VERY RARE! WWII 1945 Operation Iceberg D-Day Battle of Okinawa Air and Navy Briefing Map (VERY LARGE)




























VERY RARE! WWII 1945 Operation Iceberg D-Day Battle of Okinawa Air and Navy Briefing Map (VERY LARGE)
Comes with hand-signed C.O.A.
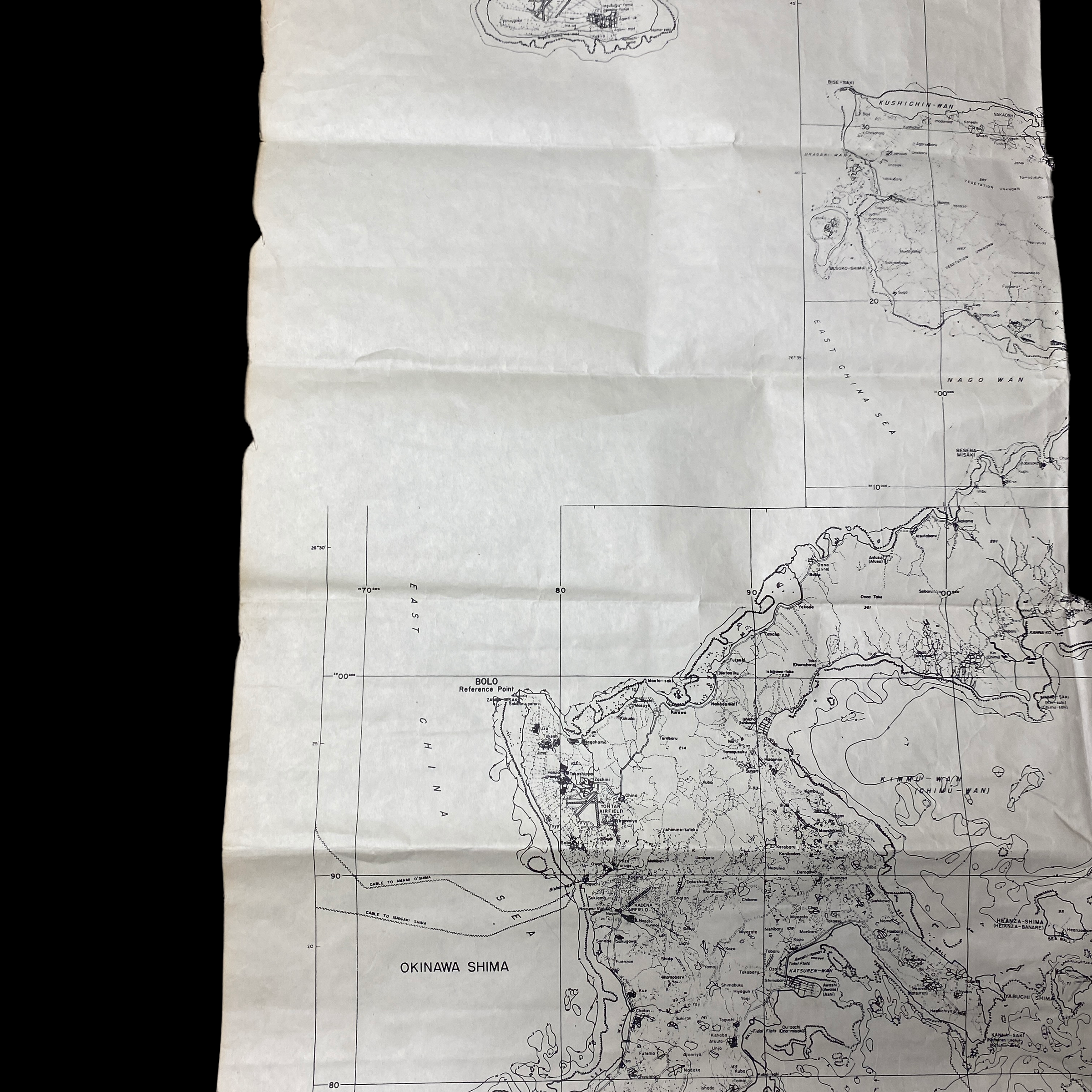
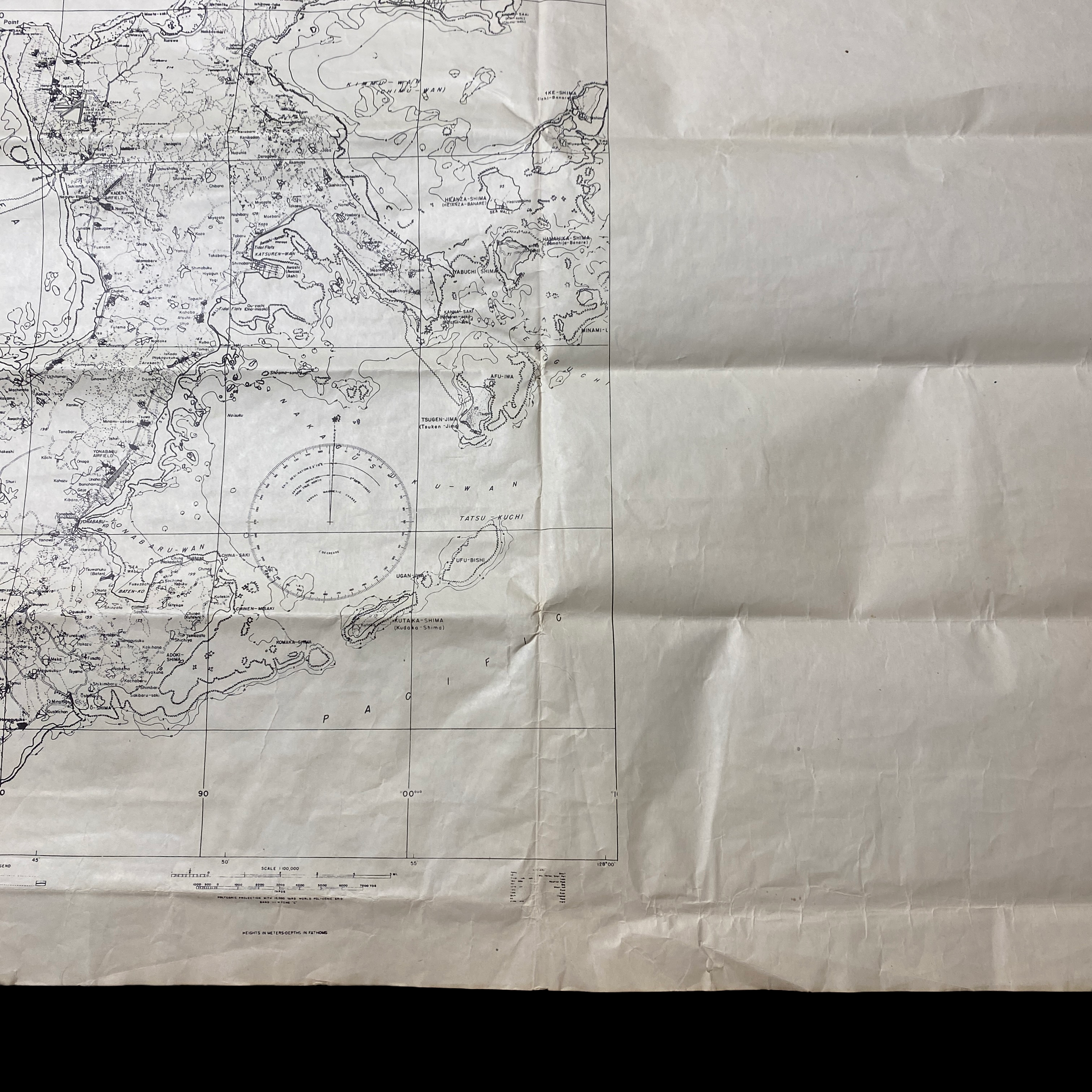
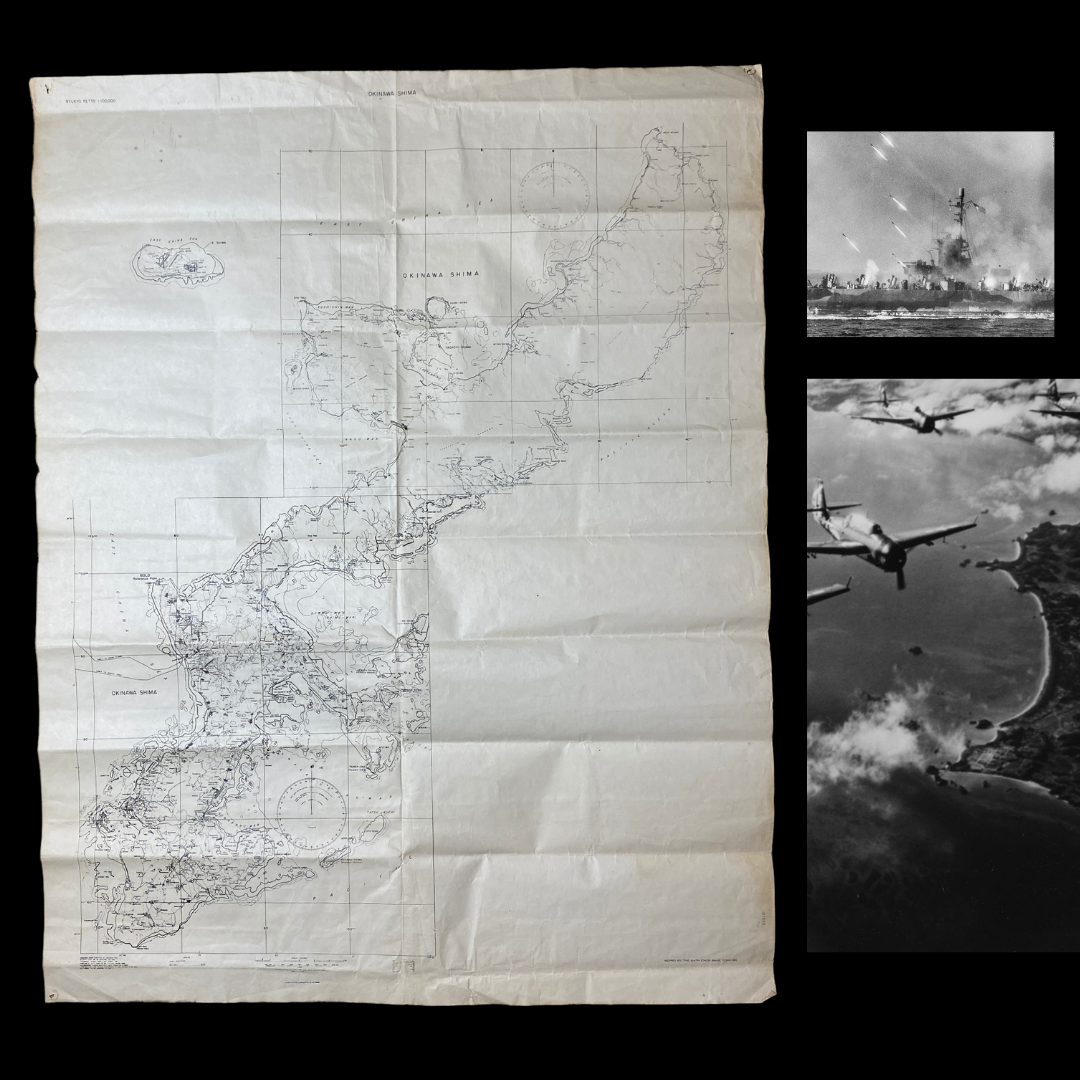
This incredily rare and museum-grade WWII briefing map is extremely large and was used as a Navy and Air (pilots) briefing map during the air and navy assaults during the Battle of Okinawa (Operation Iceberg). This map is very large and is one of the few operational maps used during teh invasion that shows the entire island of Okinawa. This briefing map was printed three months (January 1945) before the initial D-Day assault in April 1945. This map shows ALL of the D-Day landing beachhead as well as all of the Japanese airfield and the famous SHURI LINE.
In all, the US Army had over 103,000 soldiers (of these, 38,000+ were non-divisional artillery, combat support and HQ troops, with another 9,000 service troops), over 88,000 Marines and 18,000 Navy personnel (mostly Seabees and medical personnel). At the start of the Battle of Okinawa, US Tenth Army had 182,821 personnel under its command. It was planned that Lieutenant General Simon Bolivar Buckner Jr. would report to Vice Admiral Richmond K. Turner until the amphibious phase was completed, after which he would report directly to Admiral Raymond A. Spruance. Total aircraft in the American Navy, Marine and Army Air Force exceeded 3000 over the course of the battle, including fighters, attack aircraft, scout planes, bombers and dive-bombers. The invasion was supported by a fleet consisting of 18 battleships, 27 cruisers, 177 destroyers/destroyer escorts, 39 aircraft carriers (11 fleet carriers, 6 light carriers and 22 escort carriers) and various support and troop transport ships.
The Battle of Okinawa (April 1, 1945-June 22, 1945) was the last major battle of World War II, and one of the bloodiest. On April 1, 1945—Easter Sunday—the Navy’s Fifth Fleet and more than 180,000 U.S. Army and U.S. Marine Corps troops descended on the Pacific island of Okinawa for a final push towards Japan. The invasion was part of Operation Iceberg, a complex plan to invade and occupy the Ryukyu Islands, including Okinawa. Though it resulted in an Allied victory, kamikaze fighters, rainy weather and fierce fighting on land, sea and air led to a large death toll on both sides.
Landing on the Beachheads:
As dawn arrived on April 1, morale was low among American troops as the Fifth Fleet launched the largest bombardment ever to support a troop landing to soften Japanese defenses.
Soldiers and Army brass alike expected the beach landings to be a massacre worse than D-Day. But the Fifth Fleet’s offensive onslaught was almost pointless and landing troops could have literally swum to shore—surprisingly, the expected mass of awaiting Japanese troops wasn’t there.
On D-Day, American troops fought hard for every inch of beachhead—but troops landing on Okinawa’s beaches surged inland with little resistance. Wave after wave of troops, tanks, ammunition and supplies went ashore almost effortlessly within hours. The troops quickly secured both Kadena and Yontan airfields.
Japanese Army Waits:
Japan’s 32nd Army, some 130,000 men strong and commanded by Lt. Gen. Mitsuru Ushijima, defended Okinawa. The military force also included an unknown number of conscripted civilians and unarmed Home Guards known as Boeitai.
As they moved inland, American troops wondered when and where they’d finally encounter enemy resistance. What they didn’t know was the Japanese Imperial Army had them just where they wanted them.
Japanese troops had been instructed not to fire on the American landing forces but instead watch and wait for them, mostly in Shuri, a rugged area of southern Okinawa where General Ushijima had set up a triangle of defensive positions known as the Shuri Defense Line.