Japanese Dive Bomber Aichi Type 99 'Val' Aviation Training W.E.F.T.U.P. ID Posters





Japanese Dive Bomber Aichi Type 99 'Val' Aviation Training W.E.F.T.U.P. ID Posters
Size: 19 x 25 inches
This original ‘RESTRICTED’ aircraft identification poster was published by the U.S. Naval Aviation Training Division March of 1943. This poster was posted as a training tool as well as an in theater ID poster to help U.S. and other Allied pilots, bomber crews and Naval personal to identify Allied and enemy aircraft. W.E.F.T.U.P. or Wing, Engine, Fuselage, Tail, Undercarriage, Peculiarities was a system set up for the purpose of aircraft identification and recognition.
World War II saw some of the first introduction of these aircraft ID poster to prevent friendly fire and more accurate plane recognition in combat. It was believed these posters alone could save countless lives from friendly aircraft-on-aircraft or friendly anit-aircraft fire. These posters also could cut down precious second pilots, bomber gunners, and naval gun crews would have to ID a plane flying towards them intern saving their lives by shooting first.
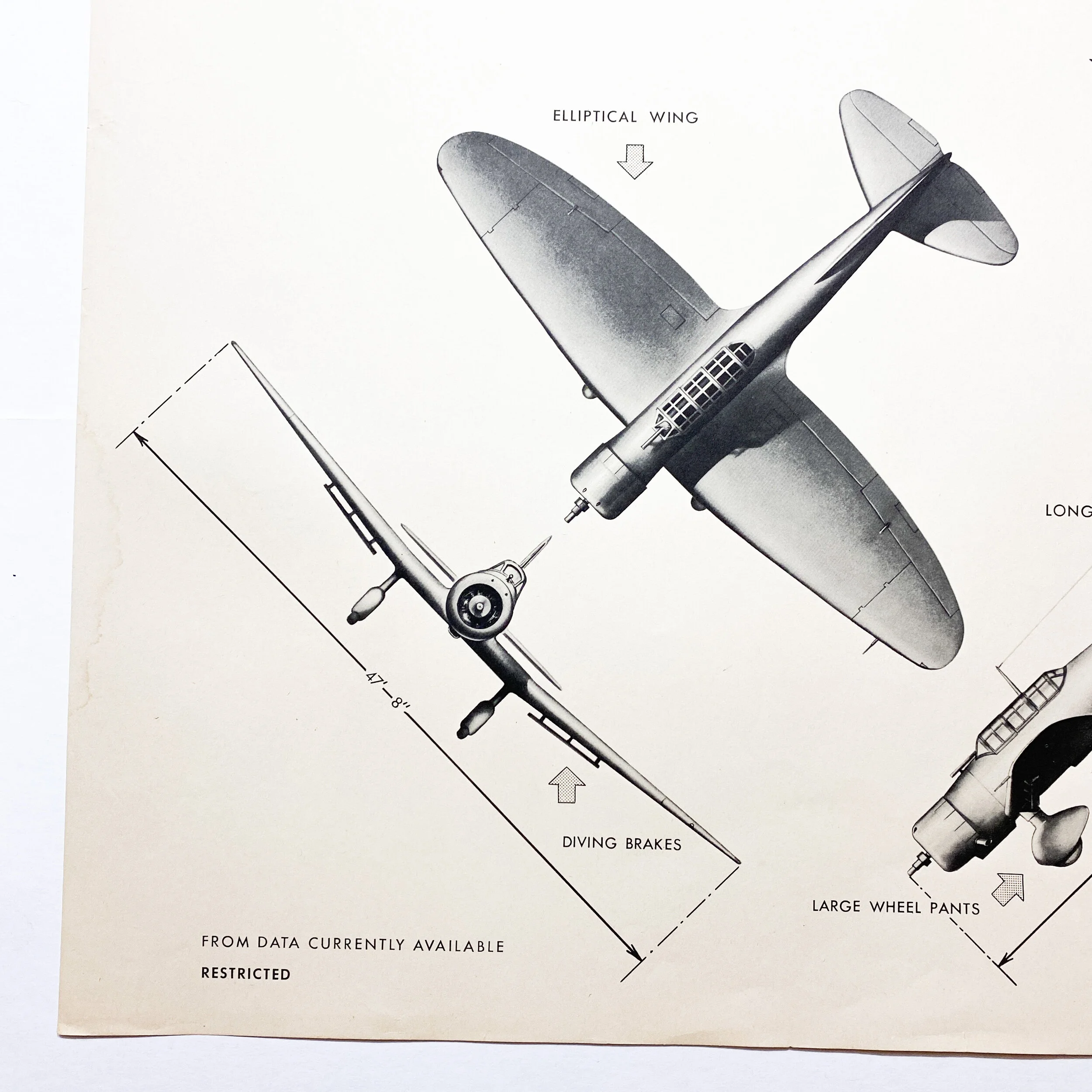
Each poster provides the silhouettes, dimensions, and relevant information to educate both air and ground personnel in aircraft identification. Immediate identification of aircraft, friendly or not, was essential in order for the observer (whether in the air e.g., pilot, gunner, or patrol observer, or on the ground, e.g., anti-aircraft crew) to determine his next course of action (e.g., acknowledge, attack, evade, or report). Each poster details a large clean sky and background image of the specified aircraft located as the main top imagine on the poster. It also contains important ‘peculiarities’ such as where certain gun emplacements are located, other special aircraft features, as well as wing and length measurements.
