 1943 United Kingdom Royal Air Force British Fighter "Hawker Typhoon" W.E.F.T.U.P. ID Poster




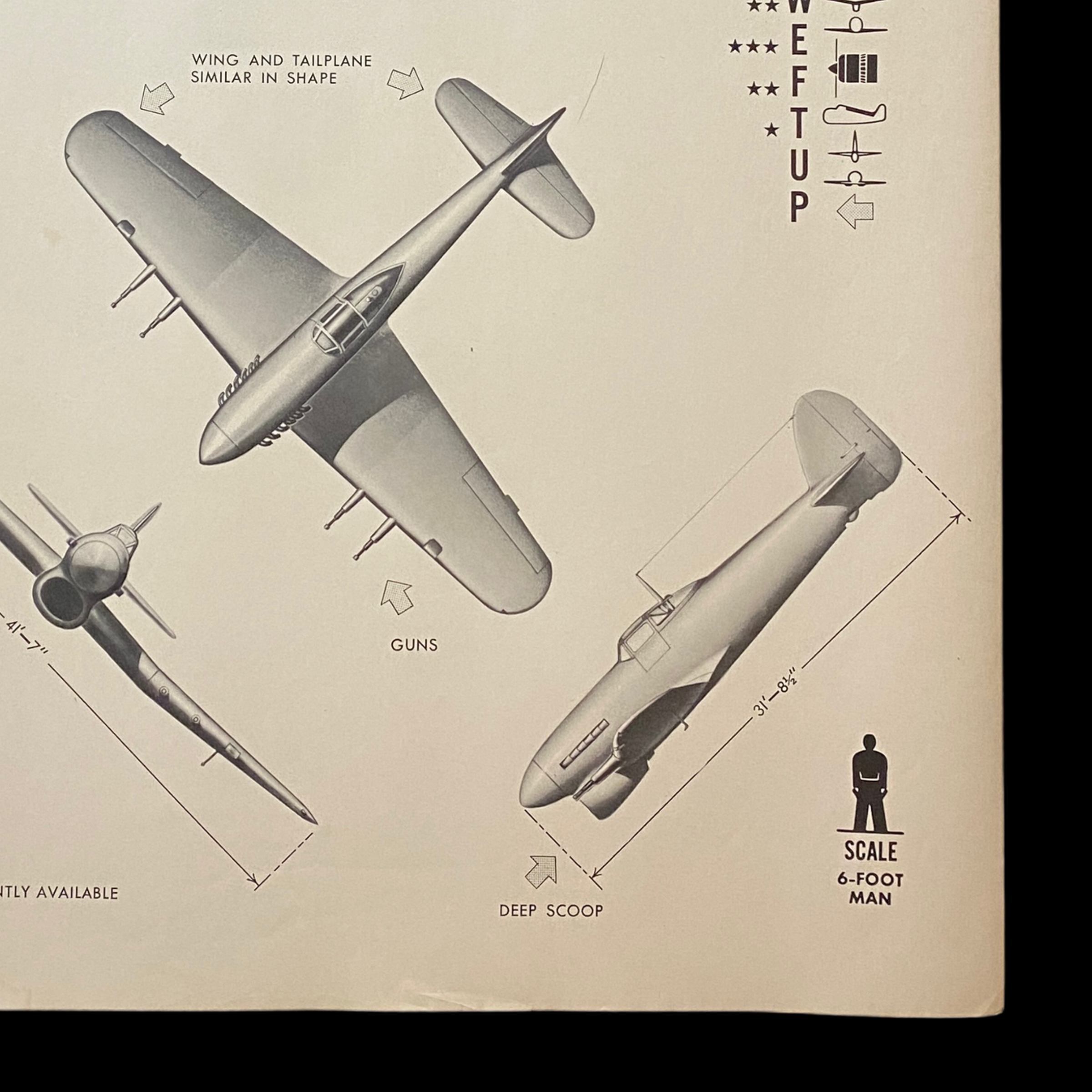


WWII 1943 United Kingdom Royal Air Force British Fighter "Hawker Typhoon" W.E.F.T.U.P. ID Poster
Size: 19 x 25 inches
This original ‘RESTRICTED’ aircraft identification poster was published by the U.S. Naval Aviation Training Division March 1943. This poster was posted as a training tool as well as an in theater ID poster to help U.S. and other Allied pilots, bomber crews and Naval personal to identify Allied and enemy aircraft. W.E.F.T.U.P. or Wing, Engine, Fuselage, Tail, Undercarriage, Peculiarities was a system set up for the purpose of aircraft identification and recognition.
World War II saw some of the first introduction of these aircraft ID poster to prevent friendly fire and more accurate plane recognition in combat. It was believed these posters alone could save countless lives from friendly aircraft-on-aircraft or friendly anit-aircraft fire. These posters also could cut down precious second pilots, bomber gunners, and naval gun crews would have to ID a plane flying towards them intern saving their lives by shooting first.
Each poster provides the silhouettes, dimensions, and relevant information to educate both air and ground personnel in aircraft identification. Immediate identification of aircraft, friendly or not, was essential in order for the observer (whether in the air e.g., pilot, gunner, or patrol observer, or on the ground, e.g., anti-aircraft crew) to determine his next course of action (e.g., acknowledge, attack, evade, or report). Each poster details a large clean sky and background image of the specified aircraft located as the main top imagine on the poster. It also contains important ‘peculiarities’ such as where certain gun emplacements are located, other special aircraft features, as well as wing and length measurements.
Hawker Typhoon:
The Hawker Typhoon (Tiffy in RAF slang) is a British single-seat fighter-bomber, produced by Hawker Aircraft. It was intended to be a medium-high altitude interceptor, as a replacement for the Hawker Hurricane but several design problems were encountered and it never completely satisfied this requirement.
The Typhoon was originally designed to mount twelve .303 inch (7.7 mm) Browning machine guns and be powered by the latest 2,000 hp engines. Its service introduction in mid-1941 was plagued with problems and for several months the aircraft faced a doubtful future.[3] When the Luftwaffe brought the formidable Focke-Wulf Fw 190 into service in 1941, the Typhoon was the only RAF fighter capable of catching it at low altitudes; as a result it secured a new role as a low-altitude interceptor.
The Typhoon became established in roles such as night-time intruder and long-range fighter. From late 1942 the Typhoon was equipped with bombs and from late 1943 RP-3 rockets were added to its armoury. With those weapons and its four 20mm Hispano autocannons, the Typhoon became one of the Second World War's most successful ground-attack aircraft.
By 1943, the RAF needed a ground attack fighter more than a "pure" fighter and the Typhoon was suited to the role (and less-suited to the pure fighter role than competing aircraft such as the Spitfire Mk IX). The powerful engine allowed the aircraft to carry a load of up to two 1,000 pounds (450 kg) bombs, equal to the light bombers of only a few years earlier. The bomb-equipped aircraft were nicknamed "Bombphoons" and entered service with No. 181 Squadron, formed in September 1942.[31][nb 7]
From September 1943, Typhoons were also armed with four "60 lb" RP-3 rockets under each wing.[nb 8] In October 1943, No. 181 Squadron made the first Typhoon rocket attacks. Although the rocket projectiles were inaccurate and took considerable skill to aim and allow for ballistic drop after firing, "the sheer firepower of just one Typhoon was equivalent to a destroyer's broadside."[citation needed] By the end of 1943, eighteen rocket-equipped Typhoon squadrons formed the basis of the RAF Second Tactical Air Force (2nd TAF) ground attack arm in Europe. In theory, the rocket rails and bomb-racks were interchangeable; in practice, to simplify supply, some 2nd TAF Typhoon squadrons (such as 198 Squadron) used the rockets only, while other squadrons were armed exclusively with bombs (this also allowed individual units to more finely hone their skills with their assigned weapons).
By the Normandy landings in June 1944, 2 TAF had eighteen operational squadrons of Typhoon IBs, while RAF Fighter Command had a further nine. The aircraft proved itself to be the most effective RAF tactical strike aircraft, on interdiction raids against communications and transport targets deep in North Western Europe prior to the invasion and in direct support of the Allied ground forces after D-Day. A system of close liaison with the ground troops was set up by the RAF and army: RAF radio operators in vehicles equipped with VHF R/T travelled with the troops close to the front line and called up Typhoons operating in a "Cab Rank", which attacked the targets, marked for them by smoke shells fired by mortar or artillery, until they were destroyed.