Aichi D3A:
The Aichi D3A Type 99 Carrier Bomber (Allied reporting name "Val") is a World War II carrier-borne dive bomber. It was the primary dive bomber of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) and was involved in almost all IJN actions, including the attack on Pearl Harbor. The Aichi D3A was the first Japanese aircraft to bomb American targets in the war, commencing with Pearl Harbor and U.S. bases in the Philippines, such as Clark Air Force Base. They sank more Allied warships than any other Axis aircraft.
An individual D3A dive bomber was commanded by the senior ranking crew member aboard, which could be the observer rather than the pilot. This was in contrast to US Navy, where the pilot was almost always the commander of a dive bomber. For example, Petty Officer First Class Kiyoto Furuta was serving as a pilot to Lieutenant Takehiko Chihaya during the Attack on Pearl Harbor, and later on to Lieutenant Keiichi Arima during the two carrier battles of the Solomon Islands campaign, both of whom were observers.
The D3A1 commenced carrier qualification trials aboard the aircraft carriers Akagi and Kaga during 1940, while a small number of aircraft made their combat debut from land bases over China. Starting with the attack on Pearl Harbor, the D3A1 took part in all major Japanese carrier operations in the first 10 months of the war. They achieved their first major success against the Royal Navy during their Indian Ocean raid in April 1942. D3A1 dive bombers scored over 80% hits with their bombs during attacks on two heavy cruisers and an aircraft carrier during the operation.
Before Indian Ocean raid, the established doctrine regarding attack against ships was to arm all D3A dive bombers with semi-AP bombs. On 5 April 1942, IJN carrier force attacked Colombo on Ceylon with half of its complement, while the other half was kept in reserve for strikes against ships. Since a second strike against Colombo was deemed necessary, the dive bombers of reserve force were rearmed from semi-AP bombs to land bombs. When British heavy cruisers were spotted soon afterwards, the reserve force was sent with a portion of D3A dive bombers armed with land bombs. In the subsequent attack, land bombs unintentionally proved very effective in suppressing the anti-aircraft fire from the ships. As a result, the doctrine was modified in order to intentionally equip the first few D3A dive bombers with land bombs. This new method was already implemented for the attack that sunk HMS Hermes just four days later, and continued to be used from then on.
During 1942, dive bombing attacks by D3A bombers significantly contributed to sinking of three US fleet carriers: Lexington at the Battle of the Coral Sea, Yorktown at the Battle of Midway and Hornet at the Battle of the Santa Cruz Islands. In addition, they damaged carrier Enterprise both at the Battle of the Eastern Solomons and at the Battle of the Santa Cruz Islands.
During the course of the war, D3A dive bombers often combined their attacks upon enemy warships with the IJN Nakajima B5N Kate torpedo bomber; consequently enemy vessels were often sunk by a combination strike of bombs and torpedoes. However, there were occasions when just the D3A's would make the attacks, or at least score the sinking hits. Discounting the Pearl Harbor strike, which also used the B5N for level bombing and torpedo attacks, D3A dive bombers were credited with sinking the following Allied warships